Abstract
Objective
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a complex inflammatory autoimmune disease with joint eruption, systemic manifestation, and numerous predisposing genetic factors. The P2X7 receptor is an essential ligand-gated channel that contributes to many physiological processes, especially inflammation. However, genetic variations can alter the P2X7 receptor function. Therefore, the present study aimed to explore the impact of P2X7 genetic polymorphisms and expression on susceptibility to RA in a sample of the Iranian population.
Methods
We enrolled 160 (145 female, 15 male) RA patients and 160 (142 female, 18 male) healthy individuals in this study. Genotyping was performed using tetra amplification refractory mutation system-polymerase chain reaction (TARMS-PCR) for rs1718119, rs2230912, rs2393799, rs28360457, rs35933842, and allele-specific PCR for rs1653624 and rs3751143. Furthermore, 44 new cases of RA and 48 healthy controls were recruited to investigate whether P2X7 mRNA expression is associated with RA susceptibility.
Results
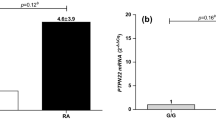
The results revealed that the rs2393799 significantly increased the risk of RA in all genetic models (p<0.05), while rs3751143 in codominant (CC vs. AA, OR=0.49, 95% CI=0.26–0.92), dominant (AC+CC, OR=0.59, 95% CI=0.37–0.94), C allele (OR=0.63, 95% CI=0.46–0.88), and rs2230912 in codominant (AG vs. AA, OR=0.56, 95% CI=0.34–0.94), dominant (AG+GG vs. AA, OR=0.59, 95% CI=0.35–0.99), and overdominant (AG vs. AA+GG, OR=0.57, 95% CI=0.33–0.98) significantly decreased the RA risk (p<0.05). Furthermore, the rs1718119 and rs1653624 were not associated with susceptibility of RA (p>0.05), and rs28360457 and rs35933842 were not polymorphic in our study. The mRNA expression level of P2X7 in both groups revealed that the P2X7 gene was significantly upregulated in RA (3.18±0.43) compared to healthy subjects (1.47±0.15, p<0.001).
Conclusion
Our results suggest that rs2393799, rs3751143, and rs2230912 variants of the P2X7 gene are associated with RA’s susceptibility in a sample of the Iranian population. Also, P2X7 mRNA expression was higher in our new RA patients. The P2X7 receptor has been considered as a potential pharmacologic target in RA.
Key Points • P2X7 variants (rs2393799, rs2230912, rs3751143) were associated with RA susceptibility in a sample of the Iranian population. • rs2393799 increases the risk of RA, while rs2230912 and rs3751143 decrease the risk of RA. • P2X7 expression was significantly upregulated in new RA patients compared to controls. |








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article or available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
References
Fan ZD, Zhang YY, Guo YH, Huang N, Ma HH, Huang H, Yu HG (2016) Involvement of P2X7 receptor signaling on regulating the differentiation of Th17 cells and type II collagen-induced arthritis in mice. Sci Rep 6:35804. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep35804
Sode J, Vogel U, Bank S, Andersen PS, Hetland ML, Locht H, Heegaard NHH, Andersen V (2018) Confirmation of an IRAK3 polymorphism as a genetic marker predicting response to anti-TNF treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. Pharm J 18(1):81–86. https://doi.org/10.1038/tpj.2016.66
Alamanos Y, Voulgari PV, Drosos AA (2006) Incidence and prevalence of rheumatoid arthritis, based on the 1987 American College of Rheumatology criteria: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36(3):182–188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2006.08.006
