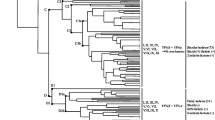
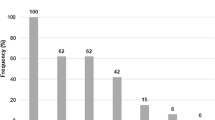
Abstract
The present study was conducted to determine the occurrence of B. cereus group members in low-moisture food products by phenotypic and genetic assessment and to evaluate the toxigenic potential of B. cereus group isolates. According to the results of their morphological shape, growth temperature range, strain-specific gene distribution, 79.5% and 20.5% among 112 isolates were identified as B. cereus sensu stricto (s.s.) and B. thuringiensis, respectively and other toxigenic B. cereus group members was not found. All B. cereus group isolates possessed nheABC, hblACD, cytK, entFM genes, and the most frequent gene was nheA. Only three B. cereus s. s. isolates exhibited as emetic toxin gene-harboring B. cereus group. Several B. cereus s.s. and B. thuringiensis isolates from a low-moisture food products were moderate biofilm formers and showed resistance to rifampicin, tetracycline, or clindamycin. The existence of B. cereus s.s. and B. thuringiensis in low-moisture food products indicates the possible risk of foodborne infections due to their virulence potential.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adang MJ, Crickmore N, Jurat-Fuentes J. Diversity of Bacillus thuringiensis crystal toxins and mechanism of action. Advances in Insect Physiology. 47: 39-70 (2014)
Almatroudi A, Tahir S. Hu H. Chowdhury D, Gosbell IB, Jensen SO, Vickery K. Staphylococcus aureus dry-surface biofilms are more resistant to heat treatment than traditional hydrated biofilms. Journal of Hospital Infection. 98: 161–167 (2018)
Andersson A, Ronener U, Granum PE. What problems does the food industry have with the spore-forming pathogens Bacillus cereus and Clostridium perfringens? International Journal of Food Microbiology. 28: 145-155 (1995)
Ankolekar C, Rahmati T. Labbe RC. Detection of toxigenic Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis spores in U.S. rice. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 128: 460–466 (2009)
Asano SI, Nukumizu Y, Bando H, Lizuka T, Yamamoto T. Cloning of novel enterotoxin genes from Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 63: 1054-1057 (1997)
Bahuguna A, Joe A, Kumar V, Lee JS, Kim S-Y, Moon J-Y, Cho S-K, Cho H, Kim M. Study on the identification methods for effective microorganisms in commercially available organic agriculture materials. Microorganisms. 8: 1568 (2020)
Banerjee M, Sarkar PK. Microbiological quality of some retail spices in India. Food Research International. 36: 469-474 (2003)
Bartoszewicz M, Bideshi DK, Kraszewska A, Modzelewska E, Swiecicka I. Natural isolates of Bacillus thuringiensis display genetic and psychrotrophic properties characteristic of Bacillus weihenstephanensis. Journal of Applied Microbiology. 106: 1967-1975 (2009)
Berthold-Pluta A, Antoni P, Monika G, Ilona S. Prevalence and toxicity characterization of Bacillus cereus in food products from Poland. Foods. 8: 269 (2019)
Beuchat L, Komitopoulou E, Betts R, Beckers H, Bourdichon F, Joosten H, Fanning S, ter Kuile B. Persistence and survival of pathogens in dry foods and dry food processing environments. ILSI Europe Report Series. 1–48 (2011)
Böhm ME, Huptas C, Krey VM, Scherer S. Massive horizontal gene transfer, strictly vertical inheritance and ancient duplications differentially shape the evolution of Bacillus cereus enterotoxin operons hbl, cytK and nhe. BMC Ecology and Evolution. 15: 246 (2015)
