Abstract
Introduction
The inflammatory involvement of joints and tendons is common in Systemic Sclerosis (SSc). Ultrasonography (US) is a non-invasive tool commonly applied for the assessment of the main inflammatory arthropathies and could be also used in identifying pathological features in SSc patients, even without clinical evidence of joint complaint. So, the aim of this study was to assess the prevalence of US pathological features in a cohort of SSc patients and assessed the role of US in the detection of subclinical joint involvement.
Methods
In this retrospective study, we collected data about the prevalence of US pathological features at the level of hands and wrists in a cohort of patients with a definite diagnosis of SSc, submitted to an ultrasound examination of hands and wrists according to the clinician’s opinion, with or without joint involvement symptoms, in order to assess the US ability in detecting subclinical inflammatory signs in SSc patients.
Results
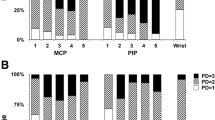
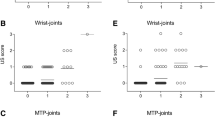
In total, 47.5% of patients reported at least one US pathological feature. The most common was synovial hypertrophy (62.1%). Other assessed lesions were effusion (48%), tenosynovitis (37.9%), power Doppler (PD) signal (31.0%), and erosions (0.7%). Effusion and PD signal appeared significantly higher in symptomatic patients, with a p<0.01 and p=0.045, respectively.
Conclusions
In this cohort of SSc subjects, almost the half of the US-positive patients were clinically asymptomatic. Therefore, the application of US could be useful to detect the musculoskeletal involvement of SSc patients, a potential markers of disease severity. Further studies are required to assess the role of US in monitoring SSc patients.
Key Points • The inflammatory involvement of joints and/or tendons is common in systemic sclerosis (SSc) but could be partially covered by other disease features. • Among the diagnostic methods able to increase the sensitivity of the musculoskeletal evaluation, Ultrasonography (US) is one of the most promising to reveal subclinical inflammation and predict the joint damage progression. • We retrospectively investigated the prevalence of US pathological features in a cohort of SSc patients, with or without symptoms of joint involvement, assessing the role of US in the detection of subclinical joint involvement. • We found that joint and tendon involvement, a potential marker of disease severity, is common in SSc. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Smith V, Scirè CA, Talarico R, Airo P, Alexander T, Allanore Y, Bruni C, Codullo V, Dalm V, De Vries-Bouwstra J, Della Rossa A (2018) Systemic sclerosis: state of the art on clinical practice guidelines. RMD Open 4(Suppl 1):e000782. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2018-000782
Lambrecht V, Cutolo M, De Keyser F, Decuman S, Ruaro B, Sulli A, Deschepper E, Smith V (2016) Reliability of the quantitative assessment of peripheral blood perfusion by laser speckle contrast analysis in a systemic sclerosis cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 75(6):1263–1264. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2015-208857
Avouac J, Walker U, Tyndall A, Kahan A, Matucci-Cerinic M, Allanore Y (2010) Characteristics of joint involvement and relationships with systemic inflammation in systemic sclerosis: results from the EULAR Scleroderma Trial and Research Group (EUSTAR) database. J Rheumatol 37(7):1488–1501. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.091165
Elhai M, Guerini H, Bazeli R, Avouac J, Freire V, Drapé JL, Kahan A, Allanore Y (2012) Ultrasonographic hand features in systemic sclerosis and correlates with clinical, biologic, and radiographic findings. Arthritis Care Res 64(8):1244–1249. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.21668
Cuomo G, Zappia M, Abignano G, Iudici M, Rotondo A, Valentini G (2009) Ultrasonographic features of the hand and wrist in systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 48(11):1414–1417. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep250
Iagnocco A, Vavala C, Vasile M, Stefanantoni K, Valesini G, Riccieri V (2013) Power Doppler ultrasound of the hand and wrist joints in systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 31(2):89–95
Lescoat A, Ballerie A, Belhomme N, Cazalets C, de Carlan M, Droitcourt C, Perdriger A, Jégo P, Coiffier G (2018) Synovial involvement assessed by power Doppler ultra-sonography in systemic sclerosis: results of a cross-sectional study. Rheumatology 57(11):2012–2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key214