Humby F, Bombardieri M, Manzo A, Kelly S, Blades MC, Kirkham B, Spencer J, Pitzalis C (2009) Ectopic lymphoid structures support ongoing production of class-switched autoantibodies in rheumatoid synovium. PLoS Med 6(1):e1
McInnes IB, Schett G (2011) The pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis. N Engl J Med 365(23):2205–2219
Kasuya G, Yamaura T, Ma XB, Nakamura R, Takemoto M, Nagumo H, Tanaka E, Dohmae N, Nakane T, Yu Y, Ishitani R, Matsuzaki O, Hattori M, Nureki O (2017) Structural insights into the competitive inhibition of the ATP-gated P2X receptor channel. Nat Commun 8(1):876. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-00887-9
Burnstock G (2007) Purine and pyrimidine receptors. Cell Mol Life Sci 64(12):1471–1483
Sluyter R, Stokes L (2011) Significance of P2X7 receptor variants to human health and disease. Recent Pat DNA Gene Seq 5(1):41–54
Di Virgilio F, Dal Ben D, Sarti AC, Giuliani AL, Falzoni S (2017) The P2X7 receptor in infection and inflammation. Immunity 47(1):15–31
Alves LA, Bezerra RJS, Faria RX, Ferreira LGB, da Silva FV (2013) Physiological roles and potential therapeutic applications of the P2X7 receptor in inflammation and pain. Molecules 18(9):10953–10972
Al-Shukaili A, Al-Kaabi J, Hassan B, Al-Araimi T, Al-Tobi M, Al-Kindi M, Al-Maniri A, Al-Gheilani A, Al-Ansari A (2011) P2X7 receptor gene polymorphism analysis in rheumatoid arthritis. Int J Immunogenet 38(5):389–396. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1744-313X.2011.01019.x
Li J, Liu D, Ke HZ, Duncan RL, Turner CH (2005) The P2X7 nucleotide receptor mediates skeletal mechanotransduction. J Biol Chem 280(52):42952–42959
Grol MW, Panupinthu N, Korcok J, Sims SM, Dixon SJ (2009) Expression, signaling, and function of P2X7 receptors in bone. Purinergic Signal 5(2):205–221
Panupinthu N, Rogers JT, Zhao L, Solano-Flores LP, Possmayer F, Sims SM, Dixon SJ (2008) P2X7 receptors on osteoblasts couple to production of lysophosphatidic acid: a signaling axis promoting osteogenesis. J Cell Biol 181(5):859–871
Gartland A, Buckley KA, Hipskind RA, Bowler WB, Gallagher JA (2003) P2 receptors in bone—modulation of osteoclast formation and activity via P2X 7 activation. Crit Rev Eukaryot Gene Expr 13(2–4):237–242
Labasi JM, Petrushova N, Donovan C, McCurdy S, Lira P, Payette MM, Brissette W, Wicks JR, Audoly L, Gabel CA (2002) Absence of the P2X7 receptor alters leukocyte function and attenuates an inflammatory response. J Immunol 168(12):6436–6445
Di Virgilio F, Ferrari D, Adinolfi E (2009) P2X(7): a growth-promoting receptor-implications for cancer. Purinergic Signal 5(2):251–256. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11302-009-9145-3
Skaper SD, Debetto P, Giusti P (2010) The P2X7 purinergic receptor: from physiology to neurological disorders. FASEB J 24(2):337–345
Ribeiro DE, Roncalho AL, Glaser T, Ulrich H, Wegener G, Joca S (2019) P2X7 receptor signaling in stress and depression. Int J Mol Sci 20(11):2778
Bahari G, Hashemi M, Taheri M, Naderi M, Moazeni-Roodi A, Kouhpayeh HR, Eskandari-Nasab E (2013) Association of P2X7 gene polymorphisms with susceptibility to pulmonary tuberculosis in Zahedan, Southeast Iran. Genet Mol Res 12(1):160–166. https://doi.org/10.4238/2013.January.24.8
Illes P, Rubini P, Huang L, Tang Y (2019) The P2X7 receptor: a new therapeutic target in Alzheimer’s disease. Expert Opin Ther Targets 23(3):165–176
Guan S, Shen Y, Ge H, Xiong W, He L, Liu L, Yin C, Wei X, Gao Y (2019) Dihydromyricetin alleviates diabetic neuropathic pain and depression comorbidity symptoms by inhibiting P2X7 receptor. Front Psychiatry 10:770
