Abstract
Objective
To describe the clinical characteristics and radiographic outcomes of vascular Behçet’s disease (BD) involving the aorta or its major branches.
Methods
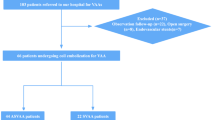
This retrospective cohort study was performed in patients with vascular BD involving the aorta or its major branches. All included patients underwent computed tomography angiography (CTA) at least two times with a 2- to 5-year interval. Radiographic progression was defined as newly developed and/or aggravated (> 20%) characteristic features on CTA.
Results
The cohort included 22 patients with BD with a median interval of 3.65 years between the initial and follow-up CTA. Five patients (22.7%) showed radiographic progression. Patients with radiographic progression had a longer disease duration at baseline than those without (6.67 vs. 0.26 years, p = 0.028). Of all patients, 21 (95.5%) had vascular aneurysms/pseudoaneurysms and 11 (50.0%) had thrombosis. The most frequently involved artery with aneurysmal change was the abdominal aorta (8/21, 38.1%), followed by the iliac arteries (5/21, 23.8%). In the case of thrombosis, the most frequently involved arteries were the femoral (4/11, 36.4%) and iliac (4/11, 36.4%) arteries. The characteristics and locations of vascular involvement did not significantly differ according to the radiographic outcome.
Conclusions
A considerable proportion of patients with BD with arterial involvement showed radiographic progression within 2–5 years. Patients with radiographic progression had a longer disease duration at baseline. The most common form of arterial involvement of BD was aneurysmal change, followed by thrombus formation.
Key Points: • This study evaluated for the first time the radiographic outcomes of 22 patients with Behçet’s disease involving the aorta or its major branches. • A considerable proportion of patients (5/22, 22.7%) showed radiographic progression. • Patients with radiographic progression had a longer disease duration at baseline than their counterparts; however, no other clinical factors were significantly different. • The most frequent form of vascular involvement was pseudoaneurysm followed by thrombosis. |

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
References
Bettiol A, Prisco D, Emmi G (2020) Behcet: the syndrome. Rheumatol (Oxford) 59:iii101–iii107. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kez626
Yazici H, Seyahi E, Hatemi G, Yazici Y (2018) Behcet syndrome: a contemporary view. Nat Rev Rheumatol 14:107–119. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2017.208
Alibaz-Oner F, Karadeniz A, Ylmaz S, Balkarl A, Kimyon G, Yazc A, Cnar M, Ylmaz S, Yldz F, Bilge SY, Bilgin E, Coskun BN, Omma A, Cetin GY, Cagatay Y, Karaaslan Y, Sayarloglu M, Pehlivan Y, Kalyoncu U, Karadag O, Kasifoglu T, Erken E, Pay S, Cefle A, Ksack B, Onat AM, Cobankara V, Direskeneli H (2015) Behcet disease with vascular involvement: effects of different therapeutic regimens on the incidence of new relapses. Medicine (Baltimore) 94:e494. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000000494
Ishibashi H (2018) What is vascular Behcet’s disease? Ann Vasc Dis 11:52–56. https://doi.org/10.3400/avd.ra.18-00002
Calamia KT, Schirmer M, Melikoglu M (2005) Major vessel involvement in Behcet disease. Curr Opin Rheumatol 17:1–8. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.bor.0000145520.76348.dd
Chung JW, Kim HC, Choi YH, Kim SJ, Lee W, Park JH (2007) Patterns of aortic involvement in Takayasu arteritis and its clinical implications: evaluation with spiral computed tomography angiography. J Vasc Surg 45:906–914. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2007.01.016
Hartlage GR, Palios J, Barron BJ, Stillman AE, Bossone E, Clements SD, Lerakis S (2014) Multimodality imaging of aortitis. JACC Cardiovasc Imaging 7:605–619. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcmg.2014.04.002
