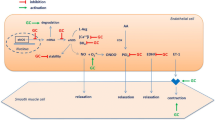
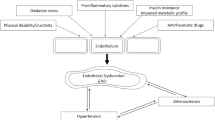
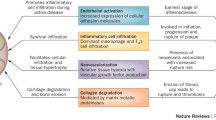
Abstract
This narrative review provides a comprehensive examination of the complex interplay between inflammatory arthritis (IA) and cardiovascular pathology. It particularly illuminates the roles of atherosclerosis initiation, endothelial dysfunction, and glycocalyx shedding. IA not only provokes tissue-specific inflammatory responses, but also engenders a considerable degree of non-specific systemic inflammation. This review underscores the accelerating influence of the chronic inflammatory milieu of IA on cardiovascular disease (CVD) progression. A focal point of our exploration is the critical function of the endothelial glycocalyx (EG) in this acceleration process, which possibly characterizes the earliest phases of atherosclerosis. We delve into the influence of inflammatory mediators on microtubule dynamics, EG modulation, immune cell migration and activation, and lipid dysregulation. We also illuminate the impact of microparticles and microRNA on endothelial function. Further, we elucidate the role of systemic inflammation and sheddases in EG degradation, the repercussions of complement activation, and the essential role of syndecans in preserving EG integrity. Our review provides insight into the complex and dynamic interface between systemic circulation and the endothelium.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bäck M, Yurdagul A Jr, Tabas I, Öörni K, Kovanen PT (2019) Inflammation and its resolution in atherosclerosis: mediators and therapeutic opportunities. Nat Rev Cardiol 16:389–406. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-019-0169-2
Vonderlin N, Siebermair J, Kaya E, Köhler M, Rassaf T, Wakili R (2019) Critical inflammatory mechanisms underlying arrhythmias. Herz 44:121–129. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00059-019-4788-5
Adamo L, Rocha-Resende C, Prabhu SD, Mann DL (2020) Reappraising the role of inflammation in heart failure. Nat Rev Cardiol 17:269–285. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-019-0315-x
Agca R, Heslinga SC, Rollefstad S et al (2017) EULAR recommendations for cardiovascular disease risk management in patients with rheumatoid arthritis and other forms of inflammatory joint disorders: 2015/2016 update. Ann Rheum Dis 76(1):17–28. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209775
Lauper K, Courvoisier DS, Chevallier P, Finckh A, Gabay C (2018) Incidence and prevalence of major adverse cardiovascular events in rheumatoid arthritis, psoriatic arthritis, and axial spondyloarthritis. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 70(12):1756–1763. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.23567
Moltó A, Nikiphorou E (2018) Comorbidities in spondyloarthritis. Front Med (Lausanne) 5:62. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmed.2018.00062
Liew JW, Ramiro S, Gensler LS (2018) Cardiovascular morbidity and mortality in ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Best Pract Res Clin Rheumatol 32:369–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.berh.2019.01.002
Polachek A, Touma Z, Anderson M, Eder L (2017) Risk of cardiovascular morbidity in patients with psoriatic arthritis: a meta-analysis of observational studies. Arthritis Care Res 69:67–74. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22926
Zimba O, Gasparyan AY (2023) Cardiovascular issues in rheumatic diseases. Clin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06656-y
Ross R (1999) Atherosclerosis—an inflammatory disease. N Engl J Med 340:115–126. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM199901143400207
Libby P, Hansson GK (2015) Inflammation and immunity in diseases of the arterial tree: players and layers. Circ Res 116:307–311. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.116.301313
Hedar AM, Stradner MH, Roessler A, Goswami N (2021) Autoimmune rheumatic diseases and vascular function: the concept of autoimmune atherosclerosis. J Clin Med 10:4427. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm10194427
