Abstract
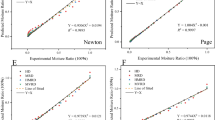
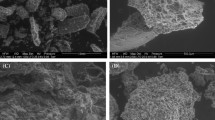
The effects of five different drying conditions on kimchi powder quality were determined by comparatively analyzing their physicochemical characteristics, volatile profile, and sensory evaluations. The moisture content of the kimchi powder obtained by each method was < 10%, and the yield after drying differed among methods ranging from 9.50 to 10.38% (p < 0.05). Electronic nose and tongue analyses demonstrated significant differences (p < 0.05) between samples based on the drying temperature. The particle size distribution did not differ considerably between drying methods, except for the ground kimchi (p < 0.05). The sensory evaluation test revealed that the flavor and taste were rated the highest for the kimchi powder prepared using HADHT. Therefore, hot-air drying at a high temperature was the most effective method for kimchi powder production owing to have a good flavor and taste and the shorter drying time.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
AOAC. Official Methods of Analysis. 15th edition. Association of Official Analytical Chemists, Washington DC, USA. 987–1009 (1990)
Chamber E, Lee J, Chun S, Miller AE. Development of a lexicon for commercially available cabbage (Baechu) kimchi. J. Sens. Stud. 27: 511–518 (2012)
Cho Y, Lee HS. A study on flavorous taste components in kimchi on free amino acids. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 11: 26–31 (1979)
Cho YB, Park WP, Jung EJ, Lee MJ, Lee YB. Analysis of volatile compounds in kimchi-flavored steak sauce. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 34: 351–355 (2012)
Choi JY, Kim KH, Chun JK. Design and evaluation of a microcomputer-based vacuum drying system for Shiitake mushrooms. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 19: 550–551 (1987)
Choi SH. Volatile aroma components of Korean semi-fermented teas. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 33: 529–533 (2001)
Codex Alimentarius Commission. Distribution of the report of the 20th session of the codex committee on processed fruits and vegetables (Alinorm 01/27). Geneva, Switzerland. 52–56 (2001)
Dymerski T, Chmiel, T, Wardencki W. Invited Review Article: An odor-sensing system-powerful technique for foodstuff studies. Rev. Sci. Instrum. 82: 1–32 (2011)
Hong SP, Lee EJ, Kim YH, Ahn DU. Effect of fermentation temperature on the volatile composition of kimchi. J. Food Sci. 81: 2623–2629 (2016)
Herbert S, Rebecca N, Bleibaum, Heather AT. Sensory evaluation practices. 4th Edition. Academic Press. Cambridge. 283–285 (2012)
Hootman. Manual on descriptive analysis testing for sensory evaluation. ASTM. ASTM manual series MNL 13. 1–50 (1992)
Jeon SY, Baek JH, Jeong EJ, Cha YJ. Volatile flavor compounds in commercial black garlic extracts. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 41: 116–122 (2012)
Jozinovic A, Subaric D, Ackar D, Babic J, Planinic M, Pavokovic M, Blazic M. Effect of screw configuration, moisture content and particle size of corn grits on properties of extrudates. Croat. J. Food Sci. Technol. 4: 95–101 (2012)
Jung JY, Lee SH, Jeon CO. Kimchi microflora: history, current status, and perspectives for industrial kimchi production. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 98: 2385–2393 (2014)
Kim HR, Seog EJ, Lee JH, Rhim JW. Physicochemical properties of onion powder as influenced by drying methods. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 36: 342–347 (2007)
Kim DW, Kim BM, Lee HJ, Jang GJ, Song SH, Lee JI, Lee SB, Shim JM, Lee KW, Kim JH, Ham KS, Chen F, Kim HJ. Effects of different salt treatments on the fermentation metabolites and bacterial profiles of kimchi. J. Food Sci. 82: 1124–1131 (2017)
Ko YT, Lee JY. Quality characteristics of kimchi prepared with Chinese radish and its quality change by freeze-drying. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 35: 937–942 (2003)
Ko YT, Kang JH, Kim TE. Quality of freeze-dried kimchi. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 33: 100–106 (2011)
Ku KH, Sunwoo JY, Park WS. Effects of ingredients on its quality characteristics during kimchi fermentation. J Korean Soc Food Sci Nutr. 34: 267–276 (2005)
Latha RS, Lakshmi PK. Electronic tongue: An analytical gustatory tool. J. Adv. Pharm. Tech. Res. 3: 3–8 (2012)
Lewicki P. Design of hot air drying for better foods. Trends Food Sci. Technol. 17: 153–163 (2006)
Meilgaard M.C, Carr T, Civille G. Sensory Evaluation Techniques. Third Edition. CRC Press Inc. New York. 141–172 (1999)
Meilgaard M.C, Civille G, Carr T. Sensory Evaluation Techniques. Fifth Edition. CRC Press Inc. New York. 165–198 (2015)
Park HJ, Lee YJ, Eun JB. Physicochemical characteristics of kimchi powder manufactured by hot air drying and freeze drying. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 5: 193–198 (2016)
Seo YC, Choi YB, Ko JR, Lee HY. Quality characteristics of dried kimchi by cyclic low pressure drying. Food Eng. Prog. 17: 319–324 (2013)
Tamang JP, Watanabe K, Holzapfel WH. Review: Diversity of microorganisms in global fermented foods and beverages. Front Microbiol. 7: 377 (2016)
Wisniewska P, Sliwinska M, Namiesnik J, Wardencki W, Dymerski T. The verification of the usefulness of electronic nose based on ultra-fast gas chromatography and four different chemometric methods for rapid analysis of spirit beverages. J. Ana. Methods Chem. 2016: 1–12 (2016)
Woo KS, Yoon HS, Lee YR, Lee JS, Kim DJ, Hong JT, Jeong HS. Characteristics and antioxidative activity of volatile compounds in heated garlic (Allium sativum). Food Sci. Biotechnol. 16: 822–827 (2007)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by grants from the World Institute of Kimchi (KE1801-4, KE1603-4), funded by the Ministry of Science, ICT, and Future Planning, Republic of Korea.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Park, J.Y., Yang, JH., Lee, MA. et al. Effects of different drying methods on physicochemical properties, volatile profile, and sensory characteristics of kimchi powder. Food Sci Biotechnol 28, 711–720 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0526-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0526-7