Abstract
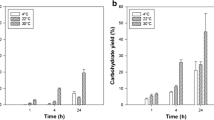
In this study, we optimized the process for extracting lipids and proteins from wet biomasses of Spirulina sp. using a 4-kHz ultrasonic osmotic shock method with ultrasound enhancement at a constant frequency of 40 kHz. Optimization was conducted using a response surface methodology (RSM) at an osmotic NaCl concentration of 10–30%, solvent:biomass ratio of 5–15 v/w, and extraction times of 20–50 min. The present osmotic shock method with ultrasound irradiation increased lipid yields to 6.65% in the presence of 11.9% NaCl, a solvent:biomass ratio of 12:1 v/w, and a 22-min extraction time, and protein yields to 43.96% with 15.12% NaCl, a solvent:biomass ratio of 10:1 v/w, and a 30-min extraction time.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anshari FA, Gupta SK, Shriwastav A, Guldhe A, Rawat I, Bux F. Evaluation of various solvent systems for lipid extraction from wet microalgal biomass and its effects on primary metabolites of lipid-extracted biomass. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 24: 15299–15307 (2017)
Bashir S, Sharif MK, Butt MS, Shahid M. Functional properties and amino acid profile of Spirulina platensis protein isolates. Pak. J. Sci. Ind. Res. Ser. B: Biol. Sci. 59: 12–19 (2016)
Cavonius LR, Carlsson N, Undeland I. Quantification of total fatty acids in microalgae: comparison of extraction and transesterification methods. Anal Bioanal. Chem. 406: 7313–7322 (2014)
Chang J, Coleman S, Lee YE, Schellenberg-Beaver T. Differential effects of sucrose or NaCl osmotic shock on β-galactosidase activity in Escherichia coli BW25993 is dependent on normalization method by total viable count or total protein content. J. Exp. Microbiol. Immunol. 18: 54–59 (2014)
Chen C-Y, Chang J-S, Chang H-Y, Chen T-Y, Wu J-H, Lee W-L. Enhancing microalgal oil/lipid production from Chlorella sorokiniana CY1 using deep-sea water supplemented cultivation medium. Biochem. Eng. J. 77: 74–81 (2013)
Cheung C, Lee J. (NaCl) and non-ionic (Sucrose) osmotic stress on the expression of β-galactosidase in wild type E. coli BW25993 and in the isogenic BW25993ΔlacI mutant. J. Exp. Microbiol. Immunol. 13: 1–6 (2009)
Diraman H, Koru E, Dibeklioglu H. Fatty acid profile of Spirulina platensis used as a food supplement. Isr. J. Aquacult. 61: 134–142 (2010)
Du Y, Schuur B, Kersten SRA, Brilman DWF. Microalgae wet extraction using N-ethyl butylamine for fatty acid production. Green Energy Environ. 1: 79–83 (2016)
El-Shimi H, Attia NK, El-Sheltawy ST, El-Diwani G I. Biodiesel production from spirulina-platensis microalgae by in-situ transesterification process. J. Sustain. Bioenergy Syst. 3: 224–233 (2013)
Hadiyanto H, Sutanto AA, Suharto Y. Ultrasound assisted extraction of antioxidant from Coleus tuberosus peels. Carpath. J. Food Sci. Technol. 6: 58–65 (2014)
Hadiyanto H, Suttrisnorhadi S. Response surface optimization of ultrasound assisted extraction (UAE) of phycocyanin from microalgae Spirulina platensis. Emir. J. Food Agric. 28(4): 227–234 (2016)
Li Y, Naghdi FG, Garg S, Adarme-Vega TC, Thurecht KJ, Ghafor WA, Tannock S, Schenk PM. A comparative study: the impact of different lipid extraction methods on current microalgal lipid research. Microbial. Cell Fact. 2014, 13: 1–9 (2014)
Lewis T, Nichols PD, McMeekin TA. Evaluation of extraction methods for recovery of fatty acids from lipid-producing microheterotrophs. J. Microbiol. Methods. 43: 107–116 (2000)
Lupatini AL, Bispo LO, Colla LM, Costa JAV, Canan C, Colla E. Protein and carbohydrate extraction from S. platensis biomass by ultrasound and mechanical agitation. Food Res. Int. 99: 1–8 (2016)
Montazeri-Najafabady N, Negahdaripour M, Salehi MH, Morowvat MH, Shaker S, Ghasemi Y. Effects of osmotic shock on production of carotene and glycerol in a naturally isolated strain of Dunaliella salina. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 6(8): 160–163 (2016)
