Abstract
Objective
To investigate whether there is a difference in the efficacy of intra-articular injection of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) inhibitor and triamcinolone acetonide (HA) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients with recurrent synovitis after the first intra-articular injection of HA.
Methods
RA patients who relapsed 12 weeks after the first HA treatment were enrolled in this study. After joint cavity extraction, recombinant human TNF receptor-antibody fusion protein (TNFR:FC) (25 mg or 12.5 mg) or HA (1 ml or 0.5 ml) was injected then. The changes in the visual analog scale (VAS), joint swelling index, and joint tenderness index before and 12 weeks after reinjection were compared and analyzed. The changes in synovial thickness, synovial blood flow, and fluid dark zone depth before and after reinjection were observed by ultrasound.
Results
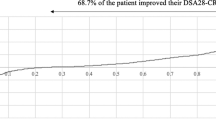
Forty-two RA patients were enrolled, including 11 males and 31 females, with an average age of 46.79 ± 12.61 years and an average disease duration of 7.76 ± 5.44 years. After 12 weeks of intra-articular injection of HA or TNFR:FC, the VAS scores were significantly lower than those before treatment (P < 0.01). After 12 weeks of injection, the scores of the joint swelling index and tenderness index in both groups were significantly decreased compared with those before treatment. There was no significant difference in synovial thickness under ultrasound in the HA group before and after injection, while the synovial thickness in the TNFR:FC group was significantly improved after 12 weeks (P < 0.01). After 12 weeks of injection, the grade of synovial blood flow signal in both groups decreased significantly compared with that before treatment, especially in the TNFR:FC group. After 12 weeks of injection, the depth of the liquid dark area under ultrasound decreased significantly in the HA group and TNFR:FC group compared with that before treatment (P < 0.01).
Conclusion
Intra-articular injection of a TNF inhibitor is an effective method for the treatment of recurrent synovitis after conventional hormone therapy. Compared with HA treatment, it can reduce synovial thickness.
Key Points • Intra-articular injection of a TNF inhibitor is an effective method for the treatment of recurrent synovitis after conventional hormone therapy. • Compared with HA treatment, intra-articular injection of biological agents combined with glucocorticoids can not only relieve joint pain but also significantly inhibit joint swelling. • Compared with HA treatment, intra-articular injection of biological agents combined with glucocorticoids cannot only improve synovial inflammation but also inhibit synovial proliferation. • For the treatment of refractory RA synovitis, biological agents combined with glucocorticoid injection are an effective and safe option. |



Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated and analyzed of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Du F, Lu LJ, Teng JL, Shen N, Ye P, Bao CD (2012) T-614 alters the production of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP-1 andMMP-3) and inhibits the migratory expansion of rheumatoid synovial fibroblasts, in vitro. Int Immunopharmacol 13(1):54–60
McInnes IB, O’Dell JR (2010) State-of-the-art: rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(11):1898–1906
Cheng OT, Souzdalnitski D, Vrooman B, Cheng J (2012) Evidence-based knee injections for the management of arthritis. Pain Med 13(6):740–753
Liang D, Huang F (2009) Intra-articular injection of tumor necrosis factor-a antagonist for inflammatory arthropathy. Chin J Rheumatol 13(1):54–56
Rudan I, Sidhu S, Papana A et al (2015) Prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis in low- and middle-income countries: a systematic review and analysis. J Glob Health 5(1):10409
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ et al (2010) 2010 rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 69(9):1580–1588
Rezaei H, Af KE, Hammer HB et al (2017) Analysis of correlation and causes for discrepancy between quantitative and semi-quantitative Doppler scores in synovitis in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 56(2):255–262
Hajialilo M, Ghorbanihaghjo A, Valaee L et al (2016) A double-blind randomized comparative study of triamcinolone hexacetonide and dexamethasone intra-articular injection for the treatment of knee joint arthritis in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 35(12):2887–2891
