Abstract
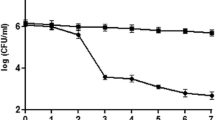
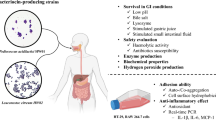
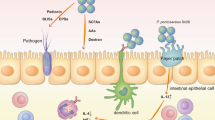
The selected strain, TAP041, showing an excellent ability to reduce the glyoxal and methylglyoxal levels, was identified by 16S rRNA gene-based phylogenetic analysis as Pediococcus pentosaceus. It demonstrated probiotic properties, including acid, bile salt, pancreatin, lysozyme tolerance, gut adhesion, and auto/coaggregation. In RAW264.7 macrophages, both live and heat-killed strains induced nitric oxide production and activated inducible nitric oxide synthase. RAW264.7 treated with P. pentosaceus TAP041 increased the expression level of tumor necrosis factor-α, interleukin (IL)-1β, IL-6, and cyclooxygenase-2, and regulated the expression of c-Jun amino-terminal kinase, p38, and extracellular signal-regulated kinase. These findings suggest that both live and heat-killed P. pentosaceus TAP041 can be used as potential immunostimulatory agents in functional food additives.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla AK, Ayyash MM, Olaimat AN, Osaili TM, Al-Nabulsi AA, Shah NP, Holley R. Exopolysaccharides as antimicrobial agents: Mechanism and spectrum of activity. Frontiers in Microbiology 12: 664395 (2021)
Ayyash MM, Abdalla AK, AlKalbani NS, Baig MA, Turner MS, Liu SQ, Shah NP. Invited review: Characterization of new probiotics from dairy and nondairy products—Insights into acid tolerance, bile metabolism and tolerance, and adhesion capability. Journal of Dairy Science 104: 8363-8379 (2021)
Balgir PP, Kaur B, Kaur T, Daroch N, Kaur G. In vitro and in vivo survival and colonic adhesion of Pediococcus acidilactici MTCC5101 in human gut. BioMed Research International 2013: 583850 (2013)
Cao Z, Pan H, Tong H, Gu D, Li S, Xu Y, Ge C, Lin Q. In vitro evaluation of probiotic potential of Pediococcus pentosaceus L1 isolated from paocai—a Chinese fermented vegetable. Annals of Microbiology 66: 963-971 (2015)
Cho Y, Han HT, Kim TR, Sohn M, Park YS. Immunostimulatory activity of Lactococcus lactis LM1185 isolated from Hydrangea macrophylla. Food Science and Biotechnology 32: 497-506 (2023)
Coleman JW. Nitric oxide in immunity and inflammation. International immunopharmacology 1: 1397-1406 (2001)
du Toit M, Franz CMAP, Dicks LMT, Schillinger U, Haberer P, Warlies B, Ahrens F, Holzapfel WH. Characterisation and selection of probiotic lactobacilli for a preliminary minipig feeding trial and their effect on serum cholesterol levels, faeces pH and faeces moisture content. International Journal of Food Microbiology 40: 93-104 (1998)
FAO/WHO. Guidelinces for the evaluation of probiotics in food. FAO/WHO working group, 1–11 (2002)
Gaens KH, Stehouwer CD, Schalkwijk CG. Advanced glycation endproducts and its receptor for advanced glycation endproducts in obesity. Current Opinion in Lipidology 24: 4-11 (2013)
García-Ruiz A, González de Llano D, Esteban-Fernández A, Requena T, Bartolomé B, Moreno-Arribas MV. Assessment of probiotic properties in lactic acid bacteria isolated from wine. Food Microbiology. 44: 220-225 (2014)
Holt JG, Krieg NR, Sneath PH, Staley JT, Williams ST. Bergey’s manual of determinative bacteriology. 9th. Baltimor: William & Wilkins (1994)
Jeong S, Kwon A, Jeong H, Park YS. Synergistic immunostimulatory activities of probiotic strains, Leuconostoc lactis and Weissella cibaria, and the prebiotic oligosaccharides they produce. Microorganisms 11: 1354 (2023)
Joung JA, You JY, Lee SS, Choi JH. Potential probiotic activity of isolated Lactobacillus harbinensis VF from taditionally fermented vinegar. Food Engineering Progress 27: 155-164 (2023)
Kwon HK, Song MJ, Lee HJ, Park TS, Kim MI, Park HJ, Pediococcus pentosaceus-fermented Cordyceps militaris inhibites inflammatory reactions and alleviates contact dermatitis. International Journal of Molecular Sciences. 9: 3504 (2018).
