Abstract
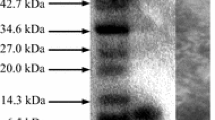
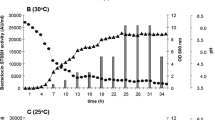
A bacteriocinogenic strain identified as Enterococcus faecium SH01 was isolated from mukeunji, a Korean traditional over-ripened kimchi with antimicrobial activities against Listeria monocytogenes KCTC 3569 and Lactobacillus curvatus KFRI 166. The maximum bacteriocin titer (1,280 AU/mL) was detected at the early stationary phase and was maintained for 28 h with no activity loss. The bacteriocin activity, which disappeared after treatment with the proteolytic enzymes α-chymotrypsin, pronase E, proteinase K, and trypsin, was partially inactivated using α-amylase. The activity of bacteriocin SH01 remained after heat treatment (121°C, 15 min) and exposure to pH values from 2–12. The molecular weight of crude bacteriocin SH01 was 3 kDa. The bacteriocin production phenotype (Bac+) was linked to a 6 kb plasmid. Bacteriocin SH1 production was not induced by the co-presence of viable cells, heat treatment, or a cell-free indicator supernatant. The mode of action of bacteriocin SH1 was bactericidal.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kim WJ. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria: Their potentials as food biopreservative. Food Rev. Int. 9: 299–313 (1993)
Klaenhammer TR. Genetics of bacteriocins produced by lactic acid bacteria. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 12: 39–85 (1993)
Cintas LM, Casaus P, Holo H, Hernandez PE, Nes IF, Havarstein LS. Enterocins L50A and L50B, two novel bacteriocins from Enterococcus faecium L50, are related to staphylococcal hemolysins. J. Bacteriol. 180: 1988–1994 (1998)
Klaenhammer TR. Bacteriocins of lactic acid bacteria. Biochimie 70: 337–349 (1998)
Joerger MC, Klaenhammer TR. Characterization and purification of helveticin J and evidence for a chromosomally determined bacteriocin produced by Lactobacillus helveticus 481. J. Bacteriol. 167: 439–446 (1986)
Settanni L, Corsetti A. Application of bacteriocins in vegetable food biopreservation. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 121: 123–138 (2008)
Kim WJ, Hong SS, Cha SK, Koo YJ. Use of bacteriocinogenic Pediococcus acidilactici in sausage fermentation. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 3: 199–203 (1993)
Elegado FB, Kim WJ, Kwon DY. Rapid purification, partial characterization, and antimicrobial spectrum of the bacteriocin pediocin AcM, from Pediococcus acidilactici M. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 37: 1–11 (1997)
Kim SE, Park MH, Lee JH, Kim TW, Kim HY. Probiotic properties of Lactobacillus brevis J-38 from mukeunji, a Korean ripened kimchi. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 136: 717–742 (2008)
O’Driscoll B, Gahan CGM, Hill C. Adaptive acid tolerance response in Listeria monocytogenes: Isolation of an acid-tolerant mutant which demonstrated increased virulence. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 62: 1693–1698 (1996)
Schuchat A, Swaminathan B, Broome CV. Epidemiology of human listeriosis. J. Clin. Microbiol. 4: 169–183 (1991)
Gill CO, Reichel MP. Growth of the cold-tolerant pathogens Yersinia enterocolitica, Aeromonas hydrophila, and Listeria monocytogenes on high pH-beef packaged under vacuum or carbon dioxide. Food Microbiol. 6: 223–230 (1989)
Palumbo SA. Is refrigeration enough to restrain food-borne pathogens? J. Food Protect. 49: 1003–1009 (1986)
Rocourt J. Risk factors for listeriosis. Food Control 7: 195–202 (1996)
Harris LJ, Daeschel M, Stiles E, Klaenhammer TR. Antimicrobial activity of lactic acid bacteria against Listeria monocytogenes. J. Food Prot. 52: 384–387 (1989)
Lee HJ, Joo YJ, Park CS, Kim SH, Hwang IK, Ahn JS, Mheen TI. Purification of characterization of a bacteriocin produced by Lactococcus lactis subsp. lactis H-559 isolated from kimchi. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 88: 153–159 (1999)
Kwon DY, Koo MS, Ryoo CR, Kang CH, Min KH, Kim WJ. Bacteriocin production by Pediococcus sp. in kimchi and its characteristics. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 12: 96–105 (2002)
Lee HJ, Kim WJ. Isolation and characterization of anti-listerial and amylase sensitive enterocin producing Enterococcus faecium DB1 from gajami-sikhae, a fermented flat fish in Korea. Food Sci. Biotech. 19: 373–381 (2010)
Kang TK, Kim WJ. Characterization of an amylase-sensitive bacteriocin DF01 produced by Lactobacillus brevis DF01 isolated from Dongchimi, Korean fermented vegetable. Korean J. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 30: 795–803 (2010)
Rojo-Bezares B, Sáenz Y, Navarro L, Zarazaga M, Ruiz-Larrea F, Torres C. Coculture-inducible bacteriocin activity of Lactobacillus plantarum strain J23 isolated from grape must. Food Microbiol. 24: 482–491 (2007)
Navarro L, Rojo-Bezares B, Sáenz Y, Díez L, Zarazaga M, Ruiz-Larrea F, Torres C. Comparative study of the pln locus of the quorum-sensing regulated bacteriocin-producing Lactobacillus plantarum J51 strain. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 128: 390–394 (2008)
Bhunia AK, Johnson MC, Ray B. Direct detection of an antimicrobial peptide of Pediococcus acidilactici in sodium dodecyl sulfate-polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2: 319–322 (1987)
Schägger H, von Jagow G. Tricine-sodium dodecyl sulfate polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis for the separation of proteins in the range from 1-100 kilo Dalton. Anal. Biochem. 166: 368–379 (1987)
Campos C, Rodriguez O, Calo-Mata P, Prado M, Barros-Velazquez J. Preliminary characterization of bacteriocins from Lactococcus lactis, Enterococcus faecium, and Enterococcus mundtii strains isolated from turbot (Psetta maxima). Food Res. Int. 39: 356–364 (2006)
Kim M-J, Kim K-S. Tyramine production among lactic acid bacteria and other species isolated from kimchi. LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 56: 406–413 (2013)
Keppler K, Geisen R, Holzapfel WH. An α-amylase sensitive bacteriocin of Leuconostoc carnosum. Food Microbiol. 11: 39–45 (1994)
Parente E, Moles M, Ricciardi A. Leucocin F10, a bacteriocin from Leuconostoc carnosum. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 33: 231–243 (1996)
Losteinkit C, Uchiyama K, Ochi S, Takaoka T, Nagahisa K, Shiyoya S. Characterization of bacteriocin N15 produced by Enterococcus faecium N15 and cloning of the related genes. J. Biosci. Bioengin. 91: 390–395 (2001)
Huot E, Barrena-Bonzalez C, Petitdemange H. Tween-80 effect on bacteriocin synthesis by Lactococcus lactic subsp. cremoris J46. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 22: 307–310 (1996)
Kim WJ, Ha DM, Ray B. Plasmid linkage of bacteriocin production and sucrose fermentation phenotypes in Pediococcus acidilactici M. J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 1: 169–175 (1991)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seo, SH., Jung, M. & Kim, W.J. Antilisterial and amylase-sensitive bacteriocin producing Enterococcus faecium SH01 from Mukeunji, a Korean over-ripened kimchi. Food Sci Biotechnol 23, 1177–1184 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0161-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0161-x