Qi L, Cai J, Mao D, Wang M, Ge X, Wu W, Jin X, Li C, Hua Y, Li M (2019) Use of contrast-enhanced computed tomographic imaging to diagnose and evaluate Behcet’s disease with vascular complications. Exp Ther Med 18:4265–4272. https://doi.org/10.3892/etm.2019.8088
Yoshida S, Akiba H, Tamakawa M, Yama N, Takeda M, Hareyama M, Nakata T, Shimamoto K (2001) The spectrum of findings in supra-aortic Takayasu’s arteritis as seen on spiral CT angiography and digital subtraction angiography. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 24:117–121. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002700000368
Lin CH, Luo D, Ma HF, Shen Y, Zou J, Guan JL (2020) Clinical characteristics and factors influencing the prognosis of Behcet’s disease complicated with vascular involvement. Vasa 49:309–318. https://doi.org/10.1024/0301-1526/a000859
Tohme A, Aoun N, El-Rassi B, Ghayad E (2003) Vascular manifestations of Behcet’s disease. Eighteen cases among 140 patients. Joint Bone Spine 70:384–389. https://doi.org/10.1016/s1297-319x(03)00076-9
Hosaka A, Miyata T, Hoshina K, Okamoto H, Shigematsu K, Oshima A (2014) Prognosis of arterial aneurysm after surgery in patients with Behcet’s disease. Int Angiol 33:419–425
Liu Q, Ye W, Liu C, Li Y, Zeng R, Ni L (2016) Outcomes of vascular intervention and use of perioperative medications for nonpulmonary aneurysms in Behcet disease. Surgery 159:1422–1429. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2015.11.022
International Team for the Revision of the International Criteria for Behcet’s D (2014) The International Criteria for Behcet’s Disease (ICBD): a collaborative study of 27 countries on the sensitivity and specificity of the new criteria. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 28:338–347. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.12107
International Study Group for Behçet’s D (1990) Criteria for diagnosis of Behcet’s disease. Lancet 335:1078–1080. https://doi.org/10.1016/0140-6736(90)92643-V
Choi SJ, Koo HJ, Yang DH, Kang JW, Oh JS, Hong S, Kim YG, Yoo B, Lee CK (2020) Comparison of clinical, angiographic features and outcome in Takayasu’s arteritis and Behçet’s disease with arterial involvement. J Rheum Dis 27:100–109. https://doi.org/10.4078/jrd.2020.27.2.100
Ideguchi H, Suda A, Takeno M, Ueda A, Ohno S, Ishigatsubo Y (2011) Characteristics of vascular involvement in Behcet’s disease in Japan: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Exp Rheumatol 29:S47-53
Saadoun D, Asli B, Wechsler B, Houman H, Geri G, Desseaux K, Piette JC, Huong DLT, Amoura Z, Salem TB, Cluzel P, Koskas F, Resche-Rigon M, Cacoub P (2012) Long-term outcome of arterial lesions in Behcet disease: a series of 101 patients. Medicine (Baltimore) 91:18–24. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0b013e3182428126
Lee S, Eun Y, Kim H, Lee J, Koh EM, Kim DK, Cha HS (2021) Factors associated with radiographic progression in patients with Takayasu’s arteritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 39(Suppl 129):46–51
Hatemi G, Christensen R, Bang D, Bodaghi B, Celik AF, Fortune F, Gaudric J, Gul A, Kotter I, Leccese P, Mahr A, Moots R, Ozguler Y, Richter J, Saadoun D, Salvarani C, Scuderi F, Sfikakis PP, Siva A, Stanford M, Tugal-Tutkun I, West R, Yurdakul S, Olivieri I, Yazici H (2018) 2018 update of the EULAR recommendations for the management of Behcet’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 77:808–818. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2018-213225
Chen Y, Cai JF, Lin CH, Guan JL (2019) Demography of vascular Behcet’s disease with different gender and age: an investigation with 166 Chinese patients. Orphanet J Rare Dis 14:88. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-019-1061-1
Fei Y, Li X, Lin S, Song X, Wu Q, Zhu Y, Gao X, Zhang W, Zhao Y, Zeng X, Zhang F (2013) Major vascular involvement in Behcet’s disease: a retrospective study of 796 patients. Clin Rheumatol 32:845–852. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2205-7
