Abstract
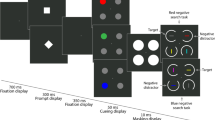
Humans and macaque monkeys, performing a Wisconsin Card Sorting Test (WCST), show a significant behavioral bias to a particular sensory dimension (e.g. color or shape); however, lesions in prefrontal cortical regions do not abolish the dimensional biases in monkeys and, therefore, it has been proposed that these biases emerge in earlier stages of visual information processing. It remains unclear whether such dimensional biases are unique to the WCST, in which attention-shifting between dimensions are required, or affect other aspects of executive functions such as ‘response inhibition’ and ‘error-induced behavioral adjustments’. To address this question, we trained six monkeys (Macaca mulatta) to perform a stop-signal task in which they had to inhibit their response when an instruction for inhibition was given by changing the color or shape of a visual stimulus. Stop Signal Reaction Time (SSRT) is an index of inhibitory processes. In all monkeys, SSRT was significantly shorter, and the probability of a successful inhibition was significantly higher, when a change in the shape dimension acted as the stop-cue. Humans show a response slowing following a failure in response inhibition and also adapt a proactive slowing after facing demands for response inhibition. We found such adaptive behavioral adjustments, with the same pattern, in monkeys’ behavior; however, the dimensional bias did not modulate them. Our findings, showing dimensional bias in monkey, with the same pattern, in two different executive control tasks support the hypothesis that the bias to shape dimension emerges in early stages of visual information processing.




Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
Matlab-written codes for data collection and extraction of parameters are available upon reasonable request from corresponding author.
References
Aron AR, Robbins TW, Poldrack RA (2014) Inhibition and the right inferior frontal cortex: one decade on. Trends Cogn Sci 18(4):177–185. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tics.2013.12.003
Bartolomeo P, Bachoud-Levi AC, De Gelder B, Denes G, Dalla Barba G, Brugieres P, Degos JD (1998) Multiple-domain dissociation between impaired visual perception and preserved mental imagery in a patient with bilateral extrastriate lesions. Neuropsychologia 36(3):239–249. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0028-3932(97)00103-6
Bissett PG, Logan GD (2011) Balancing cognitive demands: control adjustments in the stop-signal paradigm. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 37(2):392–404. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0021800
Bissett PG, Logan GD (2012a) Post-stop-signal adjustments: inhibition improves subsequent inhibition. J Exp Psychol Learn Mem Cogn 38(4):955
Bissett PG, Logan GD (2012b) Post-stop-signal slowing: strategies dominate reflexes and implicit learning. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 38(3):746–757. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0025429
Bjorklund DF, Kipp K (1996) Parental investment theory and gender differences in the evolution of inhibition mechanisms. Psychol Bull 120(2):163
Blizzard S, Fierro-Rojas A, Fallah M (2017) Response inhibition is facilitated by a change to red over green in the stop signal paradigm. Front Hum Neurosci 10:655
Boehler CN, Appelbaum LG, Krebs RM, Chen L-C, Woldorff MG (2011) The role of stimulus salience and attentional capture across the neural hierarchy in a stop-signal task. PLoS ONE 6(10):e26386
Boehler CN, Schevernels H, Hopf J-M, Stoppel CM, Krebs RM (2014) Reward prospect rapidly speeds up response inhibition via reactive control. Cognit Affect Behav Neurosci 14(2):593–609
Borgomaneri S, Serio G, Battaglia S (2020) Please, don’t do it! Fifteen years of progress of non-invasive brain stimulation in action inhibition. Cortex 132:404–422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cortex.2020.09.002
Brown AL, Campione JC (1971) Color dominance in preschool children as a function of specific cue preferences. Child Dev 42(5):1495–1500. https://doi.org/10.2307/1127913
Buckley MJ, Mansouri FA, Hoda H, Mahboubi M, Browning PG, Kwok SC, Tanaka K (2009) Dissociable components of rule-guided behavior depend on distinct medial and prefrontal regions. Science 325(5936):52–58. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1172377
Caspari N, Janssens T, Mantini D, Vandenberghe R, Vanduffel W (2015) Covert shifts of spatial attention in the macaque monkey. J Neurosci 35(20):7695–7714. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.4383-14.2015
