Abstract
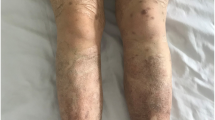
Takayasu arteritis (TA) is an uncommon chronic granulomatous large-vessel vasculitis affecting the aorta and its branches. Pyoderma gangrenosum (PG) is a chronic neutrophilic dermatosis characterized by rapidly developing painful ulcers. The association of PG with TA is relatively uncommon. We report a case of a 22-year-old lady with a history of recurrent pyoderma lesions for 4 months following which she developed right upper limb claudication. She underwent contrast-enhanced magnetic resonance angiography of the aorta and its branches and was initially diagnosed with type IIb TA. She was put on prednisolone and methotrexate but had a major relapse with new-onset lower limb claudication despite an appropriate course of immunosuppression. She was planned for tocilizumab infusion 8 mg/kg intravenous every 4 weeks. Following the first dose of tocilizumab, her vascular symptoms improved but she had a flare of PG. This was followed by another flare after the second dose. She was switched to tofacitinib which led to sustained remission of her TA activity and healing of her skin lesions, and the prednisolone dose could be reduced to 5 mg daily over the next 1 year. Various immunosuppressives were used to date for treating PG in TA. However, tofacitinib is being reported for the first time in literature for treating PG and controlling TA activity. The paradoxical flare of PG with tocilizumab is quite uncommon and is also reported in our case with literature review.


Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
The authors confirm that the data supporting this study are available within the article.
References
Zhang X, Jiao Y (2019) Takayasu arteritis with pyoderma gangrenosum: case reports and literature review. BMC Rheumatol 3:45. https://doi.org/10.1186%2Fs41927-019-0098-z
Acharya N, Chattopadhyay A, Das A, Jain S (2020) Takayasu arteritis with pyoderma gangrenosum and superficial thrombophlebitis. The Lancet Rheumatol 2(8):5-e510. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2665-9913(20)30088-6
Choong DJ, Ng JL, Vinciullo C (2021) Pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Takayasu’s arteritis in a young Caucasian woman and response to biologic therapy with tocilizumab. JAAD Case Rep 9:4–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2020.12.034
Maz M, Chung SA, Abril A, Langford CA, Gorelik M, Guyatt G et al (2021) American College of Rheumatology/Vasculitis Foundation Guideline for the Management of Giant Cell Arteritis and Takayasu Arteritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 73(8):1349–1365. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.41774
Borgia F, Sutera D, Spagnolo A, Mazza F, Bertino L, Cannavò SP, Gallizzi R (2021) Onset of pyoderma gangrenosum after tocilizumab therapy for Takayasu arteritis: a new undescribed paradoxical reaction. Br J Clin Pharmacol 87:3378–3379. https://doi.org/10.1111/bcp.14756
Maverakis E, Marzano AV, Le ST, Callen JP, Brüggen MC, Guenova E, Dissemond J, Shinkai K, Langan SM (2020) Pyoderma gangrenosum Nat Rev Dis Primers 6(1):81. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41572-020-0213-x
Guarino AD, Testa A, Mormile I, Imperatore N, Granata F, Rispo A, De Paulis A, Castiglione F (2021) Crohn’s disease and Takayasu’s arteritis: are they associated? Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 25(3):1472–1484. https://doi.org/10.26355/eurrev_202102_24855
Stamatis P (2020) Giant cell arteritis versus Takayasu arteritis: an update. Mediterr J Rheumatol. 31(2):174–182. https://doi.org/10.31138/mjr.31.2.174
Hellmich B, Agueda A, Monti S, Buttgereit F, de Boysson H, Brouwer E et al (2020) 2018 Update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of large vessel vasculitis. Ann Rheum Dis 79(1):19–30. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-215672
Nakaoka Y, Isobe M, Takei S, Tanaka Y, Ishii T, Yokota S, Nomura A, Yoshida S, Nishimoto N (2018) Efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in patients with refractory Takayasu arteritis: results from a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, phase 3 trial in Japan (the TAKT study). Ann Rheum Dis 77:348–354. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211878
Nakaoka Y, Isobe M, Tanaka Y, Ishii T, Ooka S, Niiro H et al (2020) Long-term efficacy and safety of tocilizumab in refractory Takayasu arteritis: final results of the randomized controlled phase 3 TAKT study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59:2427–2434. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez630
Misra DP, Rathore U, Patro P, Agarwal V, Sharma A (2021) Disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs for the management of Takayasu arteritis–a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Rheumatol 40(11):4391–4416. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05743-2
Mekinian A, Comarmond C, Resche-Rigon M, Mirault T, Kahn JE, Lambert M et al (2015) Efficacy of biological-targeted treatments in Takayasu arteritis multicenter, retrospective study of 49 patients. Circulation 132:1693–1700. https://doi.org/10.1161/circulationaha.114.014321
Langford CA, Cuthbertson D, Ytterberg SR, Khalidi N, Monach PA, Carette S et al (2017) A randomized, double-blind trial of abatacept (CTLA-4Ig) for the treatment of Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 69:846–853. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40037
Nakagomi D, Kronbichler A, Witte T, Mohammad AJ, Jayne DRW (2018) Comment on: Rituximab therapy for Takayasu arteritis: a seven patients experience and a review of the literature. Rheumatology (Oxford) 57:1309–1310. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kex493
