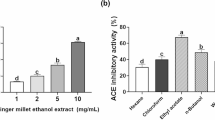
Abstract
The angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide (ACEIP) was isolated and characterized from silkworm pupae and purified using Sephadex G-25 gel filtration. The structure and physicochemical properties of pupa ACEIP were analyzed. The α-P3 fraction exhibited the most potent ACE inhibitory activity. After purification via semi-preparative reverse-phase HPLC (RP-HPLC) and HPLC, the α-P3-6-b component was revealed to have the highest ACE inhibitory activity (IC50=28.3 μg/mL). Edman degradation revealed a Val-Glu-Ile-Ser amino acid sequence in which novel active sequences were identified. Physicochemical property testing showed that purified pupa ACEIP exhibits good solubility, heat resistance, and acid resistance that all indicate ACEIP derived from silkworm pupa is an excellent food-derived ACEIP.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Vercruysse L, Smagghe G, Matsui T, Van Camp J. Purification and identification of an angiotensin I converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from the gastrointestinal hydrolysate of the cotton leafworm, Spodopter a littoralis. Proc. Biochem. 43: 900–904 (2008)
Coates D. The angiotens in converting enzyme (ACE). Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 35: 769–773 (2003)
Murray BA, FitzGerald RJ. Angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from food proteins: Biochemistry, bioactivity and production. Curr. Pharm. Des. 13: 773–791 (2007)
Liu LL, Liu LY, Lu BY, Xia DZ, Zhang Y. Evaluation of antihypertensive and antihyperlipidemic effects of bamboo shoot angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptide in vivo. J. Agr. Food Chem. 60: 11351–11358 (2012)
Liu X, Zhang MS, Zhang G. Angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory, antihypertensive, and antihyperlipidaemic activities of protein hydrolysates from Rhopilema esculentum. Food Chem. 134: 2134–2140 (2012)
Wang W, Wang N, Zhou Y, Zhang Y, Xu LH, Xu JF, Feng FQ, He GQ. Isolation of a novel peptide from silkworm pupae protein components and interaction characteristics to angiotensin Iconverting enzyme. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 232: 29–38 (2011)
Wang W, Shen SR, Chen QH, Tang B, He GQ, Ruan H, Das UN. Hydrolyzates of silkworm pupae (Bombyx mori) protein is a new source of angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides (ACEIP). Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 9: 307–314 (2008)
Li Y, Wang Y, Huang XZ, Kan JQ, Jin SK, He YP, Hu YQ, Liao C. Enzymatic preparation of ACE-inhibitory peptide from pupa protein. Shipin. Kexue. (Beijing) 11: 151–157 (2012)
Li Y, Huang XZ, Kan JQ, He J, Zhang HN. Study on macroporous resin’s purification of pupa ACE inhibitory peptides. Shipin. Gongye. Keji. 16: 281–288 (2012)
Astawan M, Wahyuni M, Yasuhara T, Yamada K, Tadokoro T, Maekawa A. Effects of angiotension I-converting enzyme inhibitory substances derived from indonesian dried-salted fish on blood pressure of rats. Biosci. Biotech. Bioch. 59: 425–429 (1995)
Kumada Y, Hashimoto N, Hasan F, Terashima M, Nakanishi K, Jungbauer A, Katoh S. Screening of ACE-inhibitory peptides from a random peptide-displayed phage library using ACE-coupled liposomes. J. Biotechnol. 131: 144–149 (2007)
Chushman DW, Cheung HS. Spectrophotometric assay and properties of the angiotensin-converting enzyme of rabbit lung. Biochem. Pharmacol. 20: 1637–1648 (1971)
Sheih IC, Fang TJ, Wu TK. Isolation and characterisation of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptide from the algae protein waste. Food Chem. 115: 279–284 (2009)
Bruno D, Ruedia. Mass spectrometry and protein analysis. Science 312: 212–217 (2006)
Bougatef A, Nedjar-Arroume N, Ravallec-Ple R, Leroy Y, Guillochon D, Barkia A, Nasri M. angiotensin I-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory activities of sardinelle (Sardinella aurita) byproducts protein hydrolysates obtained by treatment with microbial and visceral fish serine proteases. Food Chem. 111: 350–356 (2008)