Caspari N, Arsenault JT, Vandenberghe R, Vanduffel W (2018) Functional similarity of medial superior parietal areas for shift-selective attention signals in humans and monkeys. Cereb Cortex 28(6):2085–2099. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhx114
Cavina-Pratesi C, Bricolo E, Prior M, Marzi CA (2001) Redundancy gain in the stop-signal paradigm: implications for the locus of coactivation in simple reaction time. J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 27(4):932–941
Cavina-Pratesi C, Kentridge RW, Heywood CA, Milner AD (2010) Separate channels for processing form, texture, and color: evidence from FMRI adaptation and visual object agnosia. Cereb Cortex 20(10):2319–2332. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhp298
Chambers CD, Garavan H, Bellgrove MA (2009) Insights into the neural basis of response inhibition from cognitive and clinical neuroscience. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 33(5):631–646. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2008.08.016
Chang J, Hu J, Li CR, Yu R (2020) Neural correlates of enhanced response inhibition in the aftermath of stress. Neuroimage 204:116212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2019.116212
Clark L, Blackwell AD, Aron AR, Turner DC, Dowson J, Robbins TW, Sahakian BJ (2007) Association between response inhibition and working memory in adult ADHD: a link to right frontal cortex pathology? Biol Psychiatry 61(12):1395–1401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopsych.2006.07.020
Cowey A, Ellis CM (1967) Visual acuity of rhesus and squirrel monkeys. J Compr Physiol Psychol 64(1):80
Cunillera T, Brignani D, Cucurell D, Fuentemilla L, Miniussi C (2016) The right inferior frontal cortex in response inhibition: a tDCS-ERP co-registration study. Neuroimage 140:66–75. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2015.11.044
De Lillo C, Spinozzi G, Truppa V, Naylor DM (2005) A comparative analysis of global and local processing of hierarchical visual stimuli in young children (Homo sapiens) and monkeys (Cebus apella). J Comp Psychol 119(2):155
Denys K, Vanduffel W, Fize D, Nelissen K, Peuskens H, Van Essen D, Orban GA (2004) The processing of visual shape in the cerebral cortex of human and nonhuman primates: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Neurosci 24(10):2551–2565
Eben C, Billieux J, Verbruggen F (2020) Clarifying the role of negative emotions in the origin and control of impulsive actions. Psychol Belg 60(1):1–17. https://doi.org/10.5334/pb.502
Ellefson MR, Shapiro LR, Chater N (2006) Asymmetrical switch costs in children. Cognit Dev 21(2):108–130
Emeric EE, Brown JW, Boucher L, Carpenter RH, Hanes DP, Harris R, Schall JD (2007) Influence of history on saccade countermanding performance in humans and macaque monkeys. Vis Res 47(1):35–49. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.visres.2006.08.032
Fagot J, Deruelle C (1997) Processing of global and local visual information and hemispheric specialization in humans (Homo sapiens) and baboons (Papio papio). J Exp Psychol Hum Percept Perform 23(2):429
Fehring DJ, Illipparampil R, Acevedo N, Jaberzadeh S, Fitzgerald PB, Mansouri FA (2019) Interaction of task-related learning and transcranial direct current stimulation of the prefrontal cortex in modulating executive functions. Neuropsychologia 131:148–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropsychologia.2019.05.011
Found A, Müller HJ (1996) Searching for unknown feature targets on more than one dimension: Investigating a “dimension-weighting” account. Percept Psychophys 58(1):88–101
Fujita K (1997) Perception of the Ponzo illusion by rhesus monkeys, chimpanzees, and humans: similarity and difference in the three primate species. Percept Psychophys 59(2):284–292
Ghasemian S, Vardanjani MM, Sheibani V, Mansouri FA (2021) Color‐hierarchies in executive control of monkeys' behavior. Am J Primatol 83(2):e23231. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.23231
Grant DA, Curran JF (1952) Relative difficulty of number, form, and color concepts of a Weigl-type problem using unsystematic number cards. J Exp Psychol 43(6):408
Grant DA, Jones OR, Tallantis B (1949) The relative difficulty of the number, form, and color concepts of a Weigl-type problem. J Exp Psychol 39(4):552
Hendrick OM, Ide JS, Luo X, Li CS (2010) Dissociable processes of cognitive control during error and non-error conflicts: a study of the stop signal task. PLoS ONE 5(10):e13155. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0013155
Hopkins WD, Washburn DA (2002) Matching visual stimuli on the basis of global and local features by chimpanzees (Pan troglodytes) and rhesus monkeys (Macaca mulatta). Anim Cogn 5(1):27–31
Hosseini-Kamkar N, Morton JB (2014) Sex differences in self-regulation: an evolutionary perspective. Front Neurosci 8:233