Sima P, Vannucci L, Vetvicka V (2018) Atherosclerosis as autoimmune disease. Ann Transl Med 6(7):116. https://doi.org/10.21037/atm.2018.02.02
Hansson GK (2005) Inflammation, atherosclerosis, and coronary artery disease. N Engl J Med 352(16):1685–1695. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMra043430
Peters MJ, van Halm VP, Voskuyl AE, Smulders YM, Boers M, Lems WF et al (2009) Does rheumatoid arthritis equal diabetes mellitus as an independent risk factor for cardiovascular disease? A prospective study Arthritis Rheum 61(11):1571–1579. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24836
Libby P, Ridker PM, Hansson GK (2011) Progress and challenges in translating the biology of atherosclerosis. Nature 473:317–325. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature10146
Tabas I, García-Cardeña G, Owens GK (2015) Recent insights into the cellular biology of atherosclerosis. J Cell Biol 209(1):13–22. https://doi.org/10.1083/jcb.201412052
Herrington W, Lacey B, Sherliker P, Armitage J, Lewington S (2016) Epidemiology of atherosclerosis and the potential to reduce the global burden of atherothrombotic disease. Circ Res 118(4):535–546. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.115.307611
Schött U, Solomon C, Fries D, Bentzer P (2016) The endothelial glycocalyx and its disruption, protection and regeneration: a narrative review. Scand J Trauma Resusc Emerg Med 24:48. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13049-016-0239-y
Deyab G, Reine TM, Vuong TT, Jenssen T, Hjeltnes G, Agewall S et al (2021) Antirheumatic treatment is associated with reduced serum Syndecan-1 in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One. 16(7):e0253247. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0253247
Agere SA, Kim EY, Akhtar N, Ahmed S (2018) Syndecans in chronic inflammatory and autoimmune diseases: pathological insights and therapeutic opportunities. J Cell Physiol 233:6346–6358. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcp.26388
Zhang X, Sun D, Song JW, Zullo J, Lipphardt M, Coneh-Gould L, Goligorsky MS (2018) Endothelial cell dysfunction and glycocalyx — a vicious circle. Matrix Biol 71–72:421–431. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matbio.2018.01.026
Qi F, Zhou H, Gu P, Tang ZH, Zhu BF, Chen JR et al (2021) Endothelial glycocalyx degradation is associated with early organ impairment in polytrauma patients. BMC Emerg Med 21(1):52. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12873-021-00446-y
Gasparyan AY, Ayvazyan L, Blackmore H, Kitas GD (2011) Writing a narrative biomedical review: considerations for authors, peer reviewers, and editors. Rheumatol Int 31(11):1409–1417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-1999-3
Rueda-Gotor J, Genre F, Corrales A, Blanco R, Fuentevilla P, Portilla V et al (2018) Detection of high cardiovascular risk patients with ankylosing spondylitis based on the assessment of abdominal aortic calcium as compared to carotid ultrasound. Arthritis Res Ther 20(1):195. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1684-y
Tinggaard AB, Hjuler KF, Andersen IT, Winther S, Iversen L, Bøttcher M (2021) Prevalence and severity of coronary artery disease linked to prognosis in psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis patients: a multi-centre cohort study. J Intern Med 290(3):693–703. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.13311
Crowson CS, Liao KP, Davis JM 3rd, Solomon DH, Matteson EL, Knutson KL et al (2013) Rheumatoid arthritis and cardiovascular disease. Am Heart J 166(4):622-628.e1. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ahj.2013.07.010
Tekaya AB, Mehmli T, Mrad IB, Fendri A, Boukriba S, Bouden S et al (2022) Increased epicardial adipose tissue thickness correlates with endothelial dysfunction in spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 41(10):3017–3025. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-022-06261-5