Boonchai N, Asano SI, Bando HC, Wiwat C. Study on cytotoxicity and nucleotide sequences of enterotoxin FM of Bacillus cereus isolated from various food sources. Journal of the Medical Association of Thailand. 91:1425-1432 (2008)
Bourdichon F, Betts R, Dufour C, Fanning S, Farber J, McClure P, Stavropoulou DA, Wemmenhove E, Zwietering MH, Winkler A. Processing environment monitoring in low moisture food production facilities: Are we looking for the right microorganisms? International Journal of Food Microbiology. 356: 109351 (2021)
Byington CL, Enriquez FR, Hoff C, Tuohy R, Taggart EW, Hillyard DR, Carroll KC, Christenson JC. Serious bacterial infections in febrile infants 1 to 90 days old with and without viral infections. Pediatrics. 113:1662-1666 (2004)
Campbell EA, Korzheva N, Mustaev A, Murakami K, Nair S, Goldfarb A, Darst, SA. Structural mechanism for rifampicin inhibition of bacterial RNA polymerase. Cell. 104: 901-912 (2001)
Carter L, Chase HR, Gieseker CM, Hasbrouck NR, Stine CB, Khan A, Ewing-Peeples LJ, Tall BD, Gopinath GR. Analysis of enterotoxigenic Bacillus cereus strains from dried foods using whole genome sequencing, multi-locus sequence analysis and toxin gene prevalence and distribution using endpoint PCR analysis. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 284: 31-39 (2018)
Chattopadhyay A, Bhatnagar N, Bhatnagar R. Bacterial insecticidal toxins. Critical Reviews in Microbiology. 30: 33-54 (2004)
Choo E, Jang SS, Kim K, Lee KG, Heu S, Ryu S. Prevalence and genetic diversity of Bacillus cereus in dried red pepper in Korea. Journal of Food Protection. 70: 917-922 (2007)
Contzen M, Hailer M, Rau J. Isolation of Bacillus cytotoxicus from various commercial potato products. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 174:19–22 (2014)
Crowe SJ, Bottichio L, Shade LN, Whitney BM, Corral N. Shiga toxin- producing Escherichia coli infections associated with flour. New England Journal of Medicine. 377: 2036-2043 (2017)
Cui Y, Liu Y, Liu X, Xia X, Ding S, Zhu K. Evaluation of the toxicity and toxico kinetics of cereulide from an emetic Bacillus cereus strain of milk origin. Toxins. 8: 156 (2016)
Daczkowska-Kozon EG, Bednarczyk A, Biba M, Repich K. Bacteria of Bacillus cereus group in cereals at retail. Polish Journal of Food and Nutrition Sciences. 59: 53-59 (2009)
Di Franco C, Beccari E, Santini T, Pisaneschi G, Tecce G. Colony shape as a genetic trait in the pattern-forming Bacillus mycoides. BMC Microbiology. 2: 33 (2002)
EFSA Panel on Biological Hazards. Risks for public health related to the presence of Bacillus cereus and other Bacillus spp. including Bacillus thuringiensis in foodstuffs. EFSA Journal. 14: 4524 (2016)
Ehling-Schulz M, Fricker M, Grallert H, Rieck P, Wagner M, Scherer S. Cereulide synthetase gene cluster from emetic Bacillus cereus: structure and location on a mega virulence plasmid related to Bacillus anthracis toxin plasmid pXO1. BMC Microbiology. 6: 20 (2006)
Ehling-Schulz M, Guinebretiere M-H, Monthán A, Berge O, Fricker M, Svensson B. Toxin gene profiling of enterotoxic and emetic Bacillus cereus. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 260: 232-240 (2006)
The European Committee on Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing (EUCAST). Breakpoint tables for interpretation of MICs and zone diameters. Version 6.0, 2022. https://www.eucast.org/clinical_breakpoints. Accessed 03 June 2022.