Huddy VC, Aron AR, Harrison M, Barnes TR, Robbins TW, Joyce EM (2009) Impaired conscious and preserved unconscious inhibitory processing in recent onset schizophrenia. Psychol Med 39(6):907–916. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0033291708004340
Kalanthroff E, Cohen N, Henik A (2013) Stop feeling: inhibition of emotional interference following stop-signal trials. Front Hum Neurosci 7:78. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnhum.2013.00078
Kalloniatis M, Harwerth RS (1991) Effects of chromatic adaptation on opponent interactions in monkey increment-threshold spectral-sensitivity functions. JOSA A 8(11):1818–1831
Kerzel D, Schönhammer J (2013) Salient stimuli capture attention and action. Attention Percept Psychophys 75(8):1633–1643
Konishi S, Nakajima K, Uchida I, Kameyama M, Nakahara K, Sekihara K, Miyashita Y (1998) Transient activation of inferior prefrontal cortex during cognitive set shifting. Nat Neurosci 1(1):80–84. https://doi.org/10.1038/283
Kuwabara M, Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ, Tanaka K (2014) Cognitive control functions of anterior cingulate cortex in macaque monkeys performing a Wisconsin Card Sorting Test analog. J Neurosci 34(22):7531–7547. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.3405-13.2014
Lacreuse A, Gullstrand J, Fagot J (2016) Sex differences in inhibitory control in socially-housed baboons (Papio papio). Behav Brain Res 312:231–237
Li CS, Huang C, Yan P, Paliwal P, Constable RT, Sinha R (2008) Neural correlates of post-error slowing during a stop signal task: a functional magnetic resonance imaging study. J Cogn Neurosci 20(6):1021–1029. https://doi.org/10.1162/jocn.2008.20071
Liu T (2019) Feature-based attention: effects and control. Curr Opin Psychol 29:187–192. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.copsyc.2019.03.013
Logan GD, Cowan WB (1984) On the ability to inhibit thought and action: a theory of an act of control. Psychol Rev 91(3):295
Logan GD, Van Zandt T, Verbruggen F, Wagenmakers EJ (2014) On the ability to inhibit thought and action: general and special theories of an act of control. Psychol Rev 121(1):66–95. https://doi.org/10.1037/a0035230
Luijten M, Machielsen MW, Veltman DJ, Hester R, de Haan L, Franken IH (2014) Systematic review of ERP and fMRI studies investigating inhibitory control and error processing in people with substance dependence and behavioural addictions. J Psychiatry Neurosci 39(3):149–169. https://doi.org/10.1503/jpn.130052
Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ (2018) Context-dependent adjustments in executive control of goal-directed behaviour: contribution of frontal brain areas to conflict-induced behavioural adjustments in primates. Adv Neurobiol 21:71–83. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-94593-4_4
Mansouri FA, Tanaka K (2002) Behavioral evidence for working memory of sensory dimension in macaque monkeys. Behav Brain Res 136(2):415–426. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0166-4328(02)00182-1
Mansouri FA, Matsumoto K, Tanaka K (2006) Prefrontal cell activities related to monkeys’ success and failure in adapting to rule changes in a Wisconsin Card Sorting Test analog. J Neurosci 26(10):2745–2756. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.5238-05.2006
Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ, Tanaka K (2007) Mnemonic function of the dorsolateral prefrontal cortex in conflict-induced behavioral adjustment. Science 318(5852):987–990
Mansouri FA, Tanaka K, Buckley MJ (2009) Conflict-induced behavioural adjustment: a clue to the executive functions of the prefrontal cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 10(2):141–152. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn2538
Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ, Tanaka K (2014) The essential role of primate orbitofrontal cortex in conflict-induced executive control adjustment. J Neurosci 34(33):11016–11031. https://doi.org/10.1523/JNEUROSCI.1637-14.2014
Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ, Mahboubi M, Tanaka K (2015a) Behavioral consequences of selective damage to frontal pole and posterior cingulate cortices. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 112(29):E3940-3949. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1422629112
Mansouri FA, Rosa MG, Atapour N (2015b) Working memory in the service of executive control functions. Front Syst Neurosci 9:166. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnsys.2015.00166
Mansouri FA, Fehring DJ, Feizpour A, Gaillard A, Rosa MG, Rajan R, Jaberzadeh S (2016a) Direct current stimulation of prefrontal cortex modulates error-induced behavioral adjustments. Eur J Neurosci 44(2):1856–1869. https://doi.org/10.1111/ejn.13281