Dehghan P, Rajaei A, Moeineddin R, Alizadeh AM (2015) Prevalence of atherosclerosis in patients with inactive rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34:1363–1366. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2996-9
Westerlind H, Rönnelid J, Hansson M, Alfredsson L, Mathsson-Alm L, Serre G et al (2020) Anti-citrullinated protein antibody specificities, rheumatoid factor isotypes, and incident cardiovascular events in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 72(10):1658–1667. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41381
Linton MF, Yancey PG, Davies SS, Jerome WG, Linton EF, Song WL, Doran AC, Vickers KC (2019) The role of lipids and lipoproteins in atherosclerosis. In: Feingold KR, Anawalt B, Blackman MR et al (eds) Endotext. MDText.com Inc, South Dartmouth (MA). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK343489/. Accessed 30 Jun 2023
Schwartz DM, Parel P, Li H, Sorokin AV, Berg AR, Chen M et al (2022) PET/CT-based characterization of 18F-FDG uptake in various tissues reveals novel potential contributions to coronary artery disease in psoriatic arthritis. Front Immunol 13:909760. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.909760
Gerganov G, Georgiev T, Dimova M, Shivacheva T (2023) Vascular effects of biologic and targeted synthetic antirheumatic drugs approved for rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review. Clin Rheumatol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06587-8
Becker BF, Chappell D, Bruegger D, Annecke T, Jacob M (2010) Therapeutic strategies targeting the endothelial glycocalyx: acute deficits, but great potential. Cardiovasc Res 87:300–310. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvq137
Schmidt EP, Yang Y, Janssen WJ, Gandjeva A, Perez MJ, Barthel L et al (2012) The pulmonary endothelial glycocalyx regulates neutrophil adhesion and lung injury during experimental sepsis. Nat Med 18(8):1217–1223. https://doi.org/10.1038/nm.2843
Chappell D, Dörfler N, Jacob M, Rehm M, Welsch U, Conzen P, Becker BF (2010) Glycocalyx protection reduces leukocyte adhesion after ischemia/reperfusion. Shock 34:133–139. https://doi.org/10.1097/SHK.0b013e3181cdc363
Petrey AC, de la Motte CA (2014) Hyaluronan, a crucial regulator of inflammation. Front Immunol 5:101. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2014.00101
Thathiah A, Blobel CP, Carson DD (2002) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha converting enzyme/ADAM 17 mediates MUC1 shedding. J Biol Chem 278:3386–3394. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M208326200
Tarbell JM, Cancel LM (2016) The glycocalyx and its significance in human medicine. J Intern Med 280(1):97–113. https://doi.org/10.1111/joim.12465
Woodcock TE, Woodcock TM (2012) Revised Starling equation and the glycocalyx model of transvascular fluid exchange: an improved paradigm for prescribing intravenous fluid therapy. Br J Anaesth 108(3):384–394. https://doi.org/10.1093/bja/aer515
Lipowsky HH (2012) The endothelial glycocalyx as a barrier to leukocyte adhesion and its mediation by extracellular proteases. Ann Biomed Eng 40(4):840–848. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-011-0427-x
Holers VM, Banda NK (2018) Complement in the initiation and evolution of rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 9:1057. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2018.01057
Conway EM (2015) Reincarnation of ancient links between coagulation and complement. J Thromb Haemost 13:S121–S132. https://doi.org/10.1111/jth.12950
Veraldi N, Vivès RR, Blanchard-Rohner G, L’Huillier AG, Wagner N, Rohr M, Beghetti M, De Agostini A, Grazioli S (2022) Endothelial glycocalyx degradation in multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children related to COVID-19. J Mol Med (Berl) 100(5):735–746. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00109-022-02190-7
Rangarajan S, Richter JR, Richter RP, Bandari SK, Tripathi K, Vlodavsky I, Sanderson RD (2020) Heparanase-enhanced shedding of syndecan-1 and its role in driving disease pathogenesis and progression. J Histochem Cytochem 68(12):823–840. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155420937087