Lee KW, Park JY, Sa HD, Jeong JH, Jin DE, Heo HJ, Kim JH. Probiotic properties of Pediococcus strains isolated from jeotgals, salted and fermented Korean sea-food. Anaerobe 28: 199-206 (2014)
Lee MG, Joeng H, Shin J, Kim S, Lee C, Song Y, Lee BH, Park HG, Lee TH, Jiang HH, Han YS, Lee BG, Lee HJ, Park MJ, Jun YJ, Park YS. Potential probiotic properties of exopolysaccharide-producing Lacticaseibacillus paracasei EPS DA-BACS and prebiotic activity of its exopolysaccharide. Microorganisms 10: 2431 (2022)
Lin SW, Wu CH, Jao YC, Tsai YS, Chen YL, Chen CC, Fang TJ, Chau CF. Fermented supernatants of Lactobacillus plantarum GKM3 and Bifidobacterium lactis GKK2 protect against protein glycation and inhibit glycated protein ligation. Nutrients 15: 277 (2023)
Lin Y, Briandet R, Kovács ÁT. Bacillus cereus sensu lato biofilm formation and its ecological importance. Biofilm 4: 100070 (2022)
MacMicking J, Xie Qw, Nathan C. Nitric oxide and macrophage function. Annual review of immunology 15: 323-350 (1997)
Ocaña VS, Nader-Macías ME. Vaginal lactobacilli: self- and co-aggregating ability. British Journal of Biomedical Science 59: 183-190 (2002)
Ohn JE, Seol MK, Bae EY, Cho YJ, Jung HY, Kim BO. The potential probiotic and functional health effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional korean fermented foods. Journal of Life Science. 30: 581-591 (2020)
Park HY, Lee HB, Lee SY, Oh MJ, Ha SK, Do E, Lee HHL, Hur J, Lee KW, Nam MH, Park MG, Kim Y. Lactococcus lactis KF140 reduces dietary absorption of Nε - (carboxymethyl)lysine in rats and humans via β-galactosidase activity. Frontiers in Nutrition 9: 916262 (2022)
Pramanik S, Venkatraman S, Karthik P, Vaidyanathan VK. A systematic review on selection characterization and implementation of probiotics in human health. Food Science and Biotechnology 32: 423-440 (2023)
Sena CM, Matafome P, Crisóstomo J, Rodrigues L, Fernandes R, Pereira P, Seiça RM. Methylglyoxal promotes oxidative stress and endothelial dysfunction. Pharmacological Research 65: 497-506 (2012)
Shapouri‐Moghaddam A, Mohammadian S, Vazini H, Taghadosi M, Esmaeili SA, Mardani F, Seifi B, Mohammadi A, Afshari JT, Sahebkar A. Macrophage plasticity, polarization, and function in health and disease. Journal of Cellular Physiology 233: 6425-6440 (2018)
Shin JS, Jung JY, Lee SG, Shin KS, Rhee YK, Lee MK, Hong HD, Lee KT. Exopolysaccharide fraction from Pediococcus pentosaceus KFT18 induces immunostimulatory activity in macrophages and immunosuppressed mice. Journal of Applied Microbiology 120: 1390-1402 (2016)
Shukla R, Goyal A. Probiotic potential of Pediococcus pentosaceus CRAG3: A new isolate from fermented cucumber. Probiotics and Antimicrobial Proteins 6: 11-21 (2014)
Suh KS, Choi EM, Rhee SY, Kim YS. Methylglyoxal induces oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction in osteoblastic MC3T3-E1 cells. Free Radical Research 48: 206-17 (2014)
Tarique M, Abdalla A, Masad R, Al-Sbiei A, Kizhakkayil J, Osaili T, Olaimat A, Liu S-Q, Fernandez-Cabezudo M, al-Ramadi B, Ayyash M. Potential probiotics and postbiotic characteristics including immunomodulatory effects of lactic acid bacteria isolated from traditional yogurt-like products. Lwt 159: 113207 (2022)
Trunk T, Khalil HS, Leo JC. Bacterial autoaggregation. AIMS Microbiology 4: 140-164 (2018)
Uğur H, Görünmek M, Çatak J, Efe E, Özgür B, Duman S, Yaman M. Determination and assessment of the most potent precursors of advanced glycation end products in baklava and Turkish delight by HPLC. Food Science and Technology 42: e08522 (2022)
Xu X, Qiao Y, Peng Q, Shi B. Probiotic properties of Loigolactobacillus coryniformis NA-3 and in vitro comparative evaluation of live and heat-killed cells for antioxidant, anticancer and immunoregulatory activities. Foods 12: 1118 (2023)
Zhang H, Wang Z, Li Z, Wang K, Kong B, Chen Q. l-glycine and l-glutamic acid protect Pediococcus pentosaceus R1 against oxidative damage induced by hydrogen peroxide. Food Microbiology 101: 103897 (2022)
Zhu Y, Li X, Chen J, Chen T, Shi Z, Lei M, Zhang Y, Bai P, Li Y, Fei X. The pentacyclic triterpene Lupeol switches M1 macrophages to M2 and ameliorates experimental inflammatory bowel disease. International Immunopharmacology 30: 74-84 (2016)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by MetaCen Therapeutics.
Funding
This work received support from MetaCen Therapeutics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, C., Park, YS. Probiotic and immunostimulating effects of live and heat-killed Pediococcus pentosaceus TAP041. Food Sci Biotechnol (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-024-01530-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-024-01530-2