Abstract
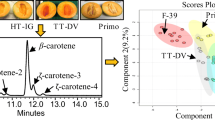
A robust and rapid HPLC method for β-carotene and β-apo-8′-carotenal analyses in various processed foods was developed. The analysis method was validated for low-fat, moderate-fat, and high-fat food matrices. The two carotenoids were identified by LC–MS/MS. The detection limits for β-carotene and β-apo-8′-carotenal in the three food matrices were 0.08–0.27 µg/g and 0.09–0.18 µg/g, respectively. The inter- and intra-day accuracy and precision were in accordance with the Codex guidelines. The validated method was applied to 57 processed food samples, possibly containing β-carotene and β-apo-8′-carotenal, obtained in Korea. The detected β-carotene and β-apo-8′-carotenal levels in the samples ranged from not detected (ND) to 6.92 µg/g and ND to 1.63 µg/g, respectively. Chocolate and cheese samples had the highest β-carotene and β-apo-8′-carotenal levels, respectively. Notably, several samples with no labeled carotenoid additives contained β-carotene. Moreover, the developed analytical method was compatible with various processed food matrices.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alothman M, Hogan SA, Hennessy D, Dillon P, Kilcawley KN, O’Donovan M, Tobin J, Fenelon MA, O’Callaghan TF. The “grass-fed” milk story: understanding the impact of pasture feeding on the composition and quality of bovine milk. Foods. 8: 350 (2019)
Anunciação PC, Giuffrida D, Murador DC, de Paula Filho GX, Dugo G, Pinheiro-Sant’Ana HM. Identification and quantification of the native carotenoid composition in fruits from the Brazilian Amazon by HPLC–DAD–APCI/MS. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 83 (2019)
AOAC. Vitamin A in margarine. Spectrophotometric method. p. Association of Official Analytical Chemists; p. 3.
Barba AIO, Hurtado MC, Mata MCS, Ruiz VF, Tejada MLSd. Application of a UV–vis detection-HPLC method for a rapid determination of lycopene and β-carotene in vegetables. Food Chemistry. 95: 328–336 (2006)
Bell T, Alamzad R, Graf BA. Effect of pH on the chemical stability of carotenoids in juice. Proc Nutr Soc. 75(OCE3)(OCE3: Summer Meeting): E94 (2016)
Biehler E, Mayer F, Hoffmann L, Krause E, Bohn T. Comparison of 3 spectrophotometric methods for carotenoid determination in frequently consumed fruits and vegetables. Journal of Food Science. 75: C55–C61 (2010)
Bohn T, Bonet ML, Borel P, Keijer J, Landrier JF, Milisav I, Ribot J, Riso P, Winklhofer-Roob B, Sharoni Y, Corte-Real J. Mechanistic aspects of carotenoid health benefits–where are we now? Nutrition Research Reviews. 34: 276–302 (2021)
Boon CS, McClements DJ, Weiss J, Decker EA. Factors influencing the chemical stability of carotenoids in foods. Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition. 50: 515–532 (2010)
Britton G, Liaaen-Jensen S, Pfander H. Carotenoids [Handbook]. 1st ed. Switzerland: Springer (2004)
Cardoso PC, Tomazini APB, Stringheta PC, Ribeiro SMR, Pinheiro-Sant’Ana HM. Vitamin C and carotenoids in organic and conventional fruits grown in Brazil. Food Chemistry. 126: 411–416 (2011)
Codex. Codex alimentarius. Harmonized IUPAC guidelines for the use of recovery information in analytical Measurement. CAC/GL 37-2001 (2001)
Codex. Codex alimentarius. Guideline on measurement uncertainty. CAC/GL 54-2004
de Freitas Santos PD, Rubio FTV, da Silva MP, Pinho LS, Favaro-Trindade CS. Microencapsulation of carotenoid-rich materials: A review. Food Research International. 147 (2021)
EFSA. Scientific opinion on the re‐evaluation of mixed carotenes (E 160a (i)) and beta‐carotene (E 160a (ii)) as a food additive. EFSA J. European Food Safety Authority:10: 2593 (2012a)
EFSA. Scientific opinion on the re‐evaluation of β‐apo‐8'‐carotenal (E 160e) as a food additive. EFSA J. European Food Safety Authority:10: 2499 (2012b)
EU. Regulation (EC) No 1333/2008 of the European parliament and of the council of on food additives. European Union (2008)
FAO. Food and Agriculture Organization. General standard for food additives codex stan 192–1995 (2019)