Mansouri FA, Fehring DJ, Gaillard A, Jaberzadeh S, Parkington H (2016b) Sex dependency of inhibitory control functions. Biology of sex Differences 7(1):1–13
Mansouri FA, Acevedo N, Illipparampil R, Fehring DJ, Fitzgerald PB, Jaberzadeh S (2017a) Interactive effects of music and prefrontal cortex stimulation in modulating response inhibition. Sci Rep 7(1):1–13
Mansouri FA, Koechlin E, Rosa MGP, Buckley MJ (2017b) Managing competing goals—a key role for the frontopolar cortex. Nat Rev Neurosci 18(11):645–657. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrn.2017.111
Mansouri FA, Buckley MJ, Fehring DJ, Tanaka K (2020a) The role of primate prefrontal cortex in bias and shift between visual dimensions. Cereb Cortex 30(1):85–99. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhz072
Mansouri FA, Freedman DJ, Buckley MJ (2020b) Emergence of abstract rules in the primate brain. Nat Rev Neurosci. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41583-020-0364-5
Matsuno T, Fujita K (2009) A comparative psychophysical approach to visual perception in primates. Primates 50(2):121–130
Maunsell JH, Treue S (2006) Feature-based attention in visual cortex. Trends Neurosci 29(6):317–322. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tins.2006.04.001
Miceli G, Fouch E, Capasso R, Shelton JR, Tomaiuolo F, Caramazza A (2001) The dissociation of color from form and function knowledge. Nat Neurosci 4(6):662–667. https://doi.org/10.1038/88497
Miller EK, Cohen JD (2001) An integrative theory of prefrontal cortex function. Annu Rev Neurosci 24:167–202. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.neuro.24.1.167
Monchi O, Petrides M, Petre V, Worsley K, Dagher A (2001) Wisconsin Card Sorting revisited: distinct neural circuits participating in different stages of the task identified by event-related functional magnetic resonance imaging. J Neurosci 21(19):7733–7741
Morein-Zamir S, Kingstone A (2006) Fixation offset and stop signal intensity effects on saccadic countermanding: a crossmodal investigation. Exp Brain Res 175(3):453–462. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00221-006-0564-x
Nakahara K, Hayashi T, Konishi S, Miyashita Y (2002) Functional MRI of macaque monkeys performing a cognitive set-shifting task. Science 295(5559):1532–1536. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1067653
Orban GA, Van Essen D, Vanduffel W (2004) Comparative mapping of higher visual areas in monkeys and humans. Trends Cognit Sci 8(7):315–324
Otto W, Askov E (1968) The role of color in learning and instruction. J Sp Educ 2(2):155–165
Paneri S, Gregoriou GG (2017) Top-down control of visual attention by the prefrontal cortex. Functional specialization and long-range interactions. Front Neurosci 11:545. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnins.2017.00545
Petrides M, Pandya DN (1999) Dorsolateral prefrontal cortex: comparative cytoarchitectonic analysis in the human and the macaque brain and corticocortical connection patterns. Eur J Neurosci 11(3):1011–1036. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1460-9568.1999.00518.x
Prevor MB, Diamond A (2005) Color–object interference in young children: a Stroop effect in children 31/2–61/2 years old. Cognit Devt 20(2):256–278
Proverbio AM, Burco F, del Zotto M, Zani A (2004) Blue piglets? Electrophysiological evidence for the primacy of shape over color in object recognition. Cognit Brain Res 18(3):288–300
Rabbitt PM (1966) Errors and error correction in choice-response tasks. J Exp Psychol 71(2):264–272. https://doi.org/10.1037/h0022853
Rajalingham R, Schmidt K, DiCarlo JJ (2015) Comparison of object recognition behavior in human and monkey. J Neurosci 35(35):12127–12136
Rubia K, Smith AB, Brammer MJ, Taylor E (2003) Right inferior prefrontal cortex mediates response inhibition while mesial prefrontal cortex is responsible for error detection. Neuroimage 20(1):351–358. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1053-8119(03)00275-1
Sakagami M, Tsutsui K, Lauwereyns J, Koizumi M, Kobayashi S, Hikosaka O (2001) A code for behavioral inhibition on the basis of color, but not motion, in ventrolateral prefrontal cortex of macaque monkey. J Neurosci 21(13):4801–4808
Schall JD, Hanes DP, Taylor TL (2000) Neural control of behavior: countermanding eye movements. Psychol Res 63(3–4):299–307. https://doi.org/10.1007/s004269900008
Schledde B, Galashan FO, Przybyla M, Kreiter AK, Wegener D (2017) Task-specific, dimension-based attentional shaping of motion processing in monkey area MT. J Neurophysiol 118(3):1542–1555. https://doi.org/10.1152/jn.00183.2017
Suda A, Osada T, Ogawa A, Tanaka M, Kamagata K, Aoki S, Konishi S (2020) Functional organization for response inhibition in the right inferior frontal cortex of individual human brains. Cereb Cortex. https://doi.org/10.1093/cercor/bhaa188
