Abstract
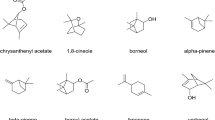
Chrysanthemum indicum Linné, belonging to the family Compositae, is a perennial herb that is widespread in Korea. C. indicum Linné flowers have been traditionally used as an oriental medicine for treatment of infectious diseases. The chemical compositions, antioxidant capacity, and neuroprotective effects of volatile components in essential oils from C. indicum Linné flowers were investigated. GC-MS analysis of essential oils revealed the 15 major components of 1,8-cineole, o-cymene, camphor, pinocarvone, chrysanthenyl acetate, bornyl acetate, trans-caryophyllene, terpinen-4-ol, umbellulone, trans-pinocarveol, cis-verbenol, borneol, α-terpineol, caryophyllene oxide, and thymol. Thymol had the highest antioxidant capacity. Essential oils and thymol dose-dependently decreased intracellular oxidative stress, exhibited anticholinesterase activities, and increased the cell viability of neuronal PC-12 cells. Essential oils and thymol from C. indicum Linné flowers can be sources of natural antioxidants and functional foods.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Singh M, Arseneault M, Sanderson T, Murthy V, Ramassamy C. Challenges for research on polyphenols from foods in Alzheimer’s disease: Bioavailability, metabolism, and cellular and molecular mechanisms. J. Agr. Food Chem. 56: 4855–4873 (2008)
Weissman L, de Souza-Pinto NC, Stevnsner T, Bohr VA. DNA repair, mitochondria, and neurodegeneration. Neuroscience 145: 1318–1329 (2007)
Han S, Lemire J, Appanna VP, Auger C, Castonguay Z, Appanna VD. How aluminum, an intracellular ROS generator promotes hepatic and neurological diseases: The metabolic tale. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 29: 75–84 (2013)
Mehta A, Prabhakar M, Kumar P, Deshmukh R, Sharma PL. Excitotoxicity: Bridge to various triggers in neurodegenerative disorders. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 698: 6–18 (2013)
Choi SS, Lee S-R, Kim SU, Lee HJ. Alzheimer's disease and stem cell therapy. Exp. Neurobiol. 23: 45–52 (2014)
Ferri CP, Prince M, Brayne C, Brodaty H, Fratiglioni L, Ganguli M, Hall K, Hasegawa K, Hendrie H, Huang Y, Jorm A, Mathers C, Menezes PR, Rimmer E, Scazufca M. Global prevalence of dementia: A Delphi consensus study. Lancet 366: 2112–2117 (2005)
Morales I, Guzmán-Martínez L, Cerda-Troncoso C, Farías GA, Maccioni RB. Neuroinflammation in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. A rational framework for the search of novel therapeutic approaches. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 8: 112 (2014)
Blennow K, Dubois B, Fagan AM, Lewczuk P, de Leon MJ, Hampel H. Clinical utility of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in the diagnosis of early Alzheimer’s disease. Alzheimers Dement. 11: 58–69 (2015)
Overk CR, Masliah E. Pathogenesis of synaptic degeneration in Alzheimer’s disease and Lewy body disease. Biochem. Pharmacol. 88: 508–516 (2014)
Chistiakov DA, Sobenin IA, Revin VV, Orekhov AN, Bobryshev YV. Mitochondrial aging and age-related dysfunction of mitochondria. Biomed Res. Int. 2014: 238463 (2014)
Dai D-F, Chiao YA, Marcinek DJ, Szeto HH, Rabinovitch PS. Mitochondrial oxidative stress in aging and healthspan. Longev. Healthspan 3: 6 (2014)
Morris JK, Honea RA, Vidoni ED, Swerdlow RH, Burns JM. Is Alzheimer’s disease a systemic disease? Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1842: 1340–1349 (2014)
Vauzour D. Effect of flavonoids on learning, memory and neurocognitive performance: Relevance and potential implications for Alzheimer’s disease pathophysiology. J. Sci. Food Agr. 94: 1042–1056 (2014)
Lim YJ, Oh C-S, Park Y-D, Kim D-O, Kim U-J, Cho Y-S, Eom SH. Physiological components of kiwifruits with in vitro antioxidant and acetylcholinesterase inhibitory activities. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 23: 943–949 (2014)