Faille C, Lebret V, Gavini F, Maingonnat J-F. Injury and lethality of heat treatment of Bacillus cereus spores suspended in buffer and in poultry meat. Journal of Food Protection. 60: 544-547 (1997)
Francis KP, Mayr R, von Stetten F, Stewart GSAB, Scherer S. Discrimination of psychrotrophic and mesophilic strains of the Bacillus cereus group by PCR targeting of major cold shock protein genes. Applied and Environmental Microbiology. 64: 3525-3529 (1998)
Granum PE, Lund T. Bacillus cereus enterotoxins. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 157: 223-228 (1997)
Guinebretiere M, Broussolle Y, Nguyen-The C. Enterotoxigenic profiles of food-poisoning and food-borne Bacillus cereus strains. Journal of Clinical Microbiology. 40: 3053–3056 (2002)
Guoping Z, Dasheng Z, Lina D, Quanxin C, Zhiming Y. Occurrence of psychrotrophic Bacillus cereus group strains in ice creams. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 137: 143-146 (2010)
Jacxsens L, Kussaga J, Luning PA, Van der Spiegel M, Devlieghere F, Uyttendaele M. A microbial assessment scheme to measure microbial performance of food safety management systems. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 134: 113-125 (2009)
Jung K, Song BS, Kim MJ, Moon BG, Go SM, Kim JK. Effect of X-ray, gamma ray, and electron beam irradiation on the hygienic and physicochemical qualities of red pepper powder. LWT - Food Science and Technology. 63: 846-851 (2015)
Heini N, Stephan R, Ehling-Schulz M, Johler S. Characterization of Bacillus cereus group isolates from powdered food products. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 283: 59–64 (2018)
Jeon JH, Park JH. Toxin gene analysis of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from cooked rice. Korean Journal of Food Science and Technology. 42: 361-367 (2010)
Johler S, Kalbhenn EM, Heini N, Brodmann P, Gautsch S, Bağcioğlu M, Ehling-Schulz M. Enterotoxin production of Bacillus thuringiensis isolates from biopesticides, foods, and outbreaks. Frontiers in Microbiology. 9: 1915 (2018)
Kim B, Bang J, Kim H, Kim Y, Kim BS, Beuchat LR, Ryu JH. Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis spores in Korean rice: prevalence and toxin production as affected by production area and degree of milling. Food Microbiology. 42: 89-94 (2014)
Kim J-B, Choi O-K, Kwon S-M, Cho S-H, Park B-J, Jin NY, Yu YM, Oh D-H. Prevalence and toxin characteristics of Bacillus thuringiensis isolated from organic vegetables. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 27: 1449-1456 (2017)
Kim M-J, Han J-K, Park J-S, Lee J-S, Lee S-H. Cho J.-I, Kim K-S. Various enterotoxin and other virulence factor genes widespread among Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis strains. Journal of Microbiology and Biotechnology. 25: 872–879 (2015)
Kim SK, Kim K-P, Jang SS, Shin EM, Kim M-J, Oh S, Ryu S. Prevalence and toxigenic profiles of Bacillus cereus isolated from dried red peppers, rice, and Sunsik in Korea. Journal of Food Protection. 72: 578-582 (2009)
Kone, KM, Douamba Z, Halleux MD, Bougoudogo F, Mahillon J. Prevalence and diversity of the thermotolerant bacterium Bacillus cytotoxicus among dried food products. Journal of Food Protection. 82:1210-1216 (2019)
Kovac J, Miller RA, Carroll LM, Kent DJ, Jian J, Beno SM. Production of hemolysin BL by Bacillus cereus group isolates of dairy origin is associated with whole-genome phylogenetic clade. BMC Genomics. 17: 581-596 (2016)
Kuroki R, Kawakami K, Qin L, Kaji C, Watanabe K, Kimura Y, Ishiguro C, Tanimura S, Tsuchiya Y, Hamaguchi I, Sakakura M, Sakabe S, Tsuji K, Inoue M, Watanabe H. Nosocomial bacteremia caused by biofilm-forming Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis. Internal Medicine. 48: 791-796 (2009)
Lechner S, Mayr R, Francis KP, Prüss BM, Kaplan T, Wiessner-Gunkel E, Stewart GS, Scherer S. Bacillus weihenstephanensis sp. nov. is a new psychrotolerant species of the Bacillus cereus group. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 48:1373–1382 (1998)
Lee DS, Kim KS, Kwon KS, Hong KW. A multiplex PCR assay for the detection and differentiation of enterotoxin-producing and emetic toxin-producing Bacillus cereus strains. Food Science and Biotechnology. 17: 761-765 (2008)
Lee N, Sun JM. Kwon KY, Kim HJ, Koo M, Chun HS. Genetic diversity, antimicrobial resistance, and toxigenic profiles of Bacillus cereus strains isolated from Sunsik. Journal of Food Protection. 75: 225–230 (2012)
Limcharoenchat P, James MK, Marks BP. Survival and thermal resistance of Salmonella enteritidis PT 30 on almonds after long-term storage. J. Food Prot. 82: 194-199 (2019)
Miller RA, Beno SM, Kent DJ, Carroll LM, Martin NH, Boor KJ. Bacillus wiedmannii sp. nov. is a new psychrotrophic and cytotoxic Bacillus cereus group species isolated from dairy foods and environments in the USA. International Journal of Systematic and Evolutionary Microbiology. 66: 4744–4753 (2016)
Ministry of Food and Drug Safety. (2022). Food Code. Ministry of Food and Drug Safety.