Freire V, Bazeli R, Elhai M, Campagna R, Pessis É, Avouac J, Allanore Y, Drapé JL, Guérini H (2013) Hand and wrist involvement in systemic sclerosis: US features. Radiology 269(3):824–830. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13121994
Sandler RD, Matucci-Cerinic M, Hughes M (2020) Musculoskeletal hand involvement in systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 50(2):329–334. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2019.11.003
Hughes M, Bruni C, Cuomo G, Delle Sedie A, Gargani L, Gutierrez M, Lepri G, Ruaro B, Santiago T, Suliman Y, Watanabe S, Iagnocco A, Furst D, Bellando-Randone S (2021) The role of ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: On the cutting edge to foster clinical and research advancement. J Scleroderma Relat Disord 6(2):123–132. https://doi.org/10.1177/2397198320970394
Lescoat A, Ballerie A, Belhomme N, Cazalets C, de Carlan M, Droitcourt C, Perdriger A, Jégo P, Coiffier G (2018) Synovial involvement assessed by power Doppler ultra-sonography in systemic sclerosis: results of a cross-sectional study. Rheumatology 57(11):2012–2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/key214
Bellocchi C, Chung A, Volkmann ER (2022) Predicting the Progression of Very Early Systemic Sclerosis: Current Insights. Open Access Rheumatol 14:171–186. https://doi.org/10.2147/OARRR.S285409
Terslev L, Ellegaard K, Christensen R, Szkudlarek M, Schmidt WA, Jensen PS, Bliddal H, Torp-Pedersen S (2012) Head-to-head comparison of quantitative and semi-quantitative ultrasound scoring systems for rheumatoid arthritis: reliability, agreement and construct validity. Rheumatology 51(11):2034–2038. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kes124
Terslev L, Naredo E, Aegerter P, Wakefield RJ, Backhaus M, Balint P, Bruyn GAW, Iagnocco A, Jousse-Joulin S, Schmidt WA, Szkudlarek M, Conaghan PG, Filippucci E, D'Agostino MA (2017) Scoring ultrasound synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis: a EULAR-OMERACT ultrasound taskforce-Part 2: reliability and application to multiple joints of a standardised consensus-based scoring system. RMD Open 3(1):e000427. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000427
Płaza M, Nowakowska-Płaza A, Pracoń G, Sudoł-Szopińska I (2016) Role of ultrasonography in the diagnosis of rheumatic diseases in light of ACR/EULAR guidelines. J Ultrason 16(64):55–64. https://doi.org/10.15557/JoU.2016.0006
Offidani A, Cellini A, Valeri G, Giovagnoni A (1998) Subclinical joint involvement in psoriasis: magnetic resonance imaging and X-ray findings. Acta Derm Venereol 78(6):463–465. https://doi.org/10.1080/000155598442809
Girolomoni G, Gisondi P (2009) Psoriasis and systemic inflammation: underdiagnosed enthesopathy. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 23(Suppl 1):3–8. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2009.03361.x
Ruaro B, Soldano S, Smith V, Paolino S, Contini P, Montagna P, Pizzorni C, Casabella A, Tardito S, Sulli A, Cutolo M (2019) Correlation between circulating fibrocytes and dermal thickness in limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis patients: a pilot study. Rheumatol Int 39(8):1369–1376. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-019-04315-7
Kowal-Bielecka O, Fransen J, Avouac J, Becker M, Kulak A, Allanore Y, Distler O, Clements P, Cutolo M, Czirjak L, Damjanov N (2017) Update of EULAR recommendations for the treatment of systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 76(8):1327–1339. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2016-209909
Littlejohn EA, Monrad SU (2018) Early diagnosis and treatment of rheumatoid arthritis. Prim Care 45(2):237–255. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pop.2018.02.010
Backhaus M, Burmester GR, Gerber T, Grassi W, Machold KP, Swen WA, Wakefield RJ, Manger B (2001) Guidelines for musculoskeletal ultrasound in rheumatology. Ann Rheum Dis 60(7):641–649. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.60.7.641
Bruyn GA, Iagnocco A, Naredo E, Balint PV, Gutierrez M, Hammer HB, Collado P, Filippou G, Schmidt WA, Jousse-Joulin S, Mandl P (2019) OMERACT definitions for ultrasonographic pathologies and elementary lesions of rheumatic disorders 15 years on. J Rheumatol 46(10):1388–1393. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.181095
Boylan M (2020) Should ultrasound be used routinely in the diagnosis of rheumatoid arthritis? Ir J Med Sci 189(2):735–748. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11845-019-02096-3