Behl T, Chadha S, Sehgal A, Singh S, Sharma N, Kaur R, Bhatia S, Al-Harrasi A, Chigurupati S, Alhowail A, Bungau S (2022) Exploring the role of cathepsin in rheumatoid arthritis. Saudi J Biol Sci 29(1):402–410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sjbs.2021.09.014
Becker BF, Jacob M, Leipert S, Salmon AH, Chappell D (2015) Degradation of the endothelial glycocalyx in clinical settings: searching for the sheddases. Br J Clin Pharmacol 80:389–402. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.12629
Lee DH, Dane MJ, van den Berg BM, Boels MG, van Teeffelen JW, de Mutsert R, den Heijer M, Rosendaal FR, van der Vlag J, van Zonneveld AJ, Vink H, Rabelink TJ, NEO study group, (2014) Deeper penetration of erythrocytes into the endothelial glycocalyx is associated with impaired microvascular perfusion. PLoS One 9:e96477. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0096477
Ikonomidis I, Pavlidis G, Katsimbri P, Lambadiari V, Parissis J, Andreadou I, Tsoumani M, Boumpas D, Kouretas D, Iliodromitis E (2020) Tocilizumab improves oxidative stress and endothelial glycocalyx: a mechanism that may explain the effects of biological treatment on COVID-19. Food Chem Toxicol 145:111694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fct.2020.111694
Garcin C, Straube A (2019) Microtubules in cell migration. Essays Biochem 63:509–520. https://doi.org/10.1042/EBC20190016
Carmeliet P (2005) Angiogenesis in life, disease and medicine. Nature 438:932–936. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04478
Tarbell JM, Simon SI, Curry FR (2014) Mechanosensing at the vascular interface. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 16:505–532. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-bioeng-071813-104908
Lawson CD, Burridge K (2014) The on-off relationship of Rho and Rac during integrin-mediated adhesion and cell migration. Small GTPases 5:e27958. https://doi.org/10.4161/sgtp.27958
Richter RP, Ashtekar AR, Zheng L, Pretorius D, Kaushlendra T, Sanderson RD, Gaggar A, Richter JR (2022) Glycocalyx heparan sulfate cleavage promotes endothelial cell angiopoietin-2 expression by impairing shear stress-related AMPK/FoxO1 signaling. JCI Insight 7:e155010. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.155010
Akwii RG, Sajib MS, Zahra FT, Mikelis CM (2019) Role of angiopoietin-2 in vascular physiology and pathophysiology. Cells 8471. https://doi.org/10.3390/cells8050471
Kruglov A, Drutskaya M, Schlienz D, Gorshkova E, Kurz K, Morawietz L, Nedospasov S (2020) Contrasting contributions of TNF from distinct cellular sources in arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 79(11):1453–1459. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-216068
Urschel K, Cicha I (2015) TNF-α in the cardiovascular system: from physiology to therapy. Int J Interferon Cytokine Mediat Res 7:9–25. https://doi.org/10.2147/IJICMR.S64894
Chappell D, Hofmann-Kiefer K, Jacob M, Rehm M, Briegel J, Welsch U, Conzen P, Becker BF (2009) TNF-alpha induced shedding of the endothelial glycocalyx is prevented by hydrocortisone and antithrombin. Basic Res Cardiol 104:78–89. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00395-008-0749-5
Wang P, Li S, Liu LN, Lv TT, Li XM, Li XP, Pan HF (2017) Circulating osteoprotegerin levels are elevated in rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 36:2193–2200. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3747-x
Jadon DR, Sengupta R, Nightingale A, Lu H, Dunphy J, Green A, Elder JT, Nair RP, Korendowych E, Lindsay MA, McHugh NJ (2017) Serum bone-turnover biomarkers are associated with the occurrence of peripheral and axial arthritis in psoriatic disease: a prospective cross-sectional comparative study. Arthritis Res Ther 19:210. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-017-1417-7
Baud’huin M, Duplomb L, Teletchea S, Lamoureux F, Ruiz-Velasco C, Maillasson M, Redini F, Heymann MF, Heymann D (2013) Osteoprotegerin: multiple partners for multiple functions. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 24:401–409. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cytogfr.2013.06.001
