Abstract
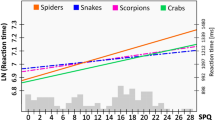
While the origin of yawning appears to be physiologic, yawns may also hold a derived communicative function in social species. In particular, the arousal reduction hypothesis states that yawning signals to others that the actor is experiencing a down regulation of arousal and vigilance. If true, seeing another individual yawn might enhance the vigilance of observers to compensate for the reduced mental processing of the yawner. This was tested in humans by assessing how exposure to yawning stimuli alters performance on visual search tasks for detecting snakes (a threatening stimulus) and frogs (a neutral stimulus). In a repeated-measures design, 38 participants completed these tasks separately after viewing yawning and control videos. Eye-tracking was used to measure detection latency and distractor fixation frequency. Replicating previous evolutionary-based research, snakes were detected more rapidly than frogs across trials. Moreover, consistent with the view that yawning holds a distinct signaling function, there were significant interactions for both detection latency and distractor fixation frequency showing that vigilance was selectively enhanced following exposure to yawns. That is, after viewing videos of other people yawning, participants detected snakes more rapidly and were less likely to fixate on distractor frogs during trials. These findings provide the first experimental evidence for a social function to yawning in any species, and imply the presence of a previously unidentified psychological adaptation for preserving group vigilance.




Similar content being viewed by others
Code availability
All statistics were performed in SPSS v.27.
References
Abtahi S, Hariri B, Shirmohammadi S (2011) Driver drowsiness monitoring based on yawning detection. In: 2011 IEEE International Instrumentation and Measurement Technology Conference (pp. 1–4). IEEE.
Anderson JR (2010) Non-human primates: a comparative developmental perspective on yawning. In: The Mystery of Yawning in Physiology and Disease (Vol. 28, pp. 63–76). Karger Publishers.
Anderson JR (2020) One thousand yawns. Primates 61:729–740
Anderson JR, Myowa–Yamakoshi M, Matsuzawa T (2004) Contagious yawning in chimpanzees. Proc R Soc B 271(suppl_6):S468–S470.
Ania J, Holmgren B, Holmgren RU, Eguibar JR (1984) Circadian variation of yawning behavior. Acta Neurobiol Exp 44:179–186
Arnott SR, Singhal A, Goodale MA (2009) An investigation of auditory contagious yawning. Cogn Affect Behav Neurosci 9(3):335–342
Baenninger R (1987) Some comparative aspects of yawning in betta splendens, homo sapiens, panthera leo, and papio sphinx. J Comp Psychol 101(4):349
Baenninger R (1997) On yawning and its functions. Psychon Bull Rev 4(2):198–207
Baenninger R, Binkley S, Baenninger M (1996) Field observations of yawning and activity in humans. Physiol Behav 59(3):421–425
Barbizet J (1958) Yawning. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 21(3):203
Bichot NP, Heard MT, DeGennaro EM, Desimone R (2015) A source for feature-based attention in the prefrontal cortex. Neuron 88(4):832–844
Campbell MW, De Waal FB (2011) Ingroup-outgroup bias in contagious yawning by chimpanzees supports link to empathy. PLOS One 6(4).
Cheng AC, Currie BJ (2004) Venomous snakebites worldwide with a focus on the Australia-Pacific region: current management and controversies. J Intensive Care Med 19(5):259–269
Darwin CR (1872) The expression of the emotions in man and animals. John Murray, London
De Vries JI, Visser GH, Prechtl HF (1982) The emergence of fetal behaviour. I Qualitative aspects. Early Hum Dev 7(4):301–322
Dinh HT, Nishimaru H, Matsumoto J et al (2018) Superior neuronal detection of snakes and conspecific faces in the macaque medial prefrontal cortex. Cereb Cortex 28(6):2131–2145
Dourish CT, Cooper SJ (1990) Neural basis of drug-induced yawning. In: Cooper SJ, Dourish CT (eds) Neurobiology of stereotyped behavior.Oxford Clarendon Press, Oxford, pp 91–116.