Balti R, Nedjar-Arroume N, Adje EY, Guillochon D, Nasri M. Analysis of novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides from enzymatic hydrolysates of Cuttlefish (Sepia officinalis) muscle proteins. J. Agr. Food Chem. 58: 3840–3846 (2010)
Quiroga AV, Aphalo P, Ventureira JL, Martinez EN, Anon MC. Physicochemical, functional and angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory properties of amaranth (Amaranthus hypochondriacus) 7S globulin. J. Sci. Food Agr. 92: 397–403 (2010)
Martin M, Wellner A, Ossowski I, Henle T. Identification and quantification of inhibitors for angiotensin-converting enzyme in hypoallergenic infant milk formulas. J. Agr. Food Chem. 56: 6333–6338 (2008)
Wu JP, Ding XL. Characterization of inhibition and stability of soy protein derived angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Food Res. Int. 35: 367–375 (2002)
Tomatsu M, Shimakage A, Shinbo M, Yamada S, Takahashi S. Novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides derived from soya milk. Food Chem. 136: 612–616 (2013)
Barbana C, Boye JI. Angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory properties of lentil protein hydrolysates: Determination of the kinetics of inhibition. Food Chem. 127: 94–101 (2011)
Terashima M, Baba T, Ikemoto N, Katayama M, Morimoto T, Matsumura S. Novel angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides derived from boneless chicken leg meat. J. Agr. Food Chem. 58: 7432–7436 (2010)
Sagardia I, Iloro I, Elortza F, Bald C. Quantitative structure-activity relationship based screening of bioactive peptides identified in ripened cheese. Int. Dairy J. 33: 184–190 (2013)
Rho SJ, Lee JS, II Chung Y, Kim YW, Lee HG. Purification and identification of an angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide from fermented soybean extract. Process. Biochem. 44: 490–493 (2009)
Nakagomi K, Ebisu H, Sadakane Y, Fujii N, Akizawa T, Tanimura T. Properties and human origin of two angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides isolated from a tryptic hydrolysate of human serum albumin. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 23: 879–883 (2000)
Cheison SC, Zhang W, Xu SY. Use of macroporous adsorption resin for simultaneous desalting and debittering of whey protein hydrolysates. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 42: 1228–1239 (2007)
Eto Y, Ito T. Nishioka S. Angiotensin I converting enzymeinhibitory dipeptides in an alkaline protease hydrolyzate or whey protein. Nihon Eiyo Shokuryo Gakkai Shi 51: 355–359 (1998)
Yang YJ, Yoshikawa M. Isolation and purification of angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitory peptides by high performance liquid chromatography. Se. Pu. 21: 202–205 (2003)
Miguel M, Alonso M, Salaices M. Antihypertensive, ACEinhibitory and vasodilator properties of an egg white hydrolysate: Effect of a simulated intestinal digestion. Food Chem. 104: 163–168 (2007)
Matsui T, Li CH, Tanaka T, Maki T, Ossajima Y, Matsumoto K. Depressor effect of wheat germ hydrolysate and its novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide, Ile-Val-Tyr, and the metabolism in rat and human plasma. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 23: 427–431 (2000)
Nakahara T, Yamaguchi H, Uchida R. Effect of temperature on the stability of various peptidases during peptide-enriched soy sauce fermentation. J. Biosci. Bioeng. 113: 355–359 (2012)
Hwang JS. Impact of processing on stability of angiotensin Iconverting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides obtained from tuna cooking juice. Food Res. Int. 43: 902–906 (2010)
Jang A, Jo C, Lee M. Storage stability of the synthetic angiotensin converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitory peptides separated from beef sareoplasmic protein extracts at different pH, temperature, and gastric digestion. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 16: 572–575 (2007)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, X., Li, Y., Huang, X. et al. Identification and characterization of a novel angiotensin I-converting enzyme inhibitory peptide (ACEIP) from silkworm pupa. Food Sci Biotechnol 23, 1017–1023 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0138-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0138-9