Dekker M, Waissi F, Silvis MJM, Bennekom JV, Schoneveld AH, de Winter RJ, Isgum I, Lessmann N, Velthuis BK, Pasterkamp G, Mosterd A, Timmers L, de Kleijn DPV (2021) High levels of osteoprotegerin are associated with coronary artery calcification in patients suspected of a chronic coronary syndrome. Sci Rep 11:18946. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-98177-4
Arida A, Nezos A, Papadaki I, Sfikakis PP, Mavragani CP (2022) Osteoprotegerin and MTHFR gene variations in rheumatoid arthritis: association with disease susceptibility and markers of subclinical atherosclerosis. Sci Rep 12:9534. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-13265-3
Shrivastava AK, Singh HV, Raizada A, Singh SK (2015) C-reactive protein, inflammation and coronary heart disease. Egypt Heart J 67(2):89–97. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ehj.2014.11.005
Rhodes B, Fürnrohr BG, Vyse TJ (2011) C-reactive protein in rheumatology: biology and genetics. Nat Rev Rheumatol 7:282–289. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2011.37
Devaraj S, Yun JM, Adamson G, Galvez J, Jialal I (2009) C-reactive protein impairs the endothelial glycocalyx resulting in endothelial dysfunction. Cardiovasc Res 84(3):479–484. https://doi.org/10.1093/cvr/cvp249
Köhler M, Kaufmann I, Briegel J, Jacob M, Goeschl J, Rachinger W, Thiel M, Rehm M (2011) The endothelial glycocalyx degenerates with increasing sepsis severity. Crit Care 15:P22. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc10391
Bian F, Yang XY, Xu G, Zheng T, Jin S (2019) CRP-induced NLRP3 inflammasome activation increases LDL transcytosis across endothelial cells. Front Pharmacol 10:40. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2019.00040
Xiong Y, Cai M, Xu Y, Dong P, Chen H, He W, Zhang J (2022) Joint together: the etiology and pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Front Immunol 13:996103. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.996103
Yin H, Liu N, Sigdel KR, Duan L (2022) Role of NLRP3 inflammasome in rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 13:931690. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.931690
Qu J, Cheng Y, Wu W, Yuan L, Liu X (2021) Glycocalyx impairment in vascular disease: focus on inflammation. Front Cell Dev Biol 9:730621. https://doi.org/10.3389/fcell.2021.730621
Stark K, Massberg S (2021) Interplay between inflammation and thrombosis in cardiovascular pathology. Nat Rev Cardiol 18:666–682. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41569-021-00552-1
Huang HS, Chang HH (2012) Platelets in inflammation and immune modulations: functions beyond hemostasis. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 60:443–451. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00005-012-0193-y
Nieuwdorp M, Meuwese MC, Vink H, Hoekstra JB, Kastelein JJ, Stroes ES (2005) The endothelial glycocalyx: a potential barrier between health and vascular disease. Curr Opin Lipidol 16:507–511. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mol.0000181325.08926.9c
Barrett TJ (2020) Macrophages in atherosclerosis regression. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol 40:20–33. https://doi.org/10.1161/ATVBAHA.119.312802
Udalova IA, Mantovani A, Feldmann M (2016) Macrophage heterogeneity in the context of rheumatoid arthritis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 12:472–485. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2016.91
Evangelatos G, Fragoulis GE, Koulouri V, Lambrou GI (2019) MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis: from pathogenesis to clinical impact. Autoimmun Rev 18(11):102391. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102391
Motta F, Pederzani A, Carena MC, Ceribelli A, Wordsworth PB, De Santis M, Selmi C, Vecellio M (2021) MicroRNAs in axial spondylarthritis: an overview of the recent progresses in the field with a focus on ankylosing spondylitis and psoriatic arthritis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 23:59. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-021-01027-5