Pazzola G, Muratore F, Pipitone N, Crescentini F, Cacoub P, Boiardi L et al (2018) Rituximab therapy for Takayasu arteritis: a seven patients experience and a review of the literature. Rheumatology (Oxford) 57:1151–1155. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kex249
Li J, Li M, Tian X, Zeng X (2020) Tofacitinib in patients with refractory Takayasu’s arteritis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 59:e95–e98. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaa281
Kong X, Sun Y, Dai X, Wang L, Ji Z, Chen H, Jin X, Ma L, Jiang L (2022) Treatment efficacy and safety of tofacitinib versus methotrexate in Takayasu arteritis: a prospective observational study. Ann Rheum Dis 81(1):117–123. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2021-220832
Orfaly VE, Kovalenko I, Tolkachjov SN, Ortega-Loayza AG, Nunley JR (2021) Tofacitinib for the treatment of refractory pyoderma gangrenosum. Clin Exp Dermatol 46(6):1082–1085. https://doi.org/10.1111/ced.14683
Choy EH, De Benedetti F, Takeuchi T, Hashizume M, John MR, Kishimoto T (2020) Translating IL-6 biology into effective treatments. Nat Rev Rheumatol 16(6):335–345. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41584-020-0419-z
Ujiie H, Sawamura D, Yokota K, Nishie W, Shichinohe R, Shimizu H (2004) Pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Takayasu’s arteritis. Clin Exp Dermatol 29:357–359. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2230.2004.01514.x
Minagawa A, Uhara H, Saida T (2010) Takayasu’s arteritis with pyoderma gangrenosum and necrotizing vasculitis. Clin Exp Dermatol 35:329–330
Ghosn S, Malek J, Shbaklo Z, Matta M, Uthman I (2008) Takayasu disease presenting as malignant pyoderma gangrenosum in a child with relapsing polychondritis. J Am Acad Dermatol 59:S84–S87. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2008.05.010
Fearfield LA, Ross JR, Farrell AM, Costelle C, Bunker CB, Staughton RC (1999) Pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Takayasu’s arteritis responding to cyclosporine. Br J Dermatol 141:339–343. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365-2133.1999.02989.x
Dagan O, Barak Y, Metzker A (1995) Pyoderma gangrenosum and sterile multifocal osteomyelitis preceding the appearance of Takayasu arteritis. Pediatr Dermatol 12:39–42. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-1470.1995.tb00122.x
Vettiyil G, Punnen A, Kumar S (2017) An unusual association of chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis, pyoderma gangrenosum and Takayasu arteritis. J Rheumatol 44:127–128. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.160491
Barrera-Vargas A, Granados J, Garcia-Hidalgo L, Hinojosa-Azaola A (2015) An unusual presentation of Takayasu’s arteritis in two Mexican siblings. Mod Rheumatol 25:802–805. https://doi.org/10.3109/14397595.2013.844384
Okamura K, Konno T, Onami K, Nikaido M, Okazaki N, Abe Y, Hayashi M, Yaguchi Y, Sato H, Konta T, Suzuki T (2017) A case of primarily facial pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Takayasu arteritis. JAAD Case Rep 3:124–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jdcr.2016.12.006
Loetscher J, Fistarol S, Walker UA (2016) Pyoderma gangrenosum and erythema nodosum revealing Takayasu’s arteritis. Case Rep Dermatol 8:354–7. https://doi.org/10.1159/000452829
Futaki K, Komine M, Hosoda S, Hirashima M, Yokokura H, Yamada T, Murata S, Matsuyama Y, Nagashima T, Nara H, Minota S, Ohtsuki M (2009) Pyoderma gangrenosum associated with Takayasu’s arteritis without typical symptoms. Eur J Dermatol 19:266–267
Aoussar A, Ismaili N, Berbich L, Tazi Mezalek Z, Alt Ourhrouil M, Senouci K, Mansouri F, Hassam B (2007) Pyoderma gangrenosum revealing Takayasu’s arteritis. Ann Dermatol Venereol 134:264–267
Kanemistu S, Shimono T, Kusagawa H, Onoda K, Yada I (2005) Successful surgical treatment of Takayasu’s arteritis associated with pyoderma gangrenosum. Ann Thorac Surg 80:1914–1916. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.athoracsur.2004.06.098
Fullerton SH, Abel EA, Getz K, el Ramahi K (1991) Cyclosporine treatment of severe recalcitrant pyoderma gangrenosum in a patient with Takayasu’s arteritis. Arch Dermatol 127:1731–2. https://doi.org/10.1001/archderm.1991.01680100135027
Frances C, Boisnic S, Bletry O, Dallot A, Thomas D, Kieffer E, Godeau P (1990) Cutaneous manifestations of Takayasu arteritis: a retrospective study of 80 cases. Dermatologica 181:266–272. https://doi.org/10.1159/000247820
Perniciaro CV, Winkelmann RK, Hunder GG (1987) Cutaneous manifestations of Takayasu’s arteritis: a clinicopathologic correlation. J Am Acad Dermatol 17:998–1005. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0190-9622(87)70289-8
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
KB: diagnosis and management of case, writing—original draft, literature search. RR: diagnosis and management of case, collection of image, review and editing. SouD: diagnosis and management of case, review and editing. SonD: diagnosis and management of case, review and editing. SM: diagnosis and management of case, review and editing. PS: diagnosis and management of case, review and editing. PG: review and editing of the case. BG: diagnosis and management of case, review and editing. All co-authors take full responsibility for the integrity and accuracy of all aspects of the work.
The paper has not been submitted to another journal and has not been published in whole or in part elsewhere previously.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Consent
Written consent has been obtained from the patient for the publication.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Bhowmick, K., Roongta, R., Dey, S. et al. Refractory Takayasu arteritis with recurrent pyoderma gangrenosum: a therapeutic challenge with case-based review. Clin Rheumatol 42, 1469–1477 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06506-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-023-06506-x