Doré A, Lucas M, Ivanco D, Medsger TA Jr, Domsic RT (2013) Significance of palpable tendon friction rubs in early diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Care Res 65(8):1385–1389. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.21964
Khanna PP, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Maranian P, Indulkar L, Khanna D (2010) Tendon friction rubs in early diffuse systemic sclerosis: prevalence, characteristics and longitudinal changes in a randomized controlled trial. Rheumatology 49(5):955–959. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep464
Avouac J, Walker UA, Hachulla E, Riemekasten G, Cuomo G, Carreira PE, Caramaschi P, Ananieva LP, Matucci-Cerinic M, Czirjak L, Denton C (2016) Joint and tendon involvement predict disease progression in systemic sclerosis: a EUSTAR prospective study. Ann Rheum Dis 75(1):103–109. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-205295
Bassel M, Hudson M, Taillefer SS, Schieir O, Baron M, Thombs BD (2011) Frequency and impact of symptoms experienced by patients with systemic sclerosis: results from a Canadian National Survey. Rheumatology 50(4):762–767. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keq310
La Montagna G, Sodano A, Capurro V, Malesci D, Valentini G (2005) The arthropathy of systemic sclerosis: a 12 month prospective clinical and imaging study. Skeletal Radiol 34(1):35–41. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-004-0830-6
Ingegnoli F, Galbiati V, Zeni S, Meani L, Zahalkova L, Lubatti C, Soldi A, Paresce E, Murgo A, Crapanzano C, Fantini F (2007) Use of antibodies recognizing cyclic citrullinated peptide in the differential diagnosis of joint involvement in systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 26(4):510–514. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-006-0313-3
Ostojic P, Damjanov N (2008) Indices of the Scleroderma Assessment Questionnaire (SAQ) can be used to demonstrate change in patients with systemic sclerosis over time. Joint Bone Spine 75(3):286–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2007.06.014
Ostojić P, Damjanov N (2006) Different clinical features in patients with limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 25(4):453–457. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-005-0041-0
Malcarne VL, Hansdottir I, McKinney A, Upchurch R, Greenbergs HL, Henstorf GH, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Weisman MH (2007) Medical signs and symptoms associated with disability, pain, and psychosocial adjustment in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 34(2):359–367
Rannou F, Poiraudeau S, Berezné A, Baubet T, Le-Guern V, Cabane J, Guillevin L, Revel M, Fermanian J, Mouthon L (2007) Assessing disability and quality of life in systemic sclerosis: construct validities of the Cochin Hand Function Scale, Health Assessment Questionnaire (HAQ), Systemic Sclerosis HAQ, and Medical Outcomes Study 36-Item Short Form Health Survey. Arthritis Rheum 57(1):94–102. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.22468
Mouthon L, Rannou F, Bérezné A, Pagnoux C, Guilpain P, Goldwasser F, Revel M, Guillevin L, Fermanian J, Poiraudeau S (2008) Patient preference disability questionnaire in systemic sclerosis: a cross-sectional survey. Arthritis Rheum 59(7):968–973. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.23819
Skare TL, Toebe BL, Boros C (2011) Hand dysfunction in scleroderma patients. Sao Paulo Med J 129(5):357–360. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1516-31802011000500012
Hubac J, Gilson M, Gaudin P, Clay M, Imbert B, Carpentier P (2020) Ultrasound prevalence of wrist, hand, ankle and foot synovitis and tenosynovitis in systemic sclerosis, and relationship with disease features and hand disability. Joint Bone Spine 87 (3):229-233. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2020.01.011.
Acknowledgements
Editorial assistance was provided by Simonetta Papa, PhD, Valentina Attanasio and Aashni Shah (Polistudium SRL, Milan, Italy). This assistance was supported by internal funds.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethics
The study was conducted in accordance with the ethical standards as laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments and within the protocol notified to the Ethics Committee Milano Area 3 (register number 427-09201). A written informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Gagliardi, C., Adinolfi, A., Belloli, L. et al. Sclerodermic hand: a retrospective study on the role of ultrasonography in the detection of subclinical joint involvement. Clin Rheumatol 42, 2873–2879 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06668-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06668-8