Abstract
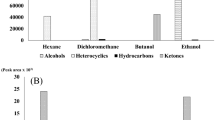
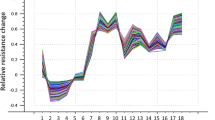
Doenjang samples were discriminated using a mass spectrometry-based electronic nose (MS-E-nose) and discriminant function analysis (DFA). Human sensory preference testing was performed using the same samples. DFA plots indicated classification of doenjang samples into 3 groups. Samples with high discriminate function (DF) 1 and low DF2 scores contained fewer volatile compounds. Grouping results using the MS-E-nose and human sensory preference testing were compared. Fully mashed doenjang samples with more diverse and intense volatile compounds showed low DF1 and high preference scores. DF2 scores for selected samples showed positive correlations to the amount of sample. The MS-E-nose was a useful tool for discrimination of the aroma of doenjang samples and for confirmation of changes in the aroma intensities of doenjang samples.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Næs T, Solheim R. Detection and interpretation of variation within and between assessors in sensory profiling. J. Sens. Stud. 6: 159–177 (1991)
Buldini PL, Ricci L, Sharma JL. Recent applications of sample preparation techniques in food analysis. J. Chromatogr. A 975: 47–70 (2002)
Delahunty CM, Eyres G, Dufour JP. Gas chromatography-olfactometry. J. Sep. Sci. 29: 2107–2125 (2006)
Noh BS. Application of electronic nose for quality control of the high quality and functional components. Korean J. Crop. Sci. 51: 40–54 (2006)
Wilson AD. Diverse applications of electronic-nose technologies in agriculture and forestry. Sensors (Basel) 13: 2295–2348 (2013)
Marsili RT. SPME-MS-MVA as an electronic nose for the study of off-flavors in milk. J. Agr. Food Chem. 47: 648–654 (1999)
Pavon JLP, Sanchez MN, Pinto CG, Laespada MF, Cordero BM, Pena AG. Strategies for qualitative and quantitative analyses with mass spectrometry based electronic nose. Trends Anal. Chem. 25: 257–266 (2006)
Drake MA, Gerard PD, Kleinhenz JP, Harper WJ. Application of an electronic nose to correlate with descriptive sensory analysis of aged Cheddar cheese. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 36: 13–20 (2003)
Bartlett PN, Elliott JM, Gardner JW. Electronic nose and their application in the food industry. Food Technol. 51: 44–48 (1997)
Schaller E, Bosset JO, Escher F. Electronic noses and their application to food. Lebensm.-Wiss. Technol. 31: 305–316 (1998)
Son HJ, Hong EJ, Ko SH, Choi JY, Noh BS. Identification of vegetable oil-added sesame oil by a mass spectrometer-based electronic nose. Food Eng. Prog. 13: 275–281 (2009)
Hong EJ, Park SJ, Choi JY, Noh BS. Discrimination of palm olein oil and palm stearin oil mixtures using a mass spectrometry based electronic nose. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 20: 809–816 (2011)
Hong HK, Park HS, Yun DH, Shin HW, Kwon CH, Lee KC. Technical trend of electronic nose system. J. Korean Inst. Electric. Electron. Material Eng. 8: 509–516 (1995)
Lee SJ, Ahn B. Comparison of volatile components in fermented soybean pastes using simultaneous distillation and extraction (SDE) with sensory characterization. Food Chem. 114: 600–609 (2009)
Chung HY, Fung PK, Kim JS. Aroma impact components in commercial plain sufu. J. Agr. Food Chem. 53: 1684–1691 (2005)
Hong Y, Jung HJ, Kim HY. Aroma characteristics of fermented Korean soybean paste (doenjang) produced by Bacillus amyloliquefaciens. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 21: 1163–1172 (2012)
Chang M, Chang HC. Characteristics of bacterial-koji and doenjang (soybean paste) made by using Bacillus subtilis DJI. Korean J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 35: 325–333 (2012)
Noh BS, Yang YM, Lee TS, Hong HK, Kwon CH, Sung YK. Prediction of fermentation time of Korean style soybean paste by using the portable electronic nose. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 30: 356–362 (1998)
Shin JA, Choi SW, Lee KT. Prediction of kimchi aging using electronic nose system. Korean J. Food Preserv. 12: 613–616 (2005)
Ku KH, Kim YJ, Koo YJ, Choi IU. Effect of pre-treated sub-ingredients and deodorization materials on the kimchi smell during fermentation. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 31: 1549–1556 (1999)
Lawless HT, Heymann H. Sensory Evaluation of Food, Principles, and Practices. Springer Science Inc., New York, NY, USA. pp. 358–368 (1998)
Lawless HT, Heymann H. Sensory Evaluation of Food, Principles, and Practices. Springer Science Inc., New York, NY, USA. pp. 702–707 (1998)
Yong HU, Lee TS, Kim JS, Baek HH, Noh BS, Lee SJ, Park JT, Shim JH, Li D, Hong IH, Nguyen DHD, Tran PL, Nguyen TLH, Oktavina EF, Kim JW, Kang HK, Park KH. Flavor characteristics of rice-grape wine with starch-hydrolyzing enzymes. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 22: 937–943 (2013)
Noh BS. Determination of Mixing Ratios in Palm Oleic Triglyceride and Palm Stearic Triglyceride Mixtures Using a Mass Spectrometry Based Electronic Nose. Final Report for the Basic Research Program of the Nongshim’s Youlchon Foundation. Seoul, Korea. pp. 57–80 (2011)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hong, Y., Noh, BS. & Kim, HY. Discrimination of doenjang samples using a mass spectrometry-based electronic nose and human sensory preference testing. Food Sci Biotechnol 24, 31–36 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0005-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-015-0005-3