Abstract
Objectives
To analyze the diagnostic utility of lung ultrasound (US) to detect interstitial lung disease (ILD) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients comparing with high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT)
Patients and methods
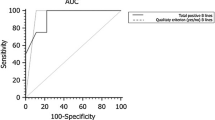
We performed a cross-sectional, observational study in patients with RA-ILD (cases) controlled with a group of RA patients without ILD (controls) paired by sex, age, and time of disease evolution. Patients were assessed using HRCT, PFT, and US. The main variables were B-line number, evaluation of the lung-US score already described, pleural irregularities, and A pattern US lost. ROC curve analysis was performed to establish the cut-off point of the US B-lines number for detecting the presence of significant RA–ILD in relation to HRCT, and logistic regression analysis was performed to identify the intercostal spaces.
Results
Seventy-one patients were included, 35 (49.2%) with ILD-RA and 36 (50.8%) RA controls. Regarding US score, we found that the detection of 5.5 lines in a reduced score of 8 intercostal spaces had a sensitivity = 62.2%, specificity = 91.3%, PPV = 88.4%, and NPV = 69.5%. In multivariate analysis, the intercostal spaces which showed independent association with ILD were 3rd right anterior axillary space (OR [IC 95%] 19.0 [1.3–27.5]), 8th right posterior axillary space (OR [IC 95%] 0.04 [0.0–0.6]), 8th right subscapular space (OR [IC 95%] 16.5 [1.8–45.5]), 9th right paravertebral space (OR [IC 95%] 7.11 [1.0–37.1]), and 2nd left clavicular middle space (OR [IC 95%] 21.9 [1.26–37.8]).
Conclusions
Lung ultrasound could be a useful tool for ILD diagnosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. A 8-space reduced score showed a similar total predictive capacity than 72-space score.
Key Points • Lung ultrasound could be a useful tool for ILD diagnosis associated with rheumatoid arthritis. • The 72-space evaluation is highly sensitive, whereas a simplified score enables a more specific and faster diagnosis. • The number of B lines is correlated with DLCO, ACPA, inflammatory activity, and physical function. |


Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
18 April 2021
A Correction to this paper has been published: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05737-0
References
Robles-Pérez A, Luburich P, Bolivar S, Dorca J, Nolla JM, Molina-Molina M, Narváez J (2020) A prospective study of lung disease in a cohort of early rheumatoid arthritis patients. Sci Rep 10(1):15640. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72768-z
Hyldgaard C, Hilberg O, Pedersen AB, Ulrichsen SP, Løkke A, Bendstrup E, Ellingsen T (2017) A population-based cohort study of rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: comorbidity and mortality. Ann Rheum Dis 76(10):1700–1706. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2017-211138
Kakutani T, Hashimoto A, Tominaga A, Kodama K, Nogi S, Tsuno H, Ogihara H, Nunokawa T, Komiya A, Furukawa H, Tohma S, Matsui T (2019) Related factors, increased mortality and causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Mod Rheumatol 30(3):458–464. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2019.1621462
Kim EJ, Elicker BM, Maldonado F, Webb WR, Ryu JH, Van Uden JH, Lee JS, King TE Jr, Collard HR (2010) Usual interstitial pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J 35(6):1322–1328. https://doi.org/10.1183/09031936.00092309
Kim HC, Choi KH, Jacob J, Song JW (2020) Prognostic role of blood KL-6 in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. PLoS One 15(3):e0229997. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0229997
Olson AL, Swigris JJ, Sprunger DB, Fischer A, Fernandez-Perez ER, Solomon J, Murphy J, Cohen M, Raghu G, Brown KK (2011) Rheumatoid arthritis-interstitial lung disease-associated mortality. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 183(3):372–378. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201004-0622OC
Sihvonen S, Korpela M, Laippala P, Mustonen J, Pasternack A (2004) Death rates and causes of death in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Scand J Rheumatol 33(4):221–227. https://doi.org/10.1080/03009740410005845
Launay D, Remy-Jardin M, Michon-Pasturel U, Mastora I, Hachulla E, Lambert M, Delannoy V, Queyrel V, Duhamel A, Matran R, De Groote P, Hatron PY (2006) High resolution computed tomography in fibrosing alveolitis associated with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 33(9):1789–1801
Sambataro D, Sambataro G, Dal Bosco Y, Campagna D, Polosa R (2017) Is there any role for thoracic ultrasound for interstitial lung disease underlying rheumatologic conditions? Reply. Intern Emerg Med 12(6):905–906. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-017-1669-x
