Abstract
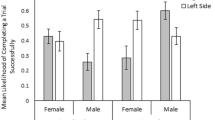
Pigs are a valuable animal model for studying neurodevelopment in humans due to similarities in brain structure and growth. The development and validation of behavioral tests to assess learning and memory in neonatal piglets are needed. The present study evaluated the capability of 2-week old piglets to acquire a novel place and direction learning spatial T-maze task. Validity of the task was assessed by the administration of scopolamine, an anti-cholinergic drug that acts on the hippocampus and other related structures, to impair spatial memory. During acquisition, piglets were trained to locate a milk reward in a constant place in space, as well as direction (east or west), in a plus-shaped maze using extra-maze visual cues. Following acquisition, reward location was reversed and piglets were re-tested to assess learning and working memory. The performance of control piglets in the maze improved over time (P < 0.0001), reaching performance criterion (80 % correct) on day 5 of acquisition. Correct choices decreased in the reversal phase (P < 0.0001), but improved over time. In a separate study, piglets were injected daily with either phosphate-buffered saline (PBS; control) or scopolamine prior to testing. Piglets administered scopolamine showed impaired performance in the maze compared to controls (P = 0.03), failing to reach performance criterion after 6 days of acquisition testing. Collectively, these data demonstrate that neonatal piglets can be tested in a spatial T-maze task to assess hippocampal-dependent learning and memory.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abraham J, Johnson RW (2009) Consuming a diet supplemented with resveratrol reduced infection-related neuroinflammation and deficits in working memory in aged mice. Rejuvenation Res 12:445–453
Archibald SL, Masliah E, Fennema-Notestine C, Marcotte TD, Ellis RJ, McCutchan JA, Heaton RK, Grant I, Mallory M, Miller A, Jernigan TL (2004) Correlation of in vivo neuroimaging abnormalities with postmortem human immunodeficiency virus encephalitis and dendritic loss. Arch Neurol 61:369–376
Arts JWM, van der Staay FJ, Ekkel ED (2009) Working and reference memory of pigs in the spatial holeboard discrimination task. Behav Brain Res 205:303–306
Croney CC, Adams KM, Washington CG, Stricklin WR (2003) A note on visual, olfactory and spatial cue use in foraging behavior of pigs: indirectly assessing cognitive abilities. Appl Anim Behav Sci 83:303–308
Davis M (1997) Neurobiology of fear responses: the role of the amygdala. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 9:382–402
Decker MW, McGaugh JL (1991) The role of interactions between the cholinergic system and other neuromodulatory systems in learning and memory. Synapse 7:151–168
Devinsky O, Morrell MJ, Vogt BA (1995) Contributions of anterior cingulate cortex to behaviour. Brain 118:279–306
Dilger RN, Johnson RW (2010) Behavioral assessment of cognitive function using a translational neonatal piglet model. Brain Behav Immun 24:1156–1165
Dobbing J, Sands J (1979) Comparative aspects of the brain growth spurt. Early Hum Dev 3:79–83
Ebert U, Kirch W (1998) Review—scopolamine model of dementia: electroencephalogram findings and cognitive performance. Eur J Clin Invest 28:944–949
Fatemi SH, Emamian ES, Kist D, Sidwell RW, Nakajima K, Akhter P, Shier A, Sheikh S, Bailey K (1999) Defective corticogenesis and reduction in reelin immunoreactivity in cortex and hippocampus of prenatally infected neonatal mice. Mol Psychiatry 4:145–154
Fitz NF, Gibbs RB, Johnson DA (2008) Selective lesion of septal cholinergic neurons in rats impairs acquisition of a delayed matching to position t-maze task by delaying the shift from a response to a place strategy. Brain Res Bull 77:356–360
Gibertini M, Newton C, Friedman H, Klein TW (1995) Spatial learning impairment in mice infected with legionella pneumophila or administered exogenous interleukin-1-β. Brain Behav Immun 9:113–128
Gieling ET, Nordquist RE, van der Staay FJ (2011a) Assessing learning and memory in pigs. Anim Cogn 14:151–173
Gieling ET, Park SY, Nordquist RE, van der Staay FJ (2011b) Cognitive performance of low- and normal-birth-weight piglets in a spatial hole-board discrimination task. Pediatr Res 71:71–76
Graeff FG, Netto CF, Zangrossi H (1998) The elevated t-maze as an experimental model of anxiety. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 23:237–246
Hagl C, Weisz DJ, Khaladj N, Griepp MM, Spielvogel D, Yang BY, de Asla RA, Bodian CA, Griepp RB (2005) Use of a maze to detect cognitive dysfunction in a porcine model of hypothermic circulatory arrest. Ann Thorac Surg 79:1307–1315