Romaine SP, Tomaszewski M, Condorelli G, Samani NJ (2015) MicroRNAs in cardiovascular disease: an introduction for clinicians. Heart 101:921–928. https://doi.org/10.1136/heartjnl-2013-305402
O’Brien J, Hayder H, Zayed Y, Peng C (2018) Overview of microRNA biogenesis, mechanisms of actions, and circulation. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne) 9:402. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2018.00402
Palte MJ, Raines RT (2012) Interaction of nucleic acids with the glycocalyx. J Am Chem Soc 134:6218–6223. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja2106477
Tanase DM, Gosav EM, Petrov D, Teodorescu DS, Buliga-Finis ON, Ouatu A, Tudorancea I, Rezus E, Rezus C (2022) MicroRNAs (miRNAs) in cardiovascular complications of rheumatoid arthritis (RA): what is new? Int J Mol Sci 23:52–54. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms23095254
Sileno S, Beji S, D’Agostino M, Carassiti A, Melillo G, Magenta A (2021) MicroRNAs involved in psoriasis and cardiovascular diseases. Vasc Biol 3(1):R49–R68. https://doi.org/10.1530/VB-21-0007
Gunter S, Michel FS, Fourie SS, Singh M, le Roux R, Manilall A, Mokotedi LP, Millen AME (2022) The effect of TNF-α inhibitor treatment on microRNAs and endothelial function in collagen induced arthritis. PLoS One. 17(2):e0264558. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0264558
Schmitz B, Niehues H, Lenders M, Thorwesten L, Klose A, Krüger M, Brand E, Brand SM (2019) Effects of high-intensity interval training on microvascular glycocalyx and associated microRNAs. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol 316:H1538–H1551. https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpheart.00751.2018
Wang Y, Yu H, He J (2020) Role of dyslipidemia in accelerating inflammation, autoimmunity, and atherosclerosis in systemic lupus erythematosus and other autoimmune diseases. Discov Med 30(159):49–56
Harding IC, Mitra R, Mensah SA et al (2019) Glycocalyx degradation induces a proinflammatory phenotype and increased leukocyte adhesion in cultured endothelial cells under flow. PLoS One 14:e0220567. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0220567
Mensah SA, Cheng MJ, Homayoni H et al (2021) Disturbed flow induces a sustained, stochastic NF-κB activation which communicates substrate topography in endothelial cells. Sci Rep 11:16526. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-95953-y
Moore KJ, Sheedy FJ, Fisher EA (2013) Macrophages in atherosclerosis: a dynamic balance. Nat Rev Immunol 13:709–721. https://doi.org/10.1038/nri3520
Arjuman A, Chandra NC (2015) Differential pro-inflammatory responses of TNF-α receptors (TNFR1 and TNFR2) on LOX-1 signalling. Mol Biol Rep 42:1039–1047. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11033-014-3841-y
Tan KT, Lip GY (2005) The potential role of platelet microparticles in atherosclerosis. Thromb Haemost 94:488–492. https://doi.org/10.1160/TH05-03-0201
Piccin A, Murphy WG, Smith OP (2007) Circulating microparticles: pathophysiology and clinical implications. Blood Rev 21:157–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.blre.2006.09.001
Boilard E, Nigrovic PA, Larabee K, Watts GF, Coblyn JS, Weinblatt ME (2010) Platelets amplify inflammation in arthritis via collagen-dependent microparticle production. Science 327:580–583. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1181928
Curtis AM, Edelberg J, Jonas R, Rogers WT, Moore JS, Syed W, Mohler ER (2013) Endothelial microparticles: sophisticated vesicles modulating vascular function. Vasc Med 18(204):214. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X13499773
Chirinos JA, Zambrano JP, Virani SS, Jimenez JJ, Jy W, Ahn E, Horstman LL, Castellanos A, Myerburg RJ, Ahn YS (2005) Correlation between apoptotic endothelial microparticles and serum interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein in healthy men. Am J Cardiol 95:1258–1260. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjcard.2005.01.063