Vizioli L, Ciccarese F, Forti P, Chiesa AM, Giovagnoli M, Mughetti M, Zompatori M, Zoli M (2017) Integrated use of lung ultrasound and chest X-ray in the detection of interstitial lung disease. Respiration 93(1):15–22. https://doi.org/10.1159/000452225
Wang Y, Gargani L, Barskova T, Furst DE, Cerinic MM (2017) Usefulness of lung ultrasound B-lines in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease: a literature review. Arthritis Res Ther 19(1):206. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-017-1409-7
Gargani LDM, D'Errico L, Frassi F, Bazzichi ML, Delle Sedie A, Scali MC, Monti S, Mondillo S, Bombardieri S, Caramella D, Picano E (2009) Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: a chest sonography hallmark of pulmonary interstitial fibrosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48(11):1382–1387. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kep263
Picano E, Frassi F, Agricola E, Gligorova S, Gargani L, Mottola G (2006) Ultrasound lung comets: a clinically useful sign of extravascular lung water. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 19(3):356–363. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.echo.2005.05.019
Barskova TGL, Guiducci S, Randone SB, Bruni C, Carnesecchi G, Conforti ML, Porta F, Pignone A, Caramella D, Picano E, Cerinic MM (2012) Lung ultrasound for the screening of interstitial lung disease in very early systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 72(3):390–395. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-201072
Cogliati C, Antivalle M, Torzillo D, Birocchi S, Norsa A, Bianco R, Costantino G, Ditto MC, Battellino M, Sarzi Puttini PC, Montano N (2014) Standard and pocket-size lung ultrasound devices can detect interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53(8):1497–1503. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keu033
Moazedi-Fuerst FC, Kielhauser SM, Scheidl S, Tripolt NJ, Lutfi A, Yazdani-Biuki B, Dejaco C, Graninger WB (2014) Ultrasound screening for interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32(2):199–203
Gutierrez M, Salaffi F, Carotti M, Tardella M, Pineda C, Bertolazzi C, Bichisecchi E, Filippucci E, Grassi W (2011) Utility of a simplified ultrasound assessment to assess interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in connective tissue disorders—preliminary results. Arthritis Res Ther 13(4):R134. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3446
Mohammadi A, Oshnoei S, Ghasemi-rad M (2014) Comparison of a new, modified lung ultrasonography technique with high-resolution CT in the diagnosis of the alveolo-interstitial syndrome of systemic scleroderma. Med Ultrason 16(1):27–31. https://doi.org/10.11152/mu.2014.2066.161.am1so2
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd et al (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62(9):2569–2581. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27584
Gigante A, Rossi Fanelli F, Lucci S, Barilaro G, Quarta S, Barbano B, Giovannetti A, Amoroso A, Rosato E (2016) Lung ultrasound in systemic sclerosis: correlation with high-resolution computed tomography, pulmonary function tests and clinical variables of disease. Intern Emerg Med 11(2):213–217. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11739-015-1329-y
Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, King TE Jr, Lynch DA, Nicholson AG et al (2013) An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188(6):733–748. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201308-1483ST
Gaujoux-Viala C, Mouterde G, Baillet A, Claudepierre P, Fautrel B, Le Loët X, Maillefert JF (2012) Evaluating disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: which composite index is best? A systematic literature analysis of studies comparing the psychometric properties of the DAS, DAS28, SDAI and CDAI. Joint Bone Spine 79(2):149–155. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.04.008
Maska L, Anderson J, Michaud K (2011) Measures of functional status and quality of life in rheumatoid arthritis: Health Assessment Questionnaire Disability Index (HAQ), Modified Health Assessment Questionnaire (MHAQ), Multidimensional Health Assessment Questionnaire (MDHAQ), Health Assessment Questionnaire II (HAQ-II), Improved Health Assessment Questionnaire (Improved HAQ), and Rheumatoid Arthritis Quality of Life (RAQoL). Arthritis Care Res 63(Suppl 11):S4–S13. https://doi.org/10.1002/acr.20620
Soldati GCR, Sher S (2009) Sonographic interstitial syndrome: the sound of lung water. J Ultrasound Med 28(2):163–174. https://doi.org/10.7863/jum.2009.28.2.163
Gabbay E, Tarala R, Will R, Carroll G, Adler B, Cameron D, Lake FR (1997) Interstitial lung disease in recent onset rheumatoid arthritis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156(2 Pt 1):528–535. https://doi.org/10.1164/ajrccm.156.2.9609016
