Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to compare optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) findings between patients with Behçet’s disease (BD) and individuals with healthy eyes.
Design
A cross-sectional study.
Methods
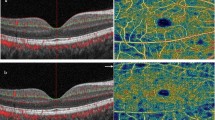
This cross-sectional study was conducted on patients (67 eyes) with BD who were referred to Feiz Hospital and healthy eyes (43 eyes). All subjects underwent Snellen visual acuity, a slit-lamp examination, measuring intraocular pressure, conducting a dilated fundus examination, OCTA imaging, and spectral-domain (SD)-OCT imaging. OCTA retinal vascular measurements including optic nerve VD, macular-associated VD( superficial and deep), foveal avascular zone (FAZ) area, FAZ perimeter (PERIM), and vessel density within a 300-μm-wide region of the FAZ (FD) were compared between the groups.
Results
A significant difference was evident between the two groups (healthy one group and BD group) in terms of parafoveal and perifoveal total retinal thickness, total pRNFL VD in all quadrants except the inferior sector (P < 0.05), and macular superficial, and deep VD in all regions except temporal and superior perifoveal VD (P < 0.05) following adjustments for age, gender, and signal strength index. When comparing the two groups, ocular Behçet’s disease (BD) and non-ocular BD, it was evident that peripapillary vessel density (VD) exhibited a significant decrease in ocular BD eyes in all sectors except for the superior and inferior ones, as compared to non-ocular BD eyes. In addition, the comparison of ocular BD and non-ocular BD showed superficial and deep VDs were lower in ocular BD than non-ocular BD in all regions.
Conclusion
According to these findings, peripapillary and macular vessel density is affected in BD.
Key Points • The study utilized OCTA to compare retinal features in Behçet’s disease (BD) patients and healthy individuals, revealing significant differences in retinal thickness and vessel density. • Ocular BD demonstrated reduced peripapillary vessel density compared to non-ocular BD. • The demonstrated association between ADMA and cIMT in patients with early SSc may suggest a role of NO/ADMA pathway in the initiation of macrovascular injury in SSc. |

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The raw data supporting the conclusions of this article will be made available by the authors.
References
Somkijrungroj T, Vongkulsiri S, Kongwattananon W, Chotcomwongse P, Luangpitakchumpol S, Jaisuekul K (2017) Assessment of vascular change using swept-source optical coherence tomography angiography: a new theory explains central visual loss in Behcet’s disease. J Ophthalmol 2017:2180723
Hedayatfar A (2013) Behçet’s Disease: Autoimmune or Autoinflammatory? J Ophthalmic Vis Res 8(3):291–293
Goker YS, Yılmaz S, Kızıltoprak H, Tekin K, Demir G (2019) Quantitative analysis of optical coherence tomography angiography features in patients with nonocular Behcet’s disease. Curr Eye Res 44(2):212–218
Balta S, Balta I, Ozturk C, Celik T, Iyisoy A (2016) Behçet’s disease and risk of vascular events. Curr Opin Cardiol 31(4):451–457
Kianersi F, Mohammadi Z, Ghanbari H, Ghoreyshi SM, Karimzadeh H, Soheilian M (2015) Clinical patterns of uveitis in an Iranian tertiary eye-care center. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 23(4):278–282
Tinti MG, Vaira F, Inglese M, Serviddio G, De Cosmo S, Marotto D et al (2020) Ocular involvement in Behçet’s disease: relevance of new diagnostic tools. Rheumatol Adv Practice 4(2):rkaa038
Yannuzzi LA, Bardal AM, Freund KB, Chen KJ, Eandi CM, Blodi B (2006) Idiopathic macular telangiectasia. Arch Ophthalmol (Chicago, Ill: 1960) 124(4):450–60
Kashani AH, Chen CL, Gahm JK, Zheng F, Richter GM, Rosenfeld PJ et al (2017) Optical coherence tomography angiography: a comprehensive review of current methods and clinical applications. Prog Retin Eye Res 60:66–100
de Carlo TE, Romano A, Waheed NK, Duker JS (2015) A review of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA). Int J Retin Vitr 1:5
Kalra G, Zarranz-Ventura J, Chahal R, Bernal-Morales C, Lupidi M, Chhablani J (2022) Optical coherence tomography (OCT) angiolytics: a review of OCT angiography quantitative biomarkers. Surv Ophthalmol 67(4):1118–1134
Greig EC, Duker JS, Waheed NK (2020) A practical guide to optical coherence tomography angiography interpretation. Int J Retin Vitr 6(1):55
Khairallah M, Abroug N, Khochtali S, Mahmoud A, Jelliti B, Coscas G et al (2017) Optical coherence tomography angiography in patients with Behçet uveitis. Retina (Philadelphia, Pa) 37(9):1678–1691
Koca S, Onan D, Kalaycı D, Allı N (2020) Comparison of optical coherence tomography angiography findings in patients with Behçet’s disease and healthy controls. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 28(5):806–813
