Abstract
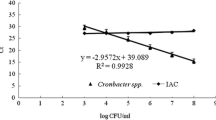
Enterobacteriaceae enrichment (EE) broth, a selective enrichment medium for Cronobacter sakazakii detection, has been shown to contain polymerase chain reaction (PCR) inhibitors. Therefore, a modified enrichment broth was developed, wherein possible PCR inhibitors, brilliant green and bile salts, were substituted with sodium citrate. Investigations were conducted to determine whether realtime PCR detection of C. sakazakii in powdered infant formula and dried vegetables with this modified medium improved compared with conventional culture methods. The detection rate of the modified EE broth was significantly higher (p<0.05) than that of the conventional EE broth for both types of food. For dried pumpkin samples, real-time PCR after culturing in modified EE broth yielded significantly higher detection rates and selectivity than those achieved using conventional culture in Druggan-Forsythe-Iversen agar. These results show that real-time PCR after enrichment in the modified EE broth may be an effective screening method for detection of C. sakazakii.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bowen A, Buchanan R, Cordier JL, Cravioto A, Dobson S, Estuningsih S, Jeffrey F, Fazil A, Forsythe S. Enterobacter sakazakii and Salmonella in powdered infant formula. FDA Meeting report P. XV (2003)
Chon JW, Song KY, Kim SY, Hyeon JY, Seo KH. Isolation and characterization of Cronobacter from desiccated foods in Korea. J. Food Sci. 77: M354–M358 (2012)
Holý O, Forsythe S. Cronobacter spp. as emerging causes of healthcareassociated infection. J. Hosp. Infect. 86: 169–177 (2014)
Iversen C, Forsythe S. Isolation of Enterobacter sakazakii and other Enterobacteriaceae from powdered infant formula milk and related products. Food Microbiol. 21: 771–777 (2004)
Seo KH, Brackett RE. Rapid, specific detection of Enterobacter sakazakii in infant formula using a real-time PCR assay. J. Food Protect. 68: 59–63 (2005)
Malorny B, Paccassoni E, Fach P, Bunge C, Martin A, Helmuth R. Diagnostic real-time PCR for detection of Salmonella in food. Appl. Environ. Microb. 70: 7064–7052 (2004)
Chon JW, Song KY, Kim SY, Hyeon JY, Kim YG, Hwang IG, Kwak HS, Seo KH. Comparison of real-time PCR and conventional culture method for detection of Cronobacter spp. in powdered foods. Microbiol. Biotechnol. Lett. 47: 87–91 (2011)
Hyeon JY, Hwang IG, Kwak HS, Park C, Choi IS, Seo KH. Evaluation of PCR inhibitory effect of enrichment broths and comparison of DNA extraction methods for detection of Salmonella enteritidis using real-time PCR assay. J. Vet. Sci. 11: 143–149 (2010)
Chon JW, Hyeon JY, Hwang IG, Kwak HS, Han JA, Kim MS, Kim JH, Song KY, Seo KH. Comparison of real-time PCR and culture methods for detection of Campylobacter jejuni in various foods. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 43: 119–123 (2011)
Kim DH, Chon JW, Kim H, Kim HS, Choi D, Kim YJ, Yim JH, Moon JS, Seo KH. Comparison of culture, conventional and real-time PCR methods for Listeria monocytogenes in foods. Korean J. Food Sci. An. 34: 665–673 (2014)
Lee JH, Song KY, Hyeon JY, Hwang IG, Kwak HS, Han JA, Chung YH, Seo KH. Comparison of standard culture method and real-time PCR assay for detection of Staphylococcus aureus in processed and unprocessed foods. Korean J. Food Sci. An. 30: 410–418 (2010)
Thippareddi H, Juneja VK, Phebus RK, Marsden JL, Kastner CL. Control of Clostridium perfringens germination and outgrowth by buffered sodium citrate during chilling of roast beef and injected pork. J. Food Protect. 66: 376–381 (2003)
Xiao XL, Li YJ, Qin YY, Yu YG, Wu H. A multipathogen selective enrichment broth for simultaneous growth of Salmonella spp., Vibrio parahaemolyticus, and Vibrio cholerae. J. Gen. Appl. Microbiol. 56: 465–474 (2010)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choi, D., Chon, JW., Kim, DH. et al. Improvement of Enterobacteriaceae enrichment broth by supplementation with sodium citrate for detection of Cronobacter sakazakii using real-time PCR. Food Sci Biotechnol 25, 1205–1209 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-016-0191-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-016-0191-7