Ribeiro DE, Müller HK, Elfving B, Eskelund A, Joca SR, Wegener G (2019) Antidepressant-like effect induced by P2X7 receptor blockade in FSL rats is associated with BDNF signalling activation. J Psychopharmacol 33(11):1436–1446
Lopez-Castejon G, Theaker J, Pelegrin P, Clifton AD, Braddock M, Surprenant A (2010) P2X7 receptor-mediated release of cathepsins from macrophages is a cytokine-independent mechanism potentially involved in joint diseases. J Immunol 185(4):2611–2619
Pelegrin P (2008) Targeting interleukin-1 signaling in chronic inflammation: focus on P2X (7) receptor and Pannexin-1. Drug News Perspect 21 (8):424-433
Tao JH, Cheng M, Tang JP, Dai XJ, Zhang Y, Li XP, Liu Q, Wang YL (2017) Single nucleotide polymorphisms associated with P2X7R function regulate the onset of gouty arthritis. PLoS One 12(8):e0181685. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0181685
Shemon AN, Sluyter R, Fernando SL, Clarke AL, Dao-Ung LP, Skarratt KK, Saunders BM, Tan KS, Gu BJ, Fuller SJ, Britton WJ, Petrou S, Wiley JS (2006) A Thr357 to Ser polymorphism in homozygous and compound heterozygous subjects causes absent or reduced P2X7 function and impairs ATP-induced mycobacterial killing by macrophages. J Biol Chem 281(4):2079–2086. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M507816200
Haas SL, Ruether A, Singer MV, Schreiber S, Bocker U (2007) Functional P2X7 receptor polymorphisms (His155Tyr, Arg307Gln, Glu496Ala) in patients with Crohn’s disease. Scand J Immunol 65(2):166–170. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3083.2006.01876.x
Gu BJ, Zhang W, Worthington RA, Sluyter R, Dao-Ung P, Petrou S, Barden JA, Wiley JS (2001) A Glu-496 to Ala polymorphism leads to loss of function of the human P2X7 receptor. J Biol Chem 276(14):11135–11142
Portales-Cervantes L, Nino-Moreno P, Salgado-Bustamante M, Garcia-Hernandez MH, Baranda-Candido L, Reynaga-Hernandez E, Barajas-Lopez C, Gonzalez-Amaro R, Portales-Perez DP (2012) The His155Tyr (489C>T) single nucleotide polymorphism of P2RX7 gene confers an enhanced function of P2X7 receptor in immune cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Cell Immunol 276(1-2):168–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cellimm.2012.05.005
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO 3rd, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JM, Hobbs K, Huizinga TW, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Menard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovsky J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62(9):2569–2581. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.27584
Hashemi M, Hanafi Bojd H, Eskandari Nasab E, Bahari A, Hashemzehi NA, Shafieipour S, Narouie B, Taheri M, Ghavami S (2013) Association of adiponectin rs1501299 and rs266729 gene polymorphisms with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepat Mon 13(5):e9527. https://doi.org/10.5812/hepatmon.9527
Szklarczyk D, Gable AL, Lyon D, Junge A, Wyder S, Huerta-Cepas J, Simonovic M, Doncheva NT, Morris JH, Bork P (2019) STRING v11: protein–protein association networks with increased coverage, supporting functional discovery in genome-wide experimental datasets. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D607–D613
Shen J, Li Z, Chen J, Song Z, Zhou Z, Shi Y (2016) SHEsisPlus, a toolset for genetic studies on polyploid species. Sci Rep 6:24095