Eguibar JR, Uribe CA, Cortes C, Bautista A, Gallup AC (2017) Yawning reduces facial temperature in the high-yawning subline of Sprague-Dawley rats. BMC Neurosci 18(1):1–8
Eldakar OT, Dauzonne M, Prilutzkaya Y et al (2015) Temperature-dependent variation in self-reported contagious yawning. Adapt Hum Behav Physiol 1(4):460–466
Eldakar OT, Tartar JL, Garcia D et al (2017) Acute physical stress modulates the temporal expression of self-reported contagious yawning in humans. Adapt Hum Behav Physiol 3(2):156–170
Ellison A, Schindler I, Pattison LL, Milner AD (2004) An exploration of the role of the superior temporal gyrus in visual search and spatial perception using TMS. Brain 127(10):2307–2315
Gallup AC (2011) Why do we yawn? Primitive versus derived features. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35(3):765–769
Gallup AC, Clark AB (2015) Commentary: Yawning, acute stressors, and arousal reduction in Nazca booby adults and nestlings. Front Psychol 6:1654
Gallup AC, Gallup GG Jr (2007) Yawning as a brain cooling mechanism: nasal breathing and forehead cooling diminish the incidence of contagious yawning. Evol Psychol 5(1):92–101
Gallup GG Jr, Gallup AC (2010) Excessive yawning and thermoregulation: two case histories of chronic, debilitating bouts of yawning. Sleep Breath 14(2):157–159
Gallup AC, Miller RR, Clark AB (2011) Changes in ambient temperature trigger yawning but not stretching in rats. Ethology 117(2):145–153
Gallup AC, Hale JJ, Sumpter DJ et al (2012) Visual attention and the acquisition of information in human crowds. Proc Natl Acad Sci 109(19):7245–7250
Gallup AC, Swartwood L, Militello J, Sackett S (2015) Experimental evidence of contagious yawning in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). Anim Cogn 18(5):1051–1058
Gallup AC, Church AM, Miller H, Risko EF, Kingstone A (2016) Social presence diminishes contagious yawning in the laboratory. Sci Rep 6:25045
Gallup AC, Herron E, Militello J, Swartwood L, Cortes C, Eguibar JR (2017) Thermal imaging reveals sizable shifts in facial temperature surrounding yawning in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). Temperature 4(4):429–435
Gallup AC, Vasilyev D, Anderson N, Kingstone A (2019) Contagious yawning in virtual reality is affected by actual, but not simulated, social presence. Sci Rep 9(1):1–10
Giganti F, Zilli I (2011) The daily time course of contagious and spontaneous yawning among humans. J Ethol 29(2):215–219
Giganti F, Zilli I, Aboudan S, Salzarulo P (2010) Sleep, sleepiness and yawning. In: The mystery of yawning in physiology and disease, vol. 28, Karger Publishers, pp. 42–46
Guggisberg AG, Mathis J, Herrmann US, Hess CW (2007) The functional relationship between yawning and vigilance. Behav Brain Res 179(1):159–166
Guggisberg AG, Mathis J, Schnider A, Hess CW (2010) Why do we yawn? Neurosci Biobehav Rev 34(8):1267–1276
Isbell LA (2006) Snakes as agents of evolutionary change in primate brains. J Hum Evol 51:1–35
Isbell LA (2009) The fruit, the tree, and the serpent: why we see so well. Harvard University Press
Kapitány R, Nielsen M (2017) Are yawns really contagious? A critique and quantification of yawn contagion. Adapt Hum Behav Physiol 3(2):134–155
Kasuya Y, Murakami T, Oshima T, Dohi S (2005) Does yawning represent a transient arousal-shift during intravenous induction of general anesthesia? Anesth Analg 101(2):382–384
Leone A, Ferrari PF, Palagi E (2014) Different yawns, different functions? Testing social hypotheses on spontaneous yawning in Theropithecus gelada. Sci Rep 4:4010
Liang AC, Grace JK, Tompkins EM, Anderson DJ (2015) Yawning, acute stressors, and arousal reduction in Nazca booby adults and nestlings. Physiol Behav 140:38–43
LoBue V, DeLoache JS (2008) Detecting the snake in the grass: attention to fear-relevant stimuli by adults and young children. Psychol Sci 19(3):284–289
Massen JJM, Gallup AC (2017) Why contagious yawning does not (yet) equate to empathy. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 80:573–585
Massen JJM, Church AM, Gallup AC (2015) Auditory contagious yawning in humans: an investigation into affiliation and status effects. Front Psychol 6:1735
Miller ML, Gallup AC, Vogel AR, Clark AB (2010) Handling stress initially inhibits, but then potentiates yawning in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). Anim Behav 80(4):615–619
Miller ML, Gallup AC, Vogel AR, Vicario SM, Clark AB (2012a) Evidence for contagious behaviors in budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus): an observational study of yawning and stretching. Behav Process 89(3):264–270
Miller ML, Gallup AC, Vogel AR, Clark AB (2012b) Auditory disturbances promote temporal clustering of yawning and stretching in small groups of budgerigars (Melopsittacus undulatus). J Comp Psychol 126(3):324
Mineka S, Davidson M, Cook M, Keir R (1984) Observational conditioning of snake fear in rhesus monkeys. J Abnorm Psychol 93(4):355–372
Mobbs D, Petrovic P, Marchant JL et al (2007) When fear is near: threat imminence elicits prefrontal-periaqueductal gray shifts in humans. Science 317(5841):1079–1083
Nahab FB, Hattori N, Saad ZS, Hallett M (2009) Contagious yawning and the frontal lobe: an fMRI study. Hum Brain Mapp 30(5):1744–1751
Nelson JT, McKinley RA, Golob EJ, Warm JS, Parasuraman R (2014) Enhancing vigilance in operators with prefrontal cortex transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS). Neuroimage 85:909–917
Norscia I, Palagi E (2011) Yawn contagion and empathy in Homo sapiens. PLOS One:6(12).
