Abstract
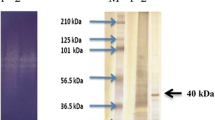
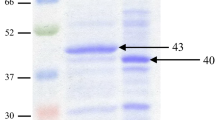
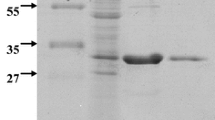
Seaweeds are considered as a health food partly due to the polysaccharide composition of the cell wall. Because conventional extraction methods have low yields and lead to environmental pollution, enzymatic methods have been proposed. In this study, a new strain of Bacillus sp. was isolated from cattle feces that produced a mannanase, a polysaccharide-degrading enzyme active against the green seaweed Codium fragile. The purified 39-kDa mannanase exhibited maximum activity at 55 °C and pH 6.0, and maintained its catalytic activity stably at temperatures up to 60 °C and at a broad pH range (5.0–11.0). Enzymatic activity was slightly enhanced by Cu2+ and Na+ but strongly inhibited by Fe2+, Ag+, and EDTA. The mannanase showed the highest specificity to the inexpensive substrates such as konjac powder and locust bean gum, and efficiently released various manno-oligosaccharides. This novel mannanase can thus be applicable in the food, feed, and pulp industries.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Holdt SL, Kraan S. Bioactive compounds in seaweed: functional food applications and legislation. J. Appl. Phycol. 23: 543–597 (2011)
Mabeau S, Fleurence J. Seaweed in food products: biochemical and nutritional aspects. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 4: 103–107 (1993)
Lordan S, Ross RP, Stanton C. Marine bioactives as functional food ingredients: potential to reduce the incidence of chronic diseases. Mar. Drugs 9: 1056 (2011)
Rioux LE, Turgeon SL, Beaulieu M. Characterization of polysaccharides extracted from brown seaweeds. Carbohydr. Polym. 69: 530–537 (2007)
Ye H, Wang K, C Zhou, J Liu, X Zeng. Purification, antitumor and antioxidant activities in vitro of polysaccharides from the brown seaweed Sargassum pallidum. Food Chem. 111: 428–432 (2008)
Wijesinghe WAJP, Jeon YJ. Enzyme-assistant extraction (EAE) of bioactive components: A useful approach for recovery of industrially important metabolites from seaweeds: A review. Fitoterapia 83: 6–12 (2012)
Siriwardhana N, Jeon YJ, Kim SH, Ha JH, Heo SJ, Lee KW. Enzymatic hydrolysis for effective extraction of antioxidative compounds from Hizikia fusiformis. Algae 19: 59–68 (2004)
Ale MT, Meyer AS. Fucoidans from brown seaweeds: an update on structures, extraction techniques and use of enzymes as tools for structural elucidation. RSC Adv. 3: 8131–8141 (2013)
Zahura UA, Rahman MM, Inoue A, Tanaka H, Ojima T. An endo-β-1,4-mannanase, AkMan, from the common sea hare Aplysia kurodai. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B. Biochem. Mol. Biol. 157: 137–143 (2010)
Tamaru Y, Araki T, Amagoi H, Mori H, Morishita T. Purification and characterization of an extracellular β-1,4-mannanase from a marine bacterium, Vibrio sp. strain MA-138. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 61: 4454–4458 (1995)
Dhawan S, Kaur J. Microbial mannanases: An overview of production and applications. Crit. Rev. Biotechnol. 27: 197–216 (2007)
Henrissat B. A classification of glycosyl hydrolases based on amino acid sequence similarities. Biochem. J. 280: 309–316 (1991)
Hogg D, Pell G, Dupree P, Goubet F, Martín-Orúe SM, Armand S, Gilbert HJ. The modular architecture of Cellvibrio japonicus mannanases in glycoside hydrolase families 5 and 26 points to differences in their role in mannan degradation. Biochem. J. 371: 1027–1043 (2003)
Ma Y, Xue Y, Dou Y, Xu Z, Tao W, Zhou P. Characterization and gene cloning of a novel β-mannanase from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. N16-5. Extremophiles 8: 447–454 (2004)
Piwpankaew Y, Sakulsirirat S, Nitisinprasert S, Nguyen TH, Haltrich D, Keawsompong S. Cloning, secretory expression and characterization of recombinant β-mannanase from Bacillus circulans NT 6.7. Springerplus 3: 430 (2014)
Yoon KH, Chung S, Lim BL. Characterization of the Bacillus subtilis WL-3 mannanase from a recombinant Escherichia coli. J. Microbiol. 46: 344 (2008)
Chauhan PS, Sharma P, Puri N, Gupta N. Purification and characterization of an alkali-thermostable β-mannanase from Bacillus nealsonii PN-11 and its application in mannooligosaccharides preparation having prebiotic potential. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 238: 927–936 (2014)
Mackie W, Sellen DB. The degree of polymerization and polydispersity of mannan from the cell wall of the green seaweed Codium fragile. Polymer 10: 621–632 (1969)
Estevez JM, Fernández PV, Kasulin L, Dupree P, Ciancia M. Chemical and in situ characterization of macromolecular components of the cell walls from the green seaweed Codium fragile. Glycobiology 19: 212–228 (2009)