FDA. Food and drug administration office of regulatory affairs ORA laboratory manual volume II. Methods, method verification and validation. ORA-LAB.5.4.5 (2020)
Food and Drug Administration. Color additive status list. Food and Drug Administration (U.S.). Available from: https://www.fda.gov/industry/color-additive-inventories/color-additive-status-list. Accessed Dec. 29, 2021 (2021)
Granado F, Olmedilla B, Gil-Martinez E, Blanco I. A fast, reliable and low-cost saponification protocol for analysis of carotenoids in vegetables. Journal of Food Composition and Analysis. 14: 479–489 (2001)
HC. List of permitted colouring agents (lists of permitted food additives). https://www.canada.ca/en/health-canada/services/food-nutrition/food-safety/food-additives/lists-permitted/3-colouring-agents.html. Health Canada. Accessed Dec. 29, 2021 (2021)
Irakli MN, Samanidou VF, Papadoyannis IN. Development and validation of an HPLC method for the simultaneous determination of tocopherols, tocotrienols and carotenoids in cereals after solid-phase extraction. Journal of Separation Science. 34: 1375–1382 (2011)
JECFA. Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. Compendium of food additive specifications. pp. 117–119 (2016)
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluations of the joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives (JECFA)-beta-apo-8'-carotenal. Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. Available from: https://apps.who.int/food-additives-contaminants-jecfa-database/chemical.aspx?chemID=941. Accessed Sept. 21, 2022 (2019a)
Joint FAO/WHO Expert Committee on Food Additives. Evaluations of the joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives (JECFA)-beta-carotene (synthetic). Joint FAO/WHO expert committee on food additives. Available from: https://apps.who.int/food-additives-contaminants-jecfa-database/chemical.aspx?chemID=1514. Accessed Sept. 21, 2022 (2019b)
Kaiser P, Surmann P, Vallentin G, Fuhrmann H. A small-scale method for quantitation of carotenoids in bacteria and yeasts. Journal of Microbiological Method. 70: 142–149 (2007)
Kim E-H, Lee KM, Lee S-Y, Kil M, Kwon O-H, Lee S-G, Lee S-K, Ryu T-H, Oh S-W. Infuence of genetic and environmental factors on the contents of carotenoids and phenolic acids in red pepper fruits (Capsicum annuum L.). Applied Biological Chemistry. 64: 1-11 (2021)
Koh E, Wimalasiri KM, Renaud EN, Mitchell AE. A comparison of flavonoids, carotenoids and vitamin C in commercial organic and conventional marinara pasta sauce. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 88: 344–354 (2008)
Liu W, Wang J, McClements DJ, Zou L. Encapsulation of β-carotene-loaded oil droplets in caseinate/alginate microparticles: Enhancement of carotenoid stability and bioaccessibility. Journal of Functional Foods. 40: 527–535 (2018)
Luzardo-Ocampo I, Ramírez-Jiménez AK, Yañez J, Mojica L, Luna-Vital DA. Technological applications of natural colorants in food systems: A review. Foods. 10: 634 (2021)
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. Food additves code - β-apo-8′-carotenal. Available from: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/foodcode/04_03.jsp?idx=289. Accessed Sept. 21, 2022 (2021a)
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.Food additves code - β-apo-8′-carotenal. Available from: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/foodcode/04_03.jsp?idx=8200285 Accessed Sept. 21, 2022 (2021b)
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.Food additives code - β-carotene. Available from: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/foodcode/04_03.jsp?idx=450 Accessed Sept. 21, 2022 (2021c)
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.Food additves code - β-carotene. Available from: https://www.foodsafetykorea.go.kr/foodcode/04_03.jsp?idx=8200447 Accessed Sept. 21, 2022 (2021d)
Mitrowska K, Vincent U, von Holst C. Separation and quantification of 15 carotenoids by reversed phase high performance liquid chromatography coupled to diode array detection with isosbestic wavelength approach. Journal of Chromatography A. 1233: 44–53 (2012)