Delle Sedie ADM, Frassi F, Gargani L, D'Errico G, Pepe P, Bazzichi L, Riente L, Caramella D, Bombardieri S (2010) Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: a useful tool to detect lung interstitial fibrosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28(5 Suppl 62):S54
Tardella M, Di Carlo M, Carotti M, Filippucci E, Grassi W, Salaffi F (2018) Ultrasound B-lines in the evaluation of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis: cut-off point definition for the presence of significant pulmonary fibrosis. Medicine 97(18):e0566. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000010566
Yin Y, Liang D, Zhao L, Li Y, Liu W, Ren Y, Li Y, Zeng X, Zhang F, Tang F, Shan G, Zhang X (2014) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody is associated with interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 9(4):e92449. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0092449
Alexiou I, Germenis A, Koutroumpas A, Kontogianni A, Theodoridou K, Sakkas LI (2008) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide-2 (CCP2) autoantibodies and extra-articular manifestations in Greek patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 27(4):511–513. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0800-1
Aubart F, Crestani B, Nicaise-Roland P, Tubach F, Bollet C, Dawidowicz K, Quintin E, Hayem G, Palazzo E, Meyer O, Chollet-Martin S, Dieudé P (2011) High levels of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide autoantibodies are associated with co-occurrence of pulmonary diseases with rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 38(6):979–982. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.101261
Mori S, Koga Y, Sugimoto M (2012) Different risk factors between interstitial lung disease and airway disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Respir Med 106(11):1591–1599. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rmed.2012.07.006
Restrepo JF, del Rincon I, Battafarano DF, Haas RW, Doria M, Escalante A (2015) Clinical and laboratory factors associated with interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34(9):1529–1536. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3025-8
Conway R, Low C, Coughlan RJ, O'Donnell MJ, Carey JJ (2014) Methotrexate and lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum 66(4):803–812. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38322
Ibfelt EH, Jacobsen RK, Kopp TI, Cordtz RL, Jakobsen AS, Seersholm N, Shaker SB, Dreyer L (2021) Methotrexate and risk of interstitial lung disease and respiratory failure in rheumatoid arthritis: a nationwide population-based study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 60(1):346–352. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keaa327
Acknowledgements
To the Spanish Rheumatology Society (SER) for the translation of the manuscript.
Funding
Grant for Medical Researchers of the “Fundación Española de Reumatología” 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
NMV participated in the design of the study, carried out patient recruitment and statistical analysis, and drafted the manuscript. FGJN, FJGN, and SMA were a contributor in including patients. They were a major contributor in writing the manuscript and they were a contributor in analyzing and interpreting the patient data. MCAH and MIPM collected radiology data and FGJM in pulmonary ultrasound data. IUG, MCRB, and FE were a major contributor in including patients. AFN: a contributor in writing the manuscript. He was a contributor in analyzing and interpreting the patient data. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
All subjects gave their informed consent for inclusion before they participated in the study. The study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki, and the protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Málaga (“Comité de Ética de la Investigación de Málaga”) (Project identification Code 1549-N-19).
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
In the original published version of this article under the Result and Conclusion sections of the “Abstract” contained errors and has been corrected above with the following updates: 1. Result: 35 (49.2%) with ILD-RA and 36 (50.8%) RA controls.; 8 intercostal spaces. 2. Conclusions: 8-space reduced.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mena-Vázquez, N., Jimenez-Núñez, F.G., Godoy-Navarrete, F.J. et al. Utility of pulmonary ultrasound to identify interstitial lung disease in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 40, 2377–2385 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05655-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05655-1