Abstract
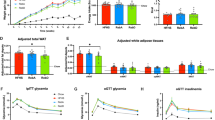
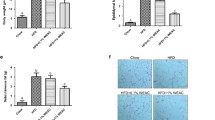
Rebaudioside A (Reb A) and neohesperidin dihydrochalcone (NHDC) are known as intense sweeteners. This study aimed to examine the anti-obesity effects of Reb A and NHDC. C57BL/6 J-ob/ob mice were supplemented with Reb A (50 mg/kg body weight [b.w.]), NHDC (100 mg/kg b.w.), or their combination (COMB) for 4 weeks. COMB-supplemented mice showed significant reduction in b.w. gain, food efficiency ratio, and fat mass. Additionally, mice in the COMB group showed suppressed levels of genes related to adipogenesis, lipogenesis, and lipolysis in the perirenal fat and the levels of hepatic triglyceride, glutamic oxaloacetic transaminase, and glutamic pyruvic transaminase. The lipogenesis and pro-inflammatory gene expressions were also downregulated in the liver, whereas β-oxidation related genes were upregulated in the COMB group. In addition, mice that received COMB showed distinct gut microbiota structure, enriched in Blautia and Parabacteroides, and depleted in Faecalibaculum and Mucispirillum, in relation to the control group. These results suggest that supplementation with Reb A and NHDC may be an effective treatment for obesity-related metabolic disorders.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berlanga A, Guiu-Jurado E, Porras JA, Auguet T. Molecular pathways in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Clinical and Experimental Gastroenterology. 7: 221–239 (2014)
Berry D, Kuzyk O, Rauch I, Heider S, Schwab C, Hainzl E, Decker T, Müller M, Strobl B, Schleper C, Urich T, Wagner M, Kenner L, Loy A. Intestinal Microbiota Signatures Associated with Inflammation History in Mice Experiencing Recurring Colitis. Front Microbiol. 6: 1408 (2015)
Berry D, Schwab C, Milinovich G, Reichert J, Ben Mahfoudh K, Decker T, Engel M, Hai B, Hainzl E, Heider S, Kenner L, Müller M, Rauch I, Strobl B, Wagner M, Schleper C, Urich T, Loy A. Phylotype-level 16S rRNA analysis reveals new bacterial indicators of health state in acute murine colitis. The ISME Journal. 6: 2091-2106 (2012)
Bolyen E, Rideout JR, Dillon MR, Bokulich NA, Abnet CC, Al-Ghalith GA, Alexander H, Alm EJ, Arumugam M, Asnicar F. Reproducible, interactive, scalable and extensible microbiome data science using QIIME 2. Nature Biotechnology. 37: 852–857 (2019)
Cai W, Xu J, Li G, Liu T, Guo X, Wang H, Luo L. Ethanol extract of propolis prevents high-fat diet-induced insulin resistance and obesity in association with modulation of gut microbiota in mice. Food Research International. 130: 108939 (2020)
Callahan BJ, McMurdie PJ, Rosen MJ, Han AW, Johnson AJA, Holmes SP. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nature Methods. 13: 581–583 (2016)
Chait A, Den Hartigh LJ. Adipose tissue distribution, inflammation and its metabolic consequences, including diabetes and cardiovascular disease. Frontiers in Cardiovascular Medicine. 7: 22 (2020)
Chen Y, Zhou J, Wang L. Role and mechanism of gut microbiota in human disease. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology. 11: 625913 (2021)
Choi J-Y, McGregor RA, Kwon E-Y, Kim YJ, Han Y, Park JHY, Lee KW, Kim S-J, Kim J, Yun JW. The metabolic response to a high-fat diet reveals obesity-prone and-resistant phenotypes in mice with distinct mRNA-seq transcriptome profiles. International Journal of Obesity. 40: 1452-1460 (2016)
Curry LL, Roberts A. Subchronic toxicity of rebaudioside A. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 46: S11-S20 (2008)