Norscia I, Zanoli A, Gamba M, Palagi E (2020) Auditory contagious yawning is highest between friends and family members: support to the emotional bias hypothesis. Front Psychol 11:442
Öhman A (2009) Of snakes and faces: an evolutionary perspective on the psychology of fear. Scand J Psychol 50(6):543–552
Öhman A, Mineka S (2003) The malicious serpent: Snakes as a prototypical stimulus for an evolved module of fear. Curr Dir Psychol Sci 12(1):5–9
Öhman A, Flykt A, Esteves F (2001) Emotion drives attention: detecting the snake in the grass. J Exp Psychol Gen 130(3):466
Palagi E, Norscia I (2013) Bonobos protect and console friends and kin. PLOS One 8(11).
Palagi E, Leone A, Mancini G, Ferrari PF (2009) Contagious yawning in gelada baboons as a possible expression of empathy. Proc Natl Acad Sci 106(46):19262–19267
Palagi E, Norscia I, Demuru E (2014) Yawn contagion in humans and bonobos: emotional affinity matters more than species. PeerJ 2:e519
Parasuraman R, Warm JS, See JE (1998). Brain systems of vigilance. In: Parasuraman R (ed) The Attentive Brain. The MIT Press, pp 221–256
Platek SM, Critton SR, Myers TE, Gallup GG Jr (2003) Contagious yawning: the role of self-awareness and mental state attribution. Cogn Brain Res 17(2):223–227
Provine RR (1986) Yawning as a stereotyped action pattern and releasing stimulus. Ethology 72(2):109–122
Provine RR (2005) Yawning: the yawn is primal, unstoppable and contagious, revealing the evolutionary and neural basis of empathy and unconscious behavior. Am Sci 93(6):532–539
Provine RR (2012). Curious behavior: yawning, laughing, hiccupping, and beyond. Harvard University Press.
Provine RR, Hamernik HB (1986) Yawning: effects of stimulus interest. Bull Psychon Soc 24(6):437–438
Provine RR, Hamernik HB, Curchack BC (1987) Yawning: relation to sleeping and stretching in humans. Ethology 76(2):152–160
Rahman R, Faiz MA, Selim S et al (2010) Annual incidence of snake bite in rural Bangladesh. PLoS Negl Trop Dis 4(10):e860
Ramirez V, Ryan CP, Eldakar OT, Gallup AC (2019) Manipulating neck temperature alters contagious yawning in humans. Physiol Behav 207:86–89
Schürmann M, Hesse MD, Stephan KE et al (2005) Yearning to yawn: the neural basis of contagious yawning. Neuroimage 24(4):1260–1264
Shibasaki M, Kawai N (2009) Rapid detection of snakes by Japanese monkeys (Macaca fuscata): an evolutionarily predisposed visual system. J Comp Psychol 123:131–135
Shoup-Knox ML, Gallup AC, Gallup G, McNay EC (2010) Yawning and stretching predict brain temperature changes in rats: support for the thermoregulatory hypothesis. Front Evol Neurosci 2:108
Smith EO (1999) Yawning: an evolutionary perspective. Hum Evol 14(3):191–198
Tesfaye Y, Lal S (1990) Hazard of yawning. CMAJ 142(1):15
Tsurumi S, Kanazawa S, Yamaguchi MK (2019) Infant brain activity in response to yawning using functional near-infrared spectroscopy. Sci Rep 9(1):1–9
Van Le Q, Isbell LA, Matsumoto J et al (2013) Pulvinar neurons reveal neurobiological evidence of past selection for rapid detection of snakes. Proc Natl Acad Sci 110(47):19000–19005
Walusinski O (2014) How yawning switches the default-mode network to the attentional network by activating the cerebrospinal fluid flow. Clin Anat 27(2):201–209
Walusinski O (2018) Pathological Yawning, Laughing and Crying. In: neurologic-psychiatric syndromes in focus-part I (Vol. 41, pp. 40–49). Karger Publishers.
Yang H, Liu L, Min W, Yang X, Xiong X (2020) Driver yawning detection based on subtle facial action recognition. IEEE Trans Multimed
Yorzinski JL, Penkunas MJ, Platt ML, Coss RG (2014) Dangerous animals capture and maintain attention in humans. Evol Psychol 12(3):147470491401200320
Zannella A, Stanyon R, Palagi E (2017) Yawning and social styles: Different functions in tolerant and despotic macaques (Macaca tonkeana and Macaca fuscata). J Comp Psychol 131(3):179
Zhang W, Murphey YL, Wang T, Xu, Q (2015) Driver yawning detection based on deep convolutional neural learning and robust nose tracking. In: 2015 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN) (pp. 1–8). IEEE.
Zilli I, Giganti F, Salzarulo P (2007) Yawning in morning and evening types. Physiol Behav 91(2–3):218–222
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors. However, this work was generously supported by the College of Arts and Sciences at SUNY Polytechnic Institute.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests.
Ethics approval
The local Institutional Review Board approved this research (#2019–8).
Availability of data and material
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article and its supplementary information files.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary file2 (AVI 15500 KB)
Supplementary file3 (AVI 15798 KB)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gallup, A.C., Meyers, K. Seeing others yawn selectively enhances vigilance: an eye-tracking study of snake detection. Anim Cogn 24, 583–592 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-020-01462-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-020-01462-4