Houle VM, Schroeder EA, Odle J, Donovan SM (1997) Small intestinal disaccharidase activity and ileal villus height are increased in piglets consuming formula containing recombinant human insulin-like growth factor-i. Pediatr Res 42:78–86
Jansen J, Bolhuis JE, Schouten WGP, Spruijt BM, Wiegant VM (2009) Spatial learning in pigs: effects of environmental enrichment and individual characteristics on behaviour and performance. Anim Cogn 12:303–315
Jarrard LE (1995) What does the hippocampus really do? Behav Brain Res 71:1–10
Kornum BR, Knudsen GM (2011) Cognitive testing of pigs (sus scrofa) in translational biobehavioral research. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 35:437–451
Kouwenberg AL, Walsh CJ, Morgan BE, Martin GM (2009) Episodic-like memory in crossbred yucatan minipigs (sus scrofa). Appl Anim Behav Sci 117:165–172
Lim GP, Calon F, Morihara T, Yang FS, Teter B, Ubeda O, Salem N, Frautschy SA, Cole GM (2005) A diet enriched with the omega-3 fatty acid docosahexaenoic acid reduces amyloid burden in an aged alzheimer mouse model. J Neurosci 25:3032–3040
Lind NM, Moustgaard A, Jelsing J, Vajta G, Cumming P, Hansen AK (2007) The use of pigs in neuroscience: modeling brain disorders. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 31:728–751
Maguire EA (2001) The retrosplenial contribution to human navigation: a review of lesion and neuroimaging findings. Scand J Psychol 42:225–238
Merali Z, Levac C, Anisman H (2003) Validation of a simple, ethologically relevant paradigm for assessing anxiety in mice. Biol Psychiatry 54:552–565
Mesulam MM, Mufson EJ, Levey AI, Wainer BH (1983) Cholinergic innervation of cortex by the basal forebrain: cytochemistry and cortical connections of the septal nuclei, nucleus basalis (substantia innominata), and hypothalamus in the rhesus monkey. J Comp Neurol 214:170–197
Morris R (1984) Developments of a water-maze procedure for studying spatial-learning in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 11:47–60
Moustgaard A, Arnfred SM, Lind NM, Hansen AK, Hemmingsen R (2004) Discriminations, reversals, and extra-dimensional shifts in the gottingen minipig. Behav Process 67:27–37
Moustgaard A, Arnfred SM, Lind NM, Hemmingsen R, Hansen AK (2005) Acquisition of visually guided conditional associative tasks in gottingen minipigs. Behav Process 68:97–102
Nakazawa K, McHugh TJ, Wilson MA, Tonegawa S (2004) Nmda receptors, place cells and hippocampal spatial memory. Nat Rev Neurosci 5:361–372
Neitz J, Jacobs GH (1989) Spectral sensitivity of cones in an ungulate. Vis Neurosci 2:97–100
Nielsen TR, Kornum BR, Moustgaard A, Gade A, Lind NM, Knudsen GM (2009) A novel spatial delayed non-match to sample (dnms) task in the gottingen minipig. Behav Brain Res 196:93–98
Pellow S, Chopin P, File SE, Briley M (1985) Validation of open: closed arm entries in an elevated plus-maze as a measure of anxiety in the rat. J Neurosci Methods 14:149–167
Schultz W, Apicella P, Scarnati E, Ljungberg T (1992) Neuronal activity in monkey ventral striatum related to the expectation of reward. J Neurosci 12:4595–4610
Siegford JM, Rucker G, Zanella AJ (2008) Effects of pre-weaning exposure to a maze on stress responses in pigs at weaning and on subsequent performance in spatial and fear-related tests. Appl Anim Behav Sci 110:189–202
Stolba A, Woodgush DGM (1989) The behavior of pigs in a semi-natural environment. Anim Prod 48:419–425
Stringer KG, Martin GM, Skinner DM (2005) The effects of hippocampal lesions on response, direction, and place learning in rats. Behav Neurosci 119:946–952
Tolman EC, Ritchie BF, Kalish D (1946) Studies in spatial learning. 2. Place learning versus response learning. J Exp Psychol 36:221–229
Vorhees CV, Williams MT (2006) Morris water maze: procedures for assessing spatial and related forms of learning and memory. Nat Protoc 1:848–858
Walsh SJ, Harley CW, Corbett D, Skinner DM, Martin GM (2008) Ca1 ischemic injury does not affect the ability of mongolian gerbils to solve response, direction, or place problems. Brain Res 1187:194–200
Wang B, Yu B, Karim M, Hu HH, Sun Y, McGreevy P, Petocz P, Held S, Brand-Miller J (2007) Dietary sialic acid supplementation improves learning and memory in piglets. Am J Clin Nutr 85:561–569
Zurkovsky L, Brown SL, Korol DL (2006) Estrogen modulates place learning through estrogen receptors in the hippocampus. Neurobiol Learn Mem 86:336–343
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Matt Conrad, Jen Rytych, and Caitlyn Getty for their assistance in the development of the spatial task.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Elmore, M.R.P., Dilger, R.N. & Johnson, R.W. Place and direction learning in a spatial T-maze task by neonatal piglets. Anim Cogn 15, 667–676 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-012-0495-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10071-012-0495-9