Abstract
Objective
This study aimed to evaluate the value of machine learning models (ML) based on MRI radiomics in diagnosing early parotid gland injury in primary Sjögren’s syndrome (pSS).
Methods
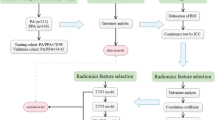
A total of 164 patients (114 in the training cohort and 50 in the testing cohort) with pSS (n=82) or healthy controls (HC) (n=82) were enrolled. Itksnap software was used to perform two-dimensional segmentation of the bilateral parotid glands on T1-weighted (T1WI) and fat-suppressed T2-weighted imaging (fs-T2WI) images. A total of 1548 texture features of the parotid glands were extracted using radiomics software. A radiomics score (Radscore) was constructed and calculated. A t-test was used to compare the Radscore between the two groups. Finally, five machine learning models were trained and tested to identify early pSS parotid injury, and the performance of the machine learning models was evaluated by calculating the acceptance operating curve (ROC) and other parameters.
Results
The Radscores between the pSS and HC groups showed significant statistical differences (p<0.001). Among the five machine learning models, the Extra Trees Classifier (ETC) model performed high predictive efficacy in identifying early pSS parotid injury, with an AUC of 0.87 in the testing set.
Conclusion
MRI radiomics–based machine learning models can effectively diagnose early parotid gland injury in primary Sjögren’s syndrome.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ewert P, Aguilera S, Alliende C, Kwon YJ, Albornoz A, Molina C et al (2010 May) Disruption of tight junction structure in salivary glands from Sjögren’s syndrome patients is linked to proinflammatory cytokine exposure. Arthritis Rheum 62(5):1280–1289
Liang Y, Yang Z, Qin B, Zhong R (2014 Jun) Primary Sjogren’s syndrome and malignancy risk: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Ann Rheum Dis 73(6):1151–1156
van Ginkel MS, Glaudemans AWJM, van der Vegt B, Mossel E, Kroese FGM, Bootsma H et al (2020) Imaging in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Clin Med 9(8):2492
Baldini C, Zabotti A, Filipovic N, Vukicevic A, Luciano N, Ferro F et al (2018) Imaging in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: the ‘obsolete and the new’. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36(Suppl 112(3)):215–221
Świecka M, Maślińska M, Paluch Ł, Zakrzewski J, Kwiatkowska B (2019) Imaging methods in primary Sjögren’s syndrome as potential tools of disease diagnostics and monitoring. Reumatologia. 57(6):336–342
Le Goff M, Cornec D, Jousse-Joulin S, Guellec D, Costa S, Marhadour T et al (2017) Comparison of 2002 AECG and 2016 ACR/EULAR classification criteria and added value of salivary gland ultrasonography in a patient cohort with suspected primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Res Ther 19(1):269
Jousse-Joulin S, Gatineau F, Baldini C, Baer A, Barone F, Bootsma H et al (2020) Weight of salivary gland ultrasonography compared to other items of the 2016 ACR/EULAR classification criteria for Primary Sjögren’s syndrome. J Intern Med 287(2):180–188
van Nimwegen JF, Mossel E, Delli K, van Ginkel MS, Stel AJ, Kroese FGM et al (2020) Incorporation of salivary gland ultrasonography into the American College of Rheumatology/European League against rheumatism criteria for primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Arthritis Care Res 72(4):583–590
Rao Y, Xu N, Zhang Y, Fang Y, Tian L, Min X et al (2023) Value of magnetic resonance imaging and sialography of the parotid gland for diagnosis of primary Sjögren syndrome. Int J Rheum Dis 26(3):454–463
Ding CW, Guo QY, Xing XF et al (2014) MRI features of the parotid gland in Sjögren’s syndrome. Chin J Radiol 48(5):386–390
Makula E, Pokorny G, Kiss M, Vörös E, Kovács L, Kovács A et al (2000) The place of magnetic resonance and ultrasonographic examinations of the parotid gland in the diagnosis and follow-up of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Rheumatol Oxf Engl 39(1):97–104
Gillies RJ, Kinahan PE, Hricak H (2016) Radiomics: images are more than pictures, they are data. Radiology. 278(2):563–577
Bruixola G, Remacha E, Jiménez-Pastor A, Dualde D, Viala A, Montón JV et al (2021) Radiomics and radiogenomics in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma: potential contribution to patient management and challenges. Cancer Treat Rev 99:102263