Loyer X, Vion AC, Tedgui A, Boulanger CM (2014) Microvesicles as cell-cell messengers in cardiovascular diseases. Circ Res 114(2):345–353. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCRESAHA.113.300858
Lukasik M, Rozalski M, Luzak B, Michalak M, Ambrosius W, Watala C, Kozubski W (2013) Enhanced platelet-derived microparticle formation is associated with carotid atherosclerosis in convalescent stroke patients. Platelets 24:63–70. https://doi.org/10.3109/09537104.2011.654292
Priou P, Gagnadoux F, Tesse A, Mastronardi ML, Agouni A, Meslier N et al (2010) Endothelial dysfunction and circulating microparticles from patients with obstructive sleep apnea. Am J Pathol 177(2):974–983. https://doi.org/10.2353/ajpath.2010.091252
Weber A, Köppen HO, Schrör K (2000) Platelet-derived microparticles stimulate coronary artery smooth muscle cell mitogenesis by a PDGF-independent mechanism. Thromb Res 98:461–466. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0049-3848(00)00192-4
Mallat Z, Hugel B, Ohan J, Lesèche G, Freyssinet JM, Tedgui A (1999) Shed membrane microparticles with procoagulant potential in human atherosclerotic plaques: a role for apoptosis in plaque thrombogenicity. Circulation 99:348–353. https://doi.org/10.1161/01.cir.99.3.348
Burger D, Schock S, Thompson CS, Montezano AC, Hakim AM, Touyz RM (2013) Microparticles: biomarkers and beyond. Clin Sci (Lond) 124:423–441. https://doi.org/10.1042/CS20120309
Curtis AM, Edelberg J, Jonas R, Rogers WT, Moore JS, Syed W (2013) Mohler EREndothelial microparticles: sophisticated vesicles modulating vascular function. Vasc Med. 18:204–214. https://doi.org/10.1177/1358863X13499773
Szotowski B, Antoniak S, Goldin-Lang P et al (2007) Antioxidative treatment inhibits the release of thrombogenic tissue factor from irradiation- and cytokine-induced endothelial cells. Cardiovasc Res 73(4):806–812. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cardiores.2006.12.018
Vince RV, Chrismas B, Midgley AW, McNaughton LR, Madden LA (2009) Hypoxia mediated release of endothelial microparticles and increased association of S100A12 with circulating neutrophils. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2:2–6. https://doi.org/10.4161/oxim.2.1.7611
Krajewska-Włodarczyk M, Owczarczyk-Saczonek A, Żuber Z, Wojtkiewicz M, Wojtkiewicz J (2019) Role of microparticles in the pathogenesis of inflammatory joint diseases. Int J Mol Sci 20:5453. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20215453
Knijff-Dutmer EA, Koerts J, Nieuwland R, Kalsbeek-Batenburg EM, van de Laar MA (2002) Elevated levels of platelet microparticles are associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 46:1498–1503. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10312
Atehortúa L, Rojas M, Vásquez G, Muñoz-Vahos CH, Vanegas-García A, Posada-Duque RA, Castaño D (2019) Endothelial activation and injury by microparticles in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 21:34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1796-4
Pamuk GE, Vural O, Turgut B, Demir M, Pamuk ON, Cakir N (2008) Increased platelet activation markers in rheumatoid arthritis: are they related with subclinical atherosclerosis? Platelets 19:146–154
Barbati C, Vomero M, Colasanti T, Diociaiuti M, Ceccarelli F, Ferrigno S, Finucci A, Miranda F, Novelli L, Perricone C, Spinelli FR, Truglia S, Conti F, Valesini G, Alessandri C (2018) TNFα expressed on the surface of microparticles modulates endothelial cell fate in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 20:273. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1768-8
Sari I, Bozkaya G, Kirbiyik H, Alacacioglu A, Ates H, Sop G, Can G, Taylan A, Piskin O, Yildiz Y, Akkoc N (2012) Evaluation of circulating endothelial and platelet microparticles in men with ankylosing spondylitis. J Rheumatol 39:594–599. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.111073
Pelletier F, Garnache-Ottou F, Biichlé S, Vivot A, Humbert P, Saas P, Seillès E, Aubin F (2014) Effects of anti-TNF-α agents on circulating endothelial-derived and platelet-derived microparticles in psoriasis. Exp Dermatol 23:924–925. https://doi.org/10.1111/exd.12551