Ngamwongsatit P, Buasri W, Pianariyanon P, Pulsrikarn C, Ohba M, Assavanig A, Panbangred W. Broad distribution of enterotoxin genes (hblCDA, nheABC, cytK, and entFM) among Bacillus thuringiensis and Bacillus cereus as shown by novel primers. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 121: 352-356 (2008)
Okinaka R, Cloud K, Hampton O, Hoffmaster A, Hill K, Keim P, Koehler T, Lamke G, Kumano S, Manter D, Martinez Y, Ricke D, Svensson R, Jackson P. Sequence, assembly and analysis of pX01 and pX02. Applied Microbiology. 87: 261-262 (1999)
Österblad M, Hadanen A, Manninen R, Leistevuo T, Peltonen R, Meurman O. A between-species comparison of antimicrobial resistance in enterobacteria in fecal flora. Journal of Antimicrobial Chemotherapy. 44: 1479-1484 (2000)
Ozcelik B, Citak S. Evaluation of antibiotic resistance of Bacillus cereus isolates in ice-cream samples sold in Ankara. Turkish Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences. 6: 231-238 (2009)
Park KM, Kim HJ, Jeong MC, Koo M. Occurrence of toxigenic Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis in Doenjang, a Korean fermented soybean paste. Journal of Food Protection. 79: 605-612 (2016)
Park KM, Jeong M, Park KJ, Koo M. Prevalence, enterotoxin genes, and antibiotic resistance of Bacillus cereus isolated from raw vegetables in Korea. Journal of Food Protection. 81: 1590-1597 (2018)
Park YB, Kim JB, Shin SW, Kim JC, Cho SH, Lee BK, Ahn J, Kim JM, Oh DH. Prevalence, genetic diversity, and antibiotic susceptibility of Bacillus cereus strains isolated from rice and cereals collected in Korea. Journal of Food Protection. 72: 612-617 (2009)
Pinto AD, Bonerba E, Bozzo G, Ceci E, Terio V, Tantillo G. Occurence of potentially enterotoxigenic Bacillus cereus in infant milk powder. European Food Research and Technology. 237: 275-279 (2013)
Rosenquist H, Smidt L, Andersen SR, Jensen GB, Wilcks A. Occurrence and significance of Bacillus cereus and Bacillus thuringiensis in ready-to-eat food. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 250: 129-136 (2005)
Ryan PA, Macmillan JD, Zilinskas BA. Molecular cloning and characterization of the genes encoding the L1 and L2 components of hemolysin BL from Bacillus cereus. Journal of Bacteriology. 179: 2551-2556 (1997)
Sacchi CT, Whitney AM, Mayer LW, Morey R, Steigerwalt A, Boras A, Popovic T. Sequencing of 16S rRNA gene: a rapid tool for identification of Bacillus anthracis. Emerging Infectious Diseases. 8: 1117 (2002)
Sagoo SK, Little CL, Greenwood M, Mithani V, Grant KA, McLauchlin J, de Pinna E, Threlfal EJ. Assessment of the microbiological safety of dried spices and herbs from production and retail premises in the United Kingdom. Food Microbiology. 26: 39–43 (2009)
Samapundo S, Heyndrickx M, Xhaferi R, Devlieghere F. Incidence, diversity and toxin gene characteristics of Bacillus cereus group strains isolated from food products marketed in Belgium. International Journal of Food Microbiology. 150: 34-41 (2011)