Stokes L, Fuller SJ, Sluyter R, Skarratt KK, Gu BJ, Wiley JS (2010) Two haplotypes of the P2X7 receptor containing the Ala-348 to Thr polymorphism exhibit a gain-of-function effect and enhanced interleukin-1β secretion. FASEB J 24(8):2916–2927
Wiley JS, Dao-Ung L-P, Li C, Shemon AN, Gu BJ, Smart ML, Fuller SJ, Barden JA, Petrou S, Sluyter R (2003) An Ile-568 to Asn polymorphism prevents normal trafficking and function of the human P2X7 receptor. J Biol Chem 278(19):17108–17113
McQuillin A, Bass N, Choudhury K, Puri V, Kosmin M, Lawrence J, Curtis D, Gurling H (2009) Case–control studies show that a non-conservative amino-acid change from a glutamine to arginine in the P2RX7 purinergic receptor protein is associated with both bipolar-and unipolar-affective disorders. Mol Psychiatry 14(6):614–620
Zhou Y, Tan C-y, Z-j M, He D, Li J, R-f H, Y-b L, Guo C-f, Guo Q, Wang L-j (2018) P2X7 receptor in spinal tuberculosis: gene polymorphisms and protein levels in Chinese Han population. Infect Genet Evol 57:138–144
Li CM, Campbell SJ, Kumararatne DS, Bellamy R, Ruwende C, McAdam KP, Hill AV, Lammas DA (2002) Association of a polymorphism in the P2X7 gene with tuberculosis in a Gambian population. J Infect Dis 186(10):1458–1462
Skarratt KK, Fuller SJ, Sluyter R, Dao-Ung L-P, Gu BJ, Wiley JS (2005) A 5′ intronic splice site polymorphism leads to a null allele of the P2X7 gene in 1–2% of the Caucasian population. FEBS Lett 579(12):2675–2678
Gu BJ, Sluyter R, Skarratt KK, Shemon AN, Dao-Ung L-P, Fuller SJ, Barden JA, Clarke AL, Petrou S, Wiley JS (2004) An Arg307 to Gln polymorphism within the ATP-binding site causes loss of function of the human P2X7 receptor. J Biol Chem 279(30):31287–31295
Al-Shukaili A, Al-Kaabi J, Hassan B (2008) A comparative study of interleukin-1beta production and p2x7 expression after ATP stimulation by peripheral blood mononuclear cells isolated from rheumatoid arthritis patients and normal healthy controls. Inflammation 31(2):84–90. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10753-007-9052-0
Portales-Cervantes L, Nino-Moreno P, Doniz-Padilla L, Baranda-Candido L, Garcia-Hernandez M, Salgado-Bustamante M, Gonzalez-Amaro R, Portales-Perez D (2010) Expression and function of the P2X(7) purinergic receptor in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus and rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol 71(8):818–825. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2010.05.008
Martín-Sánchez F, Diamond C, Zeitler M, Gomez A, Baroja-Mazo A, Bagnall J, Spiller D, White M, Daniels M, Mortellaro A (2016) Inflammasome-dependent IL-1β release depends upon membrane permeabilisation. Cell Death Differ 23(7):1219–1231
López-Castejón G, Pelegrín P (2012) Current status of inflammasome blockers as anti-inflammatory drugs. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 21(7):995–1007
Arulkumaran N, Unwin RJ, Tam FW (2011) A potential therapeutic role for P2X7 receptor (P2X7R) antagonists in the treatment of inflammatory diseases. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 20(7):897–915
Kvist TM, Schwarz P, Jørgensen NR (2014) The P2X7 receptor: a key player in immune-mediated bone loss? Sci World J 2014:954530. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/954530
Li M, Yang C, Wang Y, Song W, Jia L, Peng X, Zhao R (2020) The Expression of P2X7 receptor on Th1, Th17, and regulatory T cells in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or rheumatoid arthritis and its correlations with active disease. J Immunol 205(7):1752–1762
Gracie JA, Robertson SE, McInnes IB (2003) Interleukin-18. J Leukoc Biol 73(