Wijesekara I, Pangestuti R, Kim SK. Biological activities and potential health benefits of sulfated polysaccharides derived from marine algae. Carbohydr. Polym. 84: 14–21 (2011)
Lee JB, Ohta Y, Hayashi K, Hayashi T. Immunostimulating effects of a sulfated galactan from Codium fragile. Carbohydr. Res. 345: 1452–1454 (2010)
Ciancia M, Quintana I, Vizcargüénaga MI, Kasulin L, Dios A, Estevez JM, Cerezo AS. Polysaccharides from the green seaweeds Codium fragile and C. vermilara with controversial effects on hemostasis. Int. J. Biol. Macromole. 41: 641–649 (2007)
Seo DH, Jung JH, Kim HY, Kim YR, Ha SJ, Kim YC, Park CS. Identification of lactic acid bacteria involved in traditional Korean rice wine fermentation. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 16: 994–998 (2007)
Kim OS, Cho YJ, Lee K, Yoon SH, Kim M, Na H, Park SC, Jeon YS, Lee JH, Yi H, Won S, Chun J. Introducing EzTaxon-e: a prokaryotic 16S rRNA gene sequence database with phylotypes that represent uncultured species. Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 62: 716–721 (2012)
Miller GL. Use of dinitrosalicylic acid reagent for determination of reducing sugar. Anal. Chem. 31: 426–428 (1959)
Agrawal P, Verma D, Daniell H. Expression of Trichoderma reesei β-mannanase in tobacco chloroplasts and its utilization in lignocellulosic woody biomass hydrolysis. Plos One 6: e29302 (2011)
Cann IKO, Kocherginskaya S, King MR, White BA, Mackie RI. Molecular cloning, sequencing, and expression of a novel multidomain mannanase gene from Thermoanaerobacterium polysaccharolyticum. J. Bacteriol. 181: 1643–1651 (1999)
Jeong CS. Isolation and characterization of mannanase producing Bacillus amyloliquefaciens CS47 from horse feces. J. Life Sci. 19: 1724–1730 (2009)
El-Sharouny EE, El-Toukhy NMK, El-Sersy NA, El-Gayar AAE-A. Optimization and purification of mannanase produced by an alkaliphilic-thermotolerant Bacillus cereus N1 isolated from Bani Salama Lake in Wadi El-Natron. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 29: 315–323 (2015)
Lin SS, Dou WF, Xu HY, Li HZ, Xu ZH, Ma YH. Optimization of medium composition for the production of alkaline β-mannanase by alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. N16-5 using response surface methodology. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 75: 1015–1022 (2007)
Zhang J, He Z, Hu K. Purification and characterization of β-mannanase from Bacillus licheniformis for industrial use. Biotechnol. Lett. 22: 1375–1378 (2000)
Jiang Z, Wei Y, Li D, Li L, Chai P, Kusakabe I. High-level production, purification and characterization of a thermostable β-mannanase from the newly isolated Bacillus subtilis WY34. Carbohydr. Polym. 66: 88–96 (2006)
He X, Liu N, Li W, Zhang Z, Zhang B, Ma Y. Inducible and constitutive expression of a novel thermostable alkaline β-mannanase from alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. N16-5 in Pichia pastoris and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Enzyme Microb. Tech. 43: 13–18 (2008)
Hatada Y, Takeda N, Hirasawa K, Ohta Y, Usami R, Yoshida Y, Grant WD, Ito S, Horikoshi K. Sequence of the gene for a high-alkaline mannanase from an alkaliphilic Bacillus sp. strain JAMB-750, its expression in Bacillus subtilis and characterization of the recombinant enzyme. Extremophiles 9: 497–500 (2005)
Kweun MA, Lee MS, Choi JH, Cho KH, Yoon KH. Cloning of a Bacillus subtilis WL-7 mannanase gene and characterization of the gene product. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 14: 1295–1302 (2004)
Dionísio M, Grenha A. Locust bean gum: Exploring its potential for biopharmaceutical applications. J. Pharm. Bioall. Sci. 4: 175–185 (2012)
Liao H, Li S, Zheng H, Wei Z, Liu D, Raza W, Shen Q, Xu Y. A new acidophilic thermostable endo-1,4-β-mannanase from Penicillium oxalicum GZ-2: cloning, characterization and functional expression in Pichia pastoris. BMC Biotechnol. 14: 90 (2014)
Hakamada Y, Ohkubo Y, Ohashi S. Purification and characterization of β-mannanase from Reinekea sp. KIT-YO10 with transglycosylation activity. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 78: 722–728 (2014)
Kulcinskaja E, Rosengren A, Ibrahim R, Kolenová K, Stålbrand H. Expression and characterization of a Bifidobacterium adolescentis β-mannanase carrying mannan-binding and cell association motifs. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 79: 133–140 (2013)
Acknowledgements
This research was supported by the Main Research Program (E0170602-01) of the Korea Food Research Institute (KFRI) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, S., Lee, MH., Lee, ES. et al. Characterization of mannanase from Bacillus sp., a novel Codium fragile cell wall-degrading bacterium. Food Sci Biotechnol 27, 115–122 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0210-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-017-0210-3