Abstract
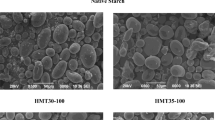
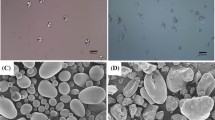
The effects of annealing on the digestibility, morphology, and physicochemical characteristics of four types of granular sweet potato starches [Yulmi (YM), Yeonwhangmi (YHM), sweet potato starch from Samyang Genex (SSPS), and commercial sweet potato starch (CSPS)] were investigated. Annealing was performed at 55°C and 90% moisture content for 72 h. Morphology, the branched chain distribution of amylopectin, and the X-ray diffraction pattern remained unchanged during the annealing process. The slowly digestible starch content in annealed YM, YHM, and SSPS starches increased, but did not change in annealed CSPS. The gelatinization temperatures increased, but the gelatinization temperature range decreased with annealing. The swelling factor and amylose leaching decreased, while the close packing concentration increased. Rapid Visco Analyser analysis revealed that annealed starches possessed thermal stability and higher pasting temperatures. It is suggested that the enhanced packing arrangement formed during annealing impacts the digestibility and physicochemical properties of sweet potato starches.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Palomar LS, Perez JA, Pascual JA. Wheat flour substitution using sweet potato or cassava in some bread and snack items. Ann. Trop. Res. 3: 8–17 (1981)
Lee JS, Ahn YS, Kim HS, Chung MN, Kim JJ, Kim JM, Jeong BC, Bang JK. A new sweet potato cultivar for table use, “Yeonhwangmi”. Korean J. Breeding 38: 149–150 (2006)
Teow CC, Truong V-D, McFeeters RF, Thompson RL, Pecota KV, Yencho GC. Antioxidant activities, phenolic and β-carotene contents of sweet potato genotypes with varying fresh colours. Food Chem. 103: 829–838 (2007)
Jayakody L, Hoover R. Effect of annealing on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of starches from different botanical origins — A review. Carbohyd. Polym. 74: 691–703 (2008)
Hoover R, Vasanthan T. The effect of annealing on the physicochemical properties of wheat, oat, potato and lentil starches. J. Food Biochem. 17: 303–325 (1994)
Jacobs H, Delcour JA. Hydrothermal modifications of granular starch, with retention of the granular structure: A review. J. Agr. Food Chem. 46: 2895–2905 (1998)
Krueger BR, Knutson CA, Inglett GE, Walker CE. A differential scanning calorimetry study on the effect of annealing on gelatinization behavior of corn starch. J. Food Sci. 52: 715–718 (1987)
Stute R. Hydrothermal modification of starches: The difference between annealing and heat/moisture-treatment. Starch-Starke 44: 205–214 (1992)
Jacobs H, Eerlingen RC, Clauwaert W, Delcour JA. Influence of annealing on the pasting properties of starches from varying botanical sources. Cereal Chem. 72: 480–487 (1995)
Tester RF, Morrison WR. Swelling and gelatinization of cereal starches. II. Waxy rice starches. Cereal Chem. 67: 558–563 (1990)
Waduge RN, Hoover R, Vasanthan T, Gao T, Li J. Effect of annealing on the structure and physicochemical properties of barley starches of varying amylose content. Food Res. Int. 39: 59–77 (2006)
Nazakawa F, Noguchi S, Takahashi J, Takada M. Thermal equilibrium state of starch-water mixture studied by differential scanning calorimetry. Agr. Biol. Chem. Tokyo 48: 2647–2653 (1984)
Englyst HN, Kingman SM, Cummings JH. Classification and measurement of nutritionally important starch fractions. Eur. J. Clin. Nutr. 46: E33–E50 (1992)
Lehmann U, Robin F. Slowly digestible starch-its structure and health implications: A review. Trends Food Sci. Tech. 18: 346–355 (2007)
Sajilata MG, Singhal RS, Kulkarni PR. Resistant starch-a review. Compr. Rev. Food Sci. F 5: 1–17 (2006)
Brumovsky JO, Thompson DB. Production of boiling-stable granular resistant starch by partial acid hydrolysis and hydrothermal treatments of high-amylose maize starch. Cereal Chem. 78: 680–689 (2001)
Shin SI, Kim HJ, Ha HJ, Lee SH, Moon TW. Effect of hydrothermal treatment on formation and structural characteristics of slowly digestible non-pasted granular sweet potato starch. Starch-Starke 57: 421–430 (2005)
Chung HJ, Liu Q, Hoover R. Impact of annealing and heat-moisture treatment on rapidly digestible, slowly digestible and resistant starch levels in native and gelatinized corn, pea and lentil staches. Carbohyd. Polym. 75: 436–447 (2009)
Moore S, Stein HW. Photometric ninhydrin method for use in the chromatography of amino acids. J. Biol. Chem. 176: 367–388 (1948)
Eerlingen RC, Jacobs H, Block K, Delcour JA. Effects of hydrothermal treatments on the rheological properties of potato starch. Carbohyd. Res. 297: 347–356 (1997)
Gilbert GA, Spragg SP. Iodimetric Determination of Amylose. Methods in Carbohydrate Chemistry. Academic Press, New York, NY, USA. pp. 168–169 (1964)
Vandeputte GE, Vermeylen R, Geeroms J, Delcour JA. Rice starches I. Structural aspcets provide insight into crystallinity characteristics and gelatinisation behaviour of granular starch. J. Cereal Sci. 38: 43–52 (2003)
Lopez-Rubio A, Flanagan BM, Gilbert EP, Gidley MJ. A novel approach for calculating starch crystallinity and its correlation with double helix content: A combined XRD and NMR study. Biopolymers 89: 761–768 (2008)
Knutson CA. Annealing of maize starches at elevated temperatures. Cereal Chem. 67: 376–384 (1990)
Lan H, Hoover R, Jayakody L, Liu Q, Donner E, Baga M, Asare EK, Hucl P, Chibbar RN. Impact of annealing on the molecular structure and physicochemical properties of normal, waxy and high amylose bread wheat starches. Food Chem. 111: 663–675 (2008)
Hizukuri S, Abe JI, Hanashiro I. Starch: Analytical Aspects. Carbohydrates in Food. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, USA. pp. 305–390 (2006)
Vermeylen R, Goderis B, Delcour JA. An X-ray study of hydrothermally treated potato starch. Carbohyd. Polym. 64: 364–375 (2006)
Hoover R, Manuel H. The effect of heat-moisture treatment on the structure and physicochemical properties of normal maize, waxy maize, dull waxy maize and amylomaize V starches. J. Cereal Sci. 23: 153–162 (1996)
O’Brien S, Wang YJ. Susceptibility of annealed starches to hydrolysis by α-amylase and glucoamylase. Carbohyd. Polym. 72: 597–607 (2008)
Vieira FC, Sarmento SBS. Heat-moisture treatment and enzymatic digestibility of Peruvian carrot, sweet potato and ginger starches. Starch-Starke 60: 223–232 (2008)
Collado LS, Corke H. Heat-moisture treatment effects on sweet potatostarches differing in amylose content. Food Chem. 65: 339–346 (1999)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Song, H.Y., Lee, S.Y., Choi, S.J. et al. Digestibility and physicochemical properties of granular sweet potato starch as affected by annealing. Food Sci Biotechnol 23, 23–31 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0004-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-014-0004-9