Mortensen A. Carotenoids and other pigments as natural colorants. Pure and Applied Chemistry. 78: 1477–1491 (2006)
Petry FC, Mercadante AZ. Composition by LC-MS/MS of new carotenoid esters in mango and citrus. Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry. 64: 8207–8224 (2016)
Rader JI, Weaver CM, Patrascu L, Ali LH, Angyal G. α-Tocopherol, total vitamin A and total fat in margarines and margarine-like products. Food Chemistry. 58: 373–379 (1997)
Ren D, Zhang S. Separation and identification of the yellow carotenoids in Potamogeton crispus L. Food Chemistry. 106: 410–414 (2008)
Rivera S, Vilaró F, Canela R. Determination of carotenoids by liquid chromatography/mass spectrometry: Effect of several dopants. Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry. 400: 1339–1346 (2011)
Rodriguez-Concepcion M, Avalos J, Bonet ML, Boronat A, Gomez-Gomez L, Hornero-Mendez D, Limon MC, Meléndez-Martínez AJ, Olmedilla-Alonso B, Palou A, et al. A global perspective on carotenoids: Metabolism, biotechnology, and benefits for nutrition and health. Progress in Lipid Research. 70: 62–93 (2018)
Rombaut R, Camp JV, Dewettinck K. Phospho- and sphingolipid distribution during processing of milk, butter and whey. International Journal of Food Science and Technology. 41: 435–443 (2006)
Santos J, Mendiola JA, Oliveira MBPP, Ibáñez E, Herrero M. Sequential determination of fat- and water-soluble vitamins in green leafy vegetables during storage. Journal of Chromatography A. 1261: 179–188 (2012)
Scotter MJ, Castle L, Croucher JM, Olivier L. Method development and analysis of retail foods and beverages for carotenoid food colouring materials E160a(ii) and E160e. Food Additives and Contaminants. 20: 115–126 (2003)
Shahid M, Shahid-ul-Islam F, Mohammad F. Recent advancements in natural dye applications: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production. 53: 310–331 (2013)
Sigurdson GT, Tang P, Giusti MM. Natural colorants: Food colorants from natural sources. Annu Rev Food Sci Technol. 8: 261–280 (2017)
Song J, Cho W. Processed food and food coloring. 10: 62–80 (1997)
USDA. The United States Department of Agriculture. USDA national nutrient database for standard reference release 28 (2015)
Vallverdú‐Queralt A, Martínez‐Huélamo M, Arranz‐Martinez S, Miralles E, Lamuela‐Raventós RM. Differences in the carotenoid content of ketchups and gazpachos through HPLC/ESI (Li+)‐MS/MS correlated with their antioxidant capacity. Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture. 92: 2043–2049 (2012)
Van Breemen RB, Dong L, Pajkovic ND. Atmospheric pressure chemical ionization tandem mass spectrometry of carotenoids. International Journal of Mass Spectrometry. 312: 163–172 (2012)
Van Rooyen J, Esterhuyse AJ, Engelbrecht AM, Du Toit EF. Health benefits of a natural carotenoid rich oil: A proposed mechanism of protection against ischaemia/reperfusion injury. Asia Pacific Journal of Clinical Nutrition. 17(1). Suppl 1: 316–319 (2008)
Wall MM, Waddell CA, Bosland PW. Variation in β-carotene and total carotenoid content in fruits of capsicum. Hortscience. 36: 746–749 (2001)
Xu M, Chen T, Butt CM. Identification of beta‐carotene degradation compounds and their structural elucidation by high‐resolution accurate mass spectrometry. J of Food Science. 84: 3535–3545 (2019)
Zhang L, Wang S, Yang R, Mao J, Jiang J, Wang X, Zhang W, Zhang Q, Li P. Simultaneous determination of tocopherols, carotenoids and phytosterols in edible vegetable oil by ultrasound-assisted saponification, LLE and LC-MS/MS. Food Chemistry. 289: 313–319 (2019)
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by grants from the Ministry of Food and Drug Safety in 2020 [Grant Numbers 18162MFDS009) and by a 2019 Chung-Ang University Graduate Research Scholarship. We thank the BT research facility center, Chung-Ang University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jang, W., Lee, C., Suh, HJ. et al. β-Carotene and β-apo-8′-carotenal contents in processed foods in Korea. Food Sci Biotechnol 32, 1501–1513 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01285-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-023-01285-2