Abstract
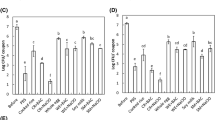
The objective of this study was to analyze the microbial risk factor of the material, employee, and machinery/instrument related to the quality of salted Chinese cabbage, but also the hygienic safety and standardization of this Chinese cabbage. The total bacteria of Chinese cabbage at cutting and salting were increased to 4.47–6.48 log CFU/g and decreased at the cleaning and dehydration process. The total bacteria in the rubber gloves and aprons of the worker were in 3–6 log CFU/g. The contamination on the machinery/instrument in the primary cleaning was in 3.88–6.07 log CFU/g and it was the highest level of the total processes. Especially, the contamination, on the conveyor belt was the highest. As a result of pH and salinity of the Chinese cabbage and salt solution, the salinity of Chinese cabbage was reduced from 2.63–2.88% in salting to 1.16–1.37% after dehydration, a decrease of 52–58%. The pH 5.87 and salinity 2.54% for the upper salt solution in a tank showed more than 2 times the difference, with pH 6.07 and 7.37% salinity for the lower salt solution in a tank.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
MIFAFF. Statistics of Vegetables Production Amount. Ministry for Food, Agriculture, Forestry, and Fishes, Kwacheon, Korea. pp. 7–10 (2008)
Kim BG. Research Report on Reuse of Brining Waste Water in Kimchi Industry. The Institute of Environmental Science and Engineering, Ministry of Environment, Seoul, Korea. pp. 14–45 (1997)
Shim YH, Ahn GJ, Yoo CH. Characterization of salted Chinese cabbage in relation to salt content, temperature, and time. Korean J. Soc. Food Cookery Sci. 19: 210–215 (2003)
Han ES, Seok MS, Park JH. Quality changes of salted baechu with packing methods during long-term storage. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 26: 283–287 (1998)
Han ES, Seok MS, Park JH. Changes of characteristics in salted baechu (Chinese cabbage) and its exudate during long term storage. Korean J. Postharv. Sci. Technol. 5: 165–169 (1998)
Han KY, Noh BS. Characterization of Chinese cabbage during soaking in sodium chloride solution. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 28: 707–713 (1996)
Song JE, Kim MS, Han JS. Effects of the salting of Chinese cabbage on taste and fermentation of kimchi. Korean J. Soc. Food Sci. 11: 226–232 (1995)
KFDA. Food Code. Korea Food & Drug Administration, Seoul, Korea. p. 4-1–2 (2008)
KFDA. Food Code. Korea Food & Drug Administration, Seoul, Korea. p. 7-1–2 (2008)
Han KY, Noh BS. Characterization of Chinese cabbage during soaking in sodium chloride solution. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 28: 707–717 (1996)
Kim JS, Jung JY, Cho SK, Kim JE, Kim TJ, Kim BS, Han NS. Microbial analysis of baechekimchi during automatic production process. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 42: 281–286 (2010)
Kim YW, Jung JK, Cho YJ, Lee SJ, Kim SH, Park KY, Kang SA. Quality changes in brined baechu cabbage using different types of polyethylene film and salt content during storage. Korean J. Food Preserv. 16: 605–611 (2009)
Han ES. Quality changes of salted Chinese cabbage by packing methods during storage. Korean J. Food Sci. Technol. 26: 283–287 (1994)
Park SY, Jung JK, Kang JM, Kim SH, Yang JY, Kang SA, Chun HK, Park KY. Monitoring of 160 kinds of pesticide residues in commercial baechu (Chinese) cabbage throughout the year. J. Korean Soc. Food Sci. Nutr. 38: 970–975 (2009)
Kim BS, Lee HO, Kim JY, Yoon DH, Cha HS, Kwon DS. Microbial contamination in a facility for processing of fresh-cut leafy vegetables. Korean J. Food Preserv. 16: 573–578 (2009)
Kim HO, Suh SR, Choi YS, Yoo SN. Optimal conditions for mechanized salting process of salt-inserting method for winter cabbage to produce kimchi. Korean J. Food. Preserv. 14: 695–705 (2007)
Ku YS, Kim MK, Kim MJ, Kim SD. Quality of kimchi fermented with various salt concentrations. J. Food Sci. Technol. 9: 65–69 (1997)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sung, JM., Lim, JH., Park, KJ. et al. Analysis on risk factor in a facility and product for processing of salted Chinese cabbage. Food Sci Biotechnol 20, 897–904 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-011-0124-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10068-011-0124-4