Baker JF, Pullman-Mooar S, Ibrahim S (2014) Management of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53(10):1721–1722
Evans CH, Kraus VB, Setton LA (2014) Progress in intra-articular therapy. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10(1):11–22
Rocha RH, Natour J, Dos Santos RM, Furtado RNV (2019) Time effect of intra-articular injection with triamcinolone hexacetonide and its correlations: a case-control prospective 12-month study. Am J Phys Med Rehabil 98(10):872–878
Vannabouathong C, Del Fabbro G, Sales B, Smith C, Li CS, Yardley D, Bhandari M, Petrisor BA (2018) Intra-articular injections in the treatment of symptoms from ankle arthritis: a systematic review. Foot Ankle Int 39(10):1141–1150
Weitoft T, Rönnelid J, Knight A, Lysholm J, Saxne T, Larsson A (2014) Outcome predictors of intra-articular glucocorticoid treatment for knee synovitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis - a prospective cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 16(3):R129
Habib GS (2009) Systemic effects of intra-articular corticosteroids. Clin Rheumatol 28(7):749–756
Taliaferro K, Crawford A, Jabara J et al (2018) Intraocular pressure increases after intraarticular knee injection with triamcinolone but not hyaluronic acid. Clin Orthop Relat Res 476(7):1420–1425
Habib GS, Saliba W, Nashashibi M (2010) Local effects of intra-articular corticosteroids. Clin Rheumatol 29(4):347–356
Bello S, Bonali C, Serafino L et al (2014) Intra-articular therapy with tumor necrosis factor-α antagonists: an update. Reumatismo 65(6):257–263
Bliddal H, Rosetzsky A, Schlichting P, Weidner MS, Andersen LA, Ibfelt HH, Christensen K, Jensen ON, Barslev J (2000) A randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over study of ginger extracts and ibuprofen in osteoarthritis. Osteoarthr Cartil 8(1):9–12
Liang D, Huang F, Zhang J, Yang C, Zhang H, Guo J, Zhao Z (2010) A randomized, single-blind, parallel, controlled clinical study of a single knee cavity injection of etanercept in the treatment of inflammatory knee osteoarthritis. Chin J Rheumatol 49(11):930–9348
Osborn TG (2002) Intra-articular etanrcept versus saline in rheumatoid arthritis:a single injection double-blind placebo controlled study. Arthritis Rheum 46(Supp1):s518
Naredo E, Iagnocco A (2016) One year in review: ultrasound in arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 34(1):1–10
Nordberg LB, Lillegraven S, Aga AB et al (2018) The impact of ultrasound on the use and efficacy of intraarticular glucocorticoid injections in early rheumatoid arthritis: secondary analyses from a randomized trial examining the benefit of ultrasound in a clinical tight control regime. Arthritis Rheumatol 70(8):1192–1199
van Kuijk AW, Reinders-Blankert P, Smeets TJ, Dijkmans BA, Tak pp. (2006) Detailed analysis of the cell infiltrate and the expression of mediators of synovial inflammation and joint destruction in the synovium of patients with psoriatic arthritis: implications for treatment. Ann Rheum Dis 65(12):1551–1557
Tracey D, Klareskog L, Sasso EH, Salfeld JG, Tak PP (2008) Tumor necrosis factor antagonist mechanisms of action: a comprehensive review. Pharmacol Ther 117(2):244–279
Fiocco U, Sfriso P, Oliviero F et al (2013) Blockade of intra-articular TNF in peripheral spondyloarthritis: its relevance to clinical scores, quantitative imaging and synovial fluid and synovial tissue biomarkers. Joint Bone Spine 80(2):165–170
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Guohua Yuan and Yong Chen designed the study; Jiali Yuan wrote the paper; Jiali Yuan performed and analyzed the experiments; Yong Chen, Jiali Yuan, and Yan Ma contributed to the editing of the manuscript. All authors reviewed the results and approved the final version of the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All animal care and experimental procedures complied with the Animal Management Regulations of the Ministry of Health, China (Document No. 55, 2001) and were approved by the Ethics Committee of The People's Hospital of Jianyang [2022056].
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, Y., Yuan, J., Cai, Z. et al. Efficacy of tumor necrosis factor inhibitor combined with intra-articular injection of triamcinolone acetonide in the treatment of refractory rheumatoid arthritis synovitis: a retrospective study. Clin Rheumatol 42, 1793–1799 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06530-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06530-x