Tortora M, Gemini L, Scaravilli A, Ugga L, Ponsiglione A, Stanzione A et al (2023) Radiomics applications in head and neck tumor imaging: a narrative review. Cancers (Basel) 15(4):1174
Chilaca-Rosas MF, Garcia-Lezama M, Moreno-Jimenez S, Roldan-Valadez E (2023) Diagnostic performance of selected MRI-derived radiomics able to discriminate progression-free and overall survival in patients with midline glioma and the H3F3AK27M mutation. Diagnostics (Basel) 13(5):849
Zheng YM, Li J, Liu S, Cui JF, Zhan JF, Pang J et al (2021) MRI-based radiomics nomogram for differentiation of benign and malignant lesions of the parotid gland. Eur Radiol 31(6):4042–4052
Xia X, Feng B, Wang J, Hua Q, Yang Y, Sheng L et al (2021) Deep learning for differentiating benign from malignant parotid lesions on MR images. Front Oncol 11:632104
Muntean DD, Bădărînză M, Ștefan PA, Lenghel ML, Rusu GM, Csutak C et al (2022) The diagnostic value of MRI-based radiomic analysis of lacrimal glands in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Int J Mol Sci 23(17):10051
Chu C, Feng Q, Zhang H, Zhu Y, Chen W, He J et al (2019) Whole-volume ADC histogram analysis in parotid glands to identify patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Sci Rep 9(1):9614
Tustison NJ, Avants BB, Cook PA, Zheng Y, Egan A, Yushkevich PA et al (2010) N4ITK: improved N3 bias correction. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 29(6):1310–1320
Kroese FGM, Haacke EA, Bombardieri M (2018) The role of salivary gland histopathology in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: promises and pitfalls. Clin Exp Rheumatol 36(Suppl 112(3)):222–233
Izumi M, Eguchi K, Nakamura H, Nagataki S, Nakamura T (1997) Premature fat deposition in the salivary glands associated with Sjögren syndrome: MR and CT evidence. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 18(5):951–958
Parmar C, Grossmann P, Bussink J, Lambin P, Aerts HJWL (2015) Machine learning methods for quantitative radiomic biomarkers. Sci Rep 17(5):13087
Chu C, Feng Q, Zhang H, Zhao S, Chen W, He J et al (2020) Evaluation of salivary gland fat fraction values in patients with primary Sjögren’s syndrome by mDIXON quant imaging: Initial findings. Eur J Radiol 123:108776
Feng Q, Chu C, Wang F, Zhao S, Zhang H, Sun L et al (2020) Application of T2 mapping in early evaluation of salivary gland injury in Sjögren’s syndrome. Chin J Med Imaging 01:27–30
Aggarwal R, Ranganathan P (2016) Common pitfalls in statistical analysis: the use of correlation techniques. Perspect Clin Res 7(4):187–190
Seror R, Baron G, Camus M, Cornec D, Perrodeau E, Bowman SJ et al (2022 Jul) Development and preliminary validation of the Sjögren’s Tool for Assessing Response (STAR): a consensual composite score for assessing treatment effect in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 81(7):979–989
Chu C, Wang F, Zhang H, Zhu Y, Wang C, Chen W et al (2018) Whole-volume ADC histogram and texture analyses of parotid glands as an image biomarker in evaluating disease activity of primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Sci Rep 8(1):15387
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
WW and GQL contributed to conception and design of the study; LL, TTD, QAS, and HYX helped with the acquisition of data; WW, HQ, YZ, and LL analyzed and interpretated the retrospective clinical study and data; LL and TTD wrote sections of the manuscript. WW and GQL reviewed the paper. All authors contributed to the article and approved the submitted version.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Key Points
• MRI-based Radscore distinguishes early parotid gland injury in primary Sjögren’s syndrome from healthy glands.
• Combining MRI radiomics and machine learning enhances early parotid gland injury diagnosis in primary Sjögren’s syndrome.
Lu Lu and Tiantian Dai are first authors.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Lu, L., Dai, T., Zhao, Y. et al. The value of MRI-based radiomics for evaluating early parotid gland injury in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 43, 1675–1682 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06935-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06935-2