Schoeni JL, Wong ACL. Bacillus cereus food poisoning and its toxins. Journal of Food Protection. 68: 636-648 (2005)
Singh AK, Prakash P, Achra A, Singh GP, Das A, Singh RK. Standardization and classification of in vitro biofilm formation by clinical isolates of Staphylococcus aureus. Journal of Global Infectious Diseases Dis. 9: 93-101 (2017)
Shaheen R, Svensson B, Andersson MA, Christiansson A, Salkinoja-Salone M. Persistence strategies of Bacillus cereus spores isolated from dairy silo tanks. Food Microbiology. 27: 347-355 (2010)
Stenfors ALP, Granum PE. Psychrotolerant species from the Bacillus cereus group are not necessarily Bacillus weihenstephanensis. FEMS Microbiology Letters. 197: 223-228 (2001)
Stepanović S, Vuković D, Dakić I, Savić B, Švabić-Vlahović MA. A modified microtiter-plate test for quantification of staphylococcal biofilm formation. Journal of Microbiological Methods. 40: 175-179 (2000)
Svensson B, Monthan A, Shaheen R, Andersson MA, Salkinoja-Salonen M, Christiansson A. Occurrence of emetic toxin producing Bacillus cereus in the dairy production chain. International Dairy Journal. 16: 740-749 (2006)
Tewari A, Singh SP, Singh R. Incidence and enterotoxigenic profile of Bacillus cereus in meat and meat products of Uttarakhand, India. Journal of Food Science and Technology. 52: 1796-1801 (2015)
Wei S, Chelliah R, Park BJ, Kim SH, Forghani F, Cho MS, Park DS, Jin YG, Oh DH. Differentiation of Bacillus thuringiensis from Bacillus cereus group using a unique marker based on real-time PCR. Frontiers in Microbiology. 10: 883 (2019)
Yang Y, Yu X, Zhan L, Chen J, Zhang Y, Zhang J, Chen H, Zhang Z, Zhang Y, Lu Y, Mei L. Multilocus sequence type profiles of Bacillus cereus isolates from infant formula in China. Food Microbiology. 62: 46-50 (2017)
Yim JH, Kim KY, Chon JW, Kim DH, Kim HS, Choi DS, Choi IS, Seo KH. Incidence, antibiotic susceptibility, and toxin profiles of Bacillus cereus sensu lato isolated from Korean fermented soybean products. Journal of Food Science. 80: 1266-1270 (2015)
Yu S, Yu P, Wang J, Li C, Guo H, Liu C, Kong L, Yu L, Wu S, Lei T, Chen M, Zeng H, Pang R, Zhang Y, Wei X, Zhang J, Wu Q, Ding Y. A study on prevalence and characterization of Bacillus cereus in ready-to-eat foods in China. Frontiers in Microbiology. 10: 3043 (2020)
Zhao S. Chen J, Fei P, Feng H, Wang Y, Ali MA, Yang W. Prevalence, molecular characterization, and antibiotic susceptibility of Bacillus cereus isolated from dairy products in China. Journal of Dairy Science. 103: 3994-4001 (2020)
Acknowledgements
This research was funded by the Korea Food Research Institute, Grant No. E0210800-01 and E0210702-02, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Park, K.M., Kim, A.Y., Kim, H.J. et al. Prevalence and characterization of toxigenic Bacillus cereus group isolated from low-moisture food products. Food Sci Biotechnol 31, 1615–1629 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-022-01144-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-022-01144-6