Moraes CC, Sala L, Cerveira GP, Kali SJ. C-Phycocyanin extraction from Spirulina platensis wet biomass. Braz. J. Chem. Eng. 28(1): 45–49 (2011)
Nee W, Phonga WN, Leb CF, Show PL, Lam HL, Linga TC. Evaluation of different solvent types on the extraction of proteins from microalgae. Chem. Eng. Trans. 52: 1063–1068 (2016)
Persson JA, Wennerholm M, O’Halloran S. Handbook for kjeldahl digestion, FOSS, DK-3400 Hilleroed, Denmark (2008)
Phong WN, Le CF, Show PL, Chang JS, Ling TC. Extractive disruption process integration using ultrasonication and an aqueous two-phase system for protein recovery from Chlorella sorokiniana. Eng. Life Sci. 17: 357–369 (2017)
Rathore AS, Bilbrey RE, Steinmeyer DE. Optimization of an osmotic shock procedure for isolation of a protein product expressed in E. coli. Biotechnol. Progress. 19(5): 1541–1546 (2003)
Safi C, Ursu AV, Laroche C, Zebib B, Merah O, Pontalier PY, Garcia CV. Aqueous extraction of proteins from microalgae: Effect of different cell disruption methods. Algal Res. 3: 1–5 (2014)
Sanchez M, Castillo JB, Rozo C, Rodríguez I. Spirulina (Arthospira): An edible microorganisme: a review. universitas scientiarium. 8(1): 7–24 (2003)
Saranraj P, Sivasakthi S. Spirulina platensis–food for future: a review. Asian J. Pharm. Sci. Technol. 4(1): 26–33 (2014)
Soares MIS., Péres VF, Dariva C, Zini CA, Abad FC, Martinez MM, Caramão EB. Optimization of the sonication extraction method of Hibiscus tiliaceus L. flowers. Ultrason. Sonochemistry. 13: 242–250 (2006)
Solana M, Rizza CS, Bertucco A. Exploiting microalgae as a source of essential fatty acids bysupercritical fluid extraction of lipids: Comparison between Scenedesmus obliquus, Chlorella protothecoides and Nannochloropsis salina. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 92: 311–318 (2014)
Tan CH, Chen CY, Show PL, Ling TC, Lam HL, Lee DJ, Chang JS. Strategies for enhancing lipid production from indigenous microalgae isolates. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 63: 189–194 (2016)
Wang M, Yuan W, Jiang X, Jing Y, Wang Z. Disruption of microalgal cells using high-frequency focused ultrasound. Bioresour. Technol. 153: 315–321 (2014)
WHO, 2007. Protein and Amino Acid Requirements in Human Nutrition, Geneva, Switzerland
Wijanarko B, Putri LD. Ekstraksi Lipid dari Mikroalga (Nanochloropsis sp.) dengan Solven Methanol dan Chloroform. Jurnal Teknologi Kimia dan Industri. 1: 130–138 (2012)
Wiyarno B, Yunus R, Mel M. Oil Algae Extraction from Nannochloropsis sp: a study of soxhlet extraction and ultrasonic assisted extraction. Int. J. Sci. Eng. 1–5 (2010)
Yazar D, Sevket G. α-Tocopherol and Fatty acids of Spirulina platensis Biomass in Glass Planel Bioreactor. Pak. J. Biol. Sci. 9(15): 2901–2904 (2006)
Yoo G, Park WK, Kim CW, Choi YE, Yang JW. Direct lipid extraction from wet Chlamydomonas reinhardtii biomass using osmotic shock. Bioresour. Technol. 123: 717–722 (2012)
Zhang Y, Kong X, Wang Z, Sun Y, Zhu S, Li L, Lv P. Optimization of enzymatic hydrolysis for effective lipid extraction from microalgae Scenedesmus sp. Renew. Energy. 125: 1049–1057 (2018)
Zeb H, Riaz A, Kim J. The Journal of Supercritical Fluids Understanding the effect of biomass-to-solvent ratio on macroalgae (Saccharina japonica) liquefaction in supercritical ethanol. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 120: 65–74 (2017)
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to thank Ministry of Research, Technology and Higher Education for their grants through Hibah Kompetensi of Year 2018. All staffs of Center of Biomass and Renewable Energy (CBIORE) are highly appreciated.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hadiyanto, H., Adetya, N.P. Response surface optimization of lipid and protein extractions from Spirulina platensis using ultrasound assisted osmotic shock method. Food Sci Biotechnol 27, 1361–1368 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0389-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-018-0389-y