Ruberto G, Baratta MT. Antioxidant activity of selected essential oil components in two lipid model systems. Food Chem. 69: 167–174 (2000)
Im S-E, Yoon H, Nam T-G, Heo HJ, Lee CY, Kim D-O. Antineurodegenerative effect of phenolic extracts and caffeic acid derivatives in romaine lettuce on neuron-like PC-12 cells. J. Med. Food 13: 779–784 (2010)
Bakkali F, Averbeck S, Averbeck D, Idaomar M. Biological effects of essential oils-A review. Food Chem. Toxicol. 46: 446–475 (2008)
Burt S. Essential oils: Their antibacterial properties and potential applications in foods-a review. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 94: 223–253 (2004)
Choi H-S, Kim G-H. Volatile flavor composition of gamguk (Chrysanthemum indicum) flower essential oils. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 20: 319–325 (2011)
Cheng W, Li J, You T, Hu C. Anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory activities of the extracts from the inflorescence of Chrysanthemum indicum Linné. J. Ethnopharmacol. 101: 334–337 (2005)
Chun HS, Kim J-M, Choi EH, Chang N. Neuroprotective effects of several Korean medicinal plants traditionally used for stroke remedy. J. Med. Food 11: 246–251 (2008)
Kim D-O, Lee KW, Lee HJ, Lee CY. Vitamin C equivalent antioxidant capacity (VCEAC) of phenolic phytochemicals. J. Agr. Food Chem. 50: 3713–3717 (2002)
Ellman GL, Courtney KD, Andres V Jr., Featherstone RM. A new and rapid colorimetric determination of acetylcholinesterase activity. Biochem. Pharmacol. 7: 88–95 (1961)
Jung E-K. Chemical composition and antimicrobial activity of the essential oil of Chrysanthemum indicum against oral bacteria. J. Bacteriol. Virol. 39: 61–69 (2009)
Aazza S, Lyoussi B, Miguel MG. Antioxidant and antiacetylcholinesterase activities of some commercial essential oils and their major compounds. Molecules 16: 7672–7690 (2011)
Kim D-O, Lee CY. Comprehensive study on vitamin C equivalent antioxidant capacity (VCEAC) of various polyphenolics in scavenging a free radical and its structural relationship. Crit. Rev. Food Sci. 44: 253–273 (2004)
LeBel CP, Ischiropoulos H, Bondy SC. Evaluation of the probe 2′,7′-dichlorofluorescin as an indicator of reactive oxygen species formation and oxidative stress. Chem. Res. Toxicol. 5: 227–231 (1992)
Girard-Lalancette K, Pichette A, Legault J. Sensitive cell-based assay using DCFH oxidation for the determination of pro- and antioxidant properties of compounds and mixtures: Analysis of fruit and vegetable juices. Food Chem. 115: 720–726 (2009)
Cai L, Wang H, Li Q, Qian Y, Yao W. Salidroside inhibits H2O2-induced apoptosis in PC 12 cells by preventing cytochrome C release and inactivating of caspase cascade. Acta Bioch. Bioph. Sin. 40: 796–802 (2008)
Özkan A, Erodgan A. A comparative evaluation of antioxidant and anticancer activity of essential oil from Origanum onites (Lamiaceae) and its two major phenolic components. Turk. J. Biol. 35: 735–742 (2011)
Chen X, Fang L, Liu J, Zhan C-G. Reaction pathway and free energy profile for butyrylcholinesterase-catalyzed hydrolysis of acetylcholine. J. Phys. Chem. B 115: 1315–1322 (2011)
Jukic M, Politeo O, Maksimovic M, Milos M, Milos M. In vitro acetylcholinesterase inhibitory properties of thymol, carvacrol, and their derivatives thymoquinone and thymohydroquinone. Phytother. Res. 21: 259–261 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, B.H., Nam, T.G., Park, W.J. et al. Antioxidative and neuroprotective effects of volatile components in essential oils from Chrysanthemum indicum Linné flowers. Food Sci Biotechnol 24, 717–723 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0093-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0093-0