Takahashi E, Ohki K, Kim DS (2013) Dissociation and convergence of the dorsal and ventral visual working memory streams in the human prefrontal cortex. Neuroimage 65:488–498. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2012.10.002
Tanaka K (1997) Mechanisms of visual object recognition: monkey and human studies. Curr Opin Neurobiol 7(4):523–529. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0959-4388(97)80032-3
Van Essen DC, Lewis JW, Drury HA, Hadjikhani N, Tootell RB, Bakircioglu M, Miller MI (2001) Mapping visual cortex in monkeys and humans using surface-based atlases. Vis Res 41(10–11):1359–1378. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0042-6989(01)00045-1
Verbruggen F, De Houwer J (2007) Do emotional stimuli interfere with response inhibition? Evidence from the stop signal paradigm. Cogn Emot 21(2):391–403
Verbruggen F, Logan GD (2008) Response inhibition in the stop-signal paradigm. Trends Cognit Sci 12(11):418–424
Verbruggen F, Chambers CD, Logan GD (2013) Fictitious inhibitory differences: how skewness and slowing distort the estimation of stopping latencies. Psychol Sci 24(3):352–362
Verbruggen F, Aron AR, Band GP, Beste C, Bissett PG, Brockett AT, Boehler CN (2019) A consensus guide to capturing the ability to inhibit actions and impulsive behaviors in the stop-signal task. Elife. https://doi.org/10.7554/eLife.46323
Wade A, Augath M, Logothetis N, Wandell B (2008) fMRI measurements of color in macaque and human. J Vis 8(10):6–6
Weinstein B, Grether W (1940) A comparison of visual acuity in the rhesus monkey and man. J Comp Psychol 30(2):187
Wessel JR, Aron AR (2014) Inhibitory motor control based on complex stopping goals relies on the same brain network as simple stopping. Neuroimage 103:225–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2014.09.048
Xu KZ, Anderson BA, Emeric EE, Sali AW, Stuphorn V, Yantis S, Courtney SM (2017) Neural basis of cognitive control over movement inhibition: human fMRI and primate electrophysiology evidence. Neuron 96(6):1447-1458e1446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2017.11.010
Yi L, Liu Y, Li Y, Fan Y, Huang D, Gao D (2012) Visual scanning patterns during the dimensional change card sorting task in children with autism spectrum disorder. Autism Res Treat 2012:123053. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/123053
Zarei SA, Sheibani V, Mansouri FA (2019a) Interaction of music and emotional stimuli in modulating working memory in macaque monkeys. Am J Primatol 81(7):e22999. https://doi.org/10.1002/ajp.22999
Zarei SA, Sheibani V, Tomaz C, Mansouri FA (2019b) The effects of oxytocin on primates’ working memory depend on the emotional valence of contextual factors. Behav Brain Res 362:82–89. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbr.2018.12.050
Zeki S, Aglioti S, McKeefry D, Berlucchi G (1999) The neurological basis of conscious color perception in a blind patient. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 96(24):14124–14129. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.96.24.14124
Zhang Y, Ide JS, Zhang S, Hu S, Valchev NS, Tang X, Li CR (2017) Distinct neural processes support post-success and post-error slowing in the stop signal task. Neuroscience 357:273–284. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroscience.2017.06.011
Funding
This research was supported by funding from Kerman University of Medical Sciences under Grant Number of 95000705. Also, this study received supports from Cognitive Sciences and Technologies Council of Iran.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SG trained the animals, collected data and contributed to the data analysis, task design and writing the manuscript. MMV contributed to the animal training and data collection. VS acquired grant, contributed to the data analysis and writing the manuscript. FAM formulated the study question, contributed to the task design, data analysis and writing the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declare no financial and non-financial competing of interests.
Ethics approval
All procedures, including animal holding, training and testing were performed according to the NIH guidelines for animal studies and also approved by Kerman University of Medical Sciences’ Animal Ethics Committee: IR.KMU.REC.1396.1691.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ghasemian, S., Vardanjani, M.M., Sheibani, V. et al. Dimensional bias and adaptive adjustments in inhibitory control of monkeys. Anim Cogn 24, 815–828 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-021-01483-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-021-01483-7