Papadavid E, Diamanti K, Spathis A, Varoudi M, Andreadou I, Gravanis K, Theodoropoulos K, Karakitsos P, Lekakis J, Rigopoulos D, Ikonomidis I (2016) Increased levels of circulating platelet-derived microparticles in psoriasis: possible implications for the associated cardiovascular risk. World J Cardiol 8:667–675. https://doi.org/10.4330/wjc.v8.i11.667
Wang GH, Ma KL, Zhang Y, Hu ZB, Liu L, Lu J, Chen PP, Lu CC, Ruan XZ, Liu BC (2019) Platelet microparticles contribute to aortic vascular endothelial injury in diabetes via the mTORC1 pathway. Acta Pharmacol Sin 40:468–476. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41401-018-0186-4
Labitigan M, Bahče-Altuntas A, Kremer JM, Reed G, Greenberg JD, Jordan N, Putterman C, Broder A (2014) Higher rates and clustering of abnormal lipids, obesity, and diabetes mellitus in psoriatic arthritis compared with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Care Res 66:600–607. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.22185
Ko J, Kang HJ, Kim DA, Kim MJ, Ryu ES, Lee S, Ryu JH, Roncal C, Johnson RJ, Kang DH (2019) Uric acid induced the phenotype transition of vascular endothelial cells via induction of oxidative stress and glycocalyx shedding. FASEB J 33:13334–13345. https://doi.org/10.1096/fj.201901148R
Thorarensen SM, Lu N, Ogdie A, Gelfand JM, Choi HK, Love TJ (2017) Physical trauma recorded in primary care is associated with the onset of psoriatic arthritis among patients with psoriasis. Ann Rheum Dis 76:521–525. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209334
Puig L, Costanzo A, Muñoz-Elías EJ, Jazra M, Wegner S, Paul CF, Conrad C (2022) The biological basis of disease recurrence in psoriasis: a historical perspective and current models. Br J Dermatol 186:773–781. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.20963
Gabel CK, Chakrala T, Dobry AS, Garza-Mayers AC, Ko LN, Nguyen ED, Shah R, St John J, Nigwekar SU, Kroshinsky D (2021) The Koebner phenomenon may contribute to the development of calciphylaxis: a case series. JAAD Case Rep 13:57–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2021.04.016
Gao X, Lv T, Li G, Tse G, Liu T (2022) Association between atherosclerosis-related cardiovascular disease and uveitis: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Diagnostics (Basel) 12:3178. https://doi.org/10.3390/diagnostics12123178
Ernst D, Baerlecken NT, Schmidt RE, Witte T (2014) Large vessel vasculitis and spondyloarthritis: coincidence or associated diseases? Scand J Rheumatol 43:246–248. https://doi.org/10.3109/03009742.2013.850737
Atzeni F, AlciatiA, (2023) Cardiovascular risk in systemic inflammatory arthritis. J Clin Med 12:2779. https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm12082779
Acknowledgements
Figures were created with BioRender.com.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors have played a substantial role in shaping the study’s conception and design. They have actively engaged in acquiring and analyzing the data, as well as interpreting the results. Furthermore, the authors have collectively contributed to both the initial draft and subsequent critical revisions of the manuscript, providing their invaluable insights. Each author has granted their final approval for the manuscript’s submission to this journal, demonstrating their commitment to taking responsibility for all aspects of the work and being accountable for any potential concerns that may arise. Lastly, all contributing authors have meticulously reviewed and endorsed the final version of the manuscript and take full responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
This article is part of the Topical Collection on Cardiovascular Issues in Rheumatic Diseases
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Angelov, A.K., Markov, M., Ivanova, M. et al. The genesis of cardiovascular risk in inflammatory arthritis: insights into glycocalyx shedding, endothelial dysfunction, and atherosclerosis initiation. Clin Rheumatol 42, 2541–2555 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06738-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06738-x