Sarica-Kucukoglu R, Akdag-Kose A, Kayabal IM, Yazganoglu KD, Disci R, Erzengin D, Azizlerli G (2006) Vascular involvement in Behcet’s disease: a retrospective analysis of 2319 cases. Int J Dermatol 45:919–921. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-4632.2006.02832.x
Barnes CG (2006) Treatment of Behcet’s syndrome. Rheumatology (Oxford) 45:245–247. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kei257
Le Thi HD, Wechsler B, Papo T, Piette JC, Bletry O, Vitoux JM, Kieffer E, Godeau P (1995) Arterial lesions in Behcet’s disease. A study in 25 patients. J Rheumatol 22:2103–2113
Iscan ZH, Vural KM, Bayazit M (2005) Compelling nature of arterial manifestations in Behcet disease. J Vasc Surg 41:53–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvs.2004.09.018
Akpolat T, Danaci M, Belet U, Erkan ML, Akar H (2000) MR imaging and MR angiography in vascular Behcet’s disease. Magn Reson Imaging 18:1089–1096. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0730-725x(00)00215-0
Ceylan N, Bayraktaroglu S, Erturk SM, Savas R, Alper H (2010) Pulmonary and vascular manifestations of Behcet disease: imaging findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 194:W158-164. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.09.2763
Demirkesen C, Öz B, Göksel S (2010) Behçet’s disease: pathology. In: Yazıcı Y, Yazıcı H (eds) Behçet’s syndrome. Springer, New York, New York, NY, pp 215–241
Matsumoto T, Uekusa T, Fukuda Y (1991) Vasculo-Behcet’s disease: a pathologic study of eight cases. Hum Pathol 22:45–51. https://doi.org/10.1016/0046-8177(91)90060-3
Kankilic N, Aslan A, Karahan O, Demirtas S, Caliskan A, Yavuz C (2018) Investigation of the arterial intima-media thickness in Behcet’s disease patients without vascular complaints. Vascular 26:356–361. https://doi.org/10.1177/1708538117742827
Duprez DA, De Buyzere ML, De Backer TL, Van De Veire N, Clement DL, Cohn JN (2000) Relationship between arterial elasticity indices and carotid artery intima-media thickness. Am J Hypertens 13:1226–1232. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0895-7061(00)01203-6
Blake T, Pickup L, Carruthers D, Damato EM, Denniston A, Hamburger J, Maxton C, Mitton D, Murray PI, Nightingale P, Poveda-Gallego A, Richards A, Whallett A, Situnayake D (2017) Birmingham Behcet’s service: classification of disease and application of the 2014 International Criteria for Behcet’s Disease (ICBD) to a UK cohort. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18:101. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-017-1463-y
Davatchi F (2012) Diagnosis/classification criteria for Behcet’s disease. Patholog Res Int 2012:607921. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/607921
Altenburg A, Bonitsis NG, Papoutsis N, Pasak M, Krause L, Zouboulis CC (2008) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria including ICBD (2006) in Adamantiades-Behcet’s disease patients in Germany. Clin Exp Rheumatol 26:S3
Davatchi F, Sadeghi Abdollahi B, Shahram F, Nadji A, Chams-Davatchi C, Shams H, Naderi N, Akhlaghi M, Faezi T, Faridar A (2010) Validation of the International Criteria for Behcet’s Disease (ICBD) in Iran. Int J Rheum Dis 13:55–60. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1756-185X.2009.01455.x
Zhang ZL, Zhou W, Hao YJ, Wang Y, Dong Y (2008) Validation of the International Criteria for Behcet’s Disease (ICBD) in China. Clin Exp Rheumatol 26:S6–S7
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection, and analysis were performed by Seulkee Lee. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Seulkee Lee and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, S., Kang, S., Eun, Y. et al. Clinical characteristics and radiographic outcomes of vascular Behçet’s disease involving the aorta or its major branches. Clin Rheumatol 41, 1769–1777 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-06031-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-06031-9