Emre S, Güven-Yılmaz S, Ulusoy MO, Ateş H (2019) Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in Behcet patients. Int Ophthalmol 39(10):2391–2399
Çömez A, Beyoğlu A, Karaküçük Y (2019) Quantitative analysis of retinal microcirculation in optical coherence tomography angiography in cases with Behçet’s disease without ocular involvement. Int Ophthalmol 39(10):2213–2221
Raafat KA, Allam R, Medhat BM (2019) Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in patients with nonocular Behçet disease. Retina (Philadelphia, Pa) 39(8):1607–1612
Accorinti M, Gilardi M, De Geronimo D, Iannetti L, Giannini D, Parravano M (2020) Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in active and inactive ocular Behçet disease. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 28(4):589–600
Karalezli A, Kaderli ST, Sul S, Pektas SD (2021) Preclinical ocular features in patients with Behçet’s disease detected by optical coherence tomography angiography. Eye (Lond) 35(10):2719–2726
Smid LM, Vermeer KA, Missotten T, van Laar JAM, van Velthoven MEJ (2021) Parafoveal microvascular alterations in ocular and non-ocular Behҫet’s disease evaluated with optical coherence tomography angiography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 62(3):8
Yan C, Li F, Hou M, Ye X, Su L, Hu Y et al (2021) Vascular abnormalities in peripapillary and macular regions of Behcet’s uveitis patients evaluated by optical coherence tomography angiography. Front Med 8:727151
Pei M, Zhao C, Gao F, Qu Y, Liang A, Xiao J et al (2021) Analysis of parafoveal microvascular abnormalities in Behcet’s uveitis using projection-resolved optical coherence tomographic angiography. Ocul Immunol Inflamm 29(3):524–529
Yılmaz Tuğan B, Sönmez HE (2022) Optical coherence tomography angiography of subclinical ocular features in pediatric Behçet disease. J AAPOS 26(1):24.e1-e6
Guo S, Liu H, Gao Y, Dai L, Xu J, Yang P (2023) Analysis of vascular changes of fundus in Behcet uveitis by widefield swept source optical coherence tomography angiography and fundus fluorescein angiography. Retina (Philadelphia, Pa) 43(5):841–850
Türkcü FM, Şahin A, Karaalp Ü, Çınar Y, Şahin M, Özkurt ZG et al (2020) Automated quantification of the foveal avascular zone and vascular density in Behçet’s disease. Ir J Med Sci 189(1):349–354
Cheng D, Wang Y, Huang S, Wu Q, Chen Q, Shen M et al (2016) Macular inner retinal layer thickening and outer retinal layer damage correlate with visual acuity during remission in Behcet’s disease. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 57(13):5470–5478
Atas N, Bitik B, Varan O, Babaoglu H, Tufan A, Haznedaroglu S et al (2019) Clinical characteristics of avascular necrosis in patients with Behçet disease: a case series and literature review. Rheumatol Int 39(1):153–159
Cheng D, Shen M, Zhuang X, Lin D, Dai M, Chen S et al (2018) Inner retinal microvasculature damage correlates with outer retinal disruption during remission in Behçet’s posterior uveitis by optical coherence tomography angiography. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci 59(3):1295–1304
Yilmaz PT, Ozdemir EY, Alp MN (2021) Optical coherence tomography angiography findings in patients with ocular and non-ocular Behcet disease. Arq Bras Oftalmol 84(3):235–240
Küçük MF, Yaprak L, Erol MK, Ayan A, Kök M (2022) Quantitative changes in peripapillary, macular, and choriocapillaris microvasculature of patients with non-ocular Behçet’s disease and relationship with systemic vascular involvement, an optical coherence tomography angiography study. Photodiagn Photodyn Ther 38:102749
Eser-Ozturk H, Ismayilova L, Yucel OE, Sullu Y (2021) Quantitative measurements with optical coherence tomography angiography in Behçet uveitis. Eur J Ophthalmol 31(3):1047–1055
Panahi MM (2004) The study of ophthalmologic involvement in 28 Behçet’s syndrome patients. Avicenna J Clin Med 11(1):22–25
Ghlayani P, Babadi F (2012) Frequency of clinical manifestations of Behçet’s syndrome in the patient’s referring to Isfahan Al-Zahra Hospital during 1998–2008. Journal of Isfahan Dental School 7(5): 862–865
Moghimi J, Daraee GH (2009) A case report on the dramatic response of refractory panuveitis of Behcet disease to short-term therapy with Infliximab followed by Cellcept. KOOMESH 10(3–31):225–227
Hussein MA, Eissa IM, Dahab AA (2018) Vision-threatening Behcet’s disease: severity of ocular involvement predictors. J Ophthalmol 2018:9518065
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Kianersi, F., Bazvand, M., Fatemi, A. et al. Comparative analysis of optical coherence tomography angiography (OCTA) results between Behçet’s disease patients and a healthy control group. Clin Rheumatol 43, 1155–1170 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06874-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-024-06874-y