Farzanegi P, Dana A, Ebrahimpoor Z, Asadi M, Azarbayjani MA. Mechanisms of beneficial effects of exercise training on non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD): Roles of oxidative stress and inflammation. European Journal of Sport Science. 19: 994–1003 (2019)
Frydman A, Weisshaus O, Huhman DV, Sumner LW, Bar-Peled M, Lewinsohn E, Fluhr R, Gressel J, Eyal Y. Metabolic engineering of plant cells for biotransformation of hesperedin into neohesperidin, a substrate for production of the low-calorie sweetener and flavor enhancer NHDC. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 53: 9708–9712 (2005)
Jakab J, Miškić B, Mikšić Š, Juranić B, Ćosić V, Schwarz D, Včev A. Adipogenesis as a potential anti-obesity target: A review of pharmacological treatment and natural products. Diabetes, Metabolic Syndrome and Obesity: Targets and Therapy. 14: 67-83 (2021)
Kakleas K, Christodouli F, Karavanaki K. Nonalcoholic fatty liver disease, insulin resistance, and sweeteners: a literature review. Expert Review of Endocrinology & Metabolism. 15: 83-93 (2020)
Katoh K, Misawa K, Kuma Ki, Miyata T. MAFFT: a novel method for rapid multiple sequence alignment based on fast Fourier transform. Nucleic Acids Research. 30: 3059-3066 (2002)
Kim WR, Flamm SL, Di Bisceglie AM, Bodenheimer HC. Serum activity of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) as an indicator of health and disease. Hepatology. 47: 1363-1370 (2008)
Kroeze JH. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone is not a taste enhancer in aqueous sucrose solutions. Chemical Senses 25: 555–559 (2000)
Kwok KH, Lam KS, Xu A. Heterogeneity of white adipose tissue: molecular basis and clinical implications. Experimental & Molecular Medicine. 48: e215–e215 (2016)
Kwon M, Kim Y, Lee J, Manthey JA, Kim Y, Kim Y. Neohesperidin dihydrochalcone and neohesperidin dihydrochalcone-O-glycoside attenuate subcutaneous fat and lipid accumulation by regulating PI3K/AKT/mTOR pathway in vivo and in vitro. Nutrients. 14: 1087 (2022)
Lee HW, Kim KJ, Jung KS, Chon YE, Huh JH, Park KH, Chung JB, Kim CO, Han K-H, Park JY. The relationship between visceral obesity and hepatic steatosis measured by controlled attenuation parameter. PLoS One. 12: e0187066 (2017)
Lina B, Dreef-van der Meulen H, Leegwater D. Subchronic (13-week) oral toxicity of neohesperidin dihydrochalcone in rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology. 28: 507-513 (1990)
Lujan PV, Esmel EV, Meseguer SE. Overview of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and the role of sugary food consumption and other dietary components in its development. Nutrients. 13: 1442 (2021)
Mn M, Smvk P, Battula KK, Kalashikam RR. Differential response of rat strains to obesogenic diets underlines the importance of genetic makeup of an individual towards obesity. Scientific Reports. 7: 9162 (2017)
Ozato N, Saito S, Yamaguchi T, Katashima M, Tokuda I, Sawada K, Katsuragi Y, Kakuta M, Imoto S, Ihara K. Blautia genus associated with visceral fat accumulation in adults 20–76 years of age. NPJ Biofilms and Microbiomes. 5: 28 (2019)
Park HJ, DiNatale DA, Chung M-Y, Park Y-K, Lee J-Y, Koo SI, O'Connor M, Manautou JE, Bruno RS. Green tea extract attenuates hepatic steatosis by decreasing adipose lipogenesis and enhancing hepatic antioxidant defenses in ob/ob mice. The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry. 22: 393–400 (2011)
Price MN, Dehal PS, Arkin AP. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS One. 5: e9490 (2010)
Qian M, Hu H, Yao Y, Zhao D, Wang S, Pan C, Duan X, Gao Y, Liu J, Zhang Y, Yang S, Qi L-W, Wang L. Coordinated changes of gut microbiome and lipidome differentiates nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) from isolated steatosis. Liver International. 40: 622-637 (2020)
Romieu I, Dossus L, Barquera S, Blottière HM, Franks PW, Gunter M, Hwalla N, Hursting S D, Leitzmann M, Margetts B. Energy balance and obesity: what are the main drivers? Cancer Causes & Control. 28: 247–258 (2017)
Segata N, Izard J, Waldron L, Gevers D, Miropolsky L, Garrett WS, Huttenhower C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biology. 12: 1–18 (2011)
Skat‐Rørdam J, Højland Ipsen D, Lykkesfeldt J, Tveden-Nyborg P. A role of peroxisome proliferator‐activated receptor γ in non‐alcoholic fatty liver disease. Basic & Clinical Pharmacology & Toxicology. 124:528–537 (2019)
Suez J, Korem T, Zilberman-Schapira G, Segal E, Elinav E. Non-caloric artificial sweeteners and the microbiome: findings and challenges. Gut Microbes. 6: 149–155 (2015)
Suriano F, Vieira-Silva S, Falony G, Roumain M, Paquot A, Pelicaen R, Régnier M, Delzenne NM, Raes J, Muccioli GG. Novel insights into the genetically obese (ob/ob) and diabetic (db/db) mice: Two sides of the same coin. Microbiome. 9: 1-20 (2021)
Thompson LR, Sanders JG, McDonald D, Amir A, Ladau J, Locey KJ, Prill RJ, Tripathi A, Gibbons SM, Ackermann G. A communal catalogue reveals Earth’s multiscale microbial diversity. Nature. 551: 457-463 (2017)
Wang Y, Chen L, Li Y, Li Y, Yan M, Chen K, Hao N, Xu L. Efficient enzymatic production of rebaudioside A from stevioside. Bioscience, Biotechnology, and Biochemistry. 80: 67-73 (2016)
WHO. Obesity and overweight. Available from: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/obesity-and-overweight. Oct. 20 (2022)
Wu TR, Lin CS, Chang CJ, Lin TL, Martel J, Ko YF, Ojcius DM, Lu CC, Young JD, Lai HC. Gut commensal Parabacteroides goldsteinii plays a predominant role in the anti-obesity effects of polysaccharides isolated from Hirsutella sinensis. Gut. 68: 248-262 (2019)
Wutthi-In M, Cheevadhanarak S, Yasom S, Kerdphoo S, Thiennimitr P, Phrommintikul A, Chattipakorn N, Kittichotirat W, Chattipakorn S. Gut microbiota profiles of treated metabolic syndrome patients and their relationship with metabolic health. Scientific Reports. 10: 10085 (2020)
Xi D, Bhattacharjee J, Salazar-Gonzalez R-M, Park S, Jang A, Warren M, Merritt R, Michail S, Bouret S, Kohli R. Rebaudioside affords hepatoprotection ameliorating sugar sweetened beverage-induced nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Scientific Reports. 10: 6689 (2020)
Yilmaz P, Parfrey LW, Yarza P, Gerken J, Pruesse E, Quast C, Schweer T, Peplies J, Ludwig W, Glöckner FO. The SILVA and “all-species living tree project (LTP)” taxonomic frameworks. Nucleic Acids Research. 42: D643–D648 (2014)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Korea Institute of Planning and Evaluation for Technology in Food, Agriculture, and Forestry (IPET) through the Innovative Food Product and Natural Food Materials Development Program, funded by the Ministry of Agriculture, Food and Rural Affairs (MAFRA) (119020-03-2-HD040).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, Y., Han, H., Oh, Y. et al. A combination of rebaudioside A and neohesperidin dihydrochalcone suppressed weight gain by regulating visceral fat and hepatic lipid metabolism in ob/ob mice. Food Sci Biotechnol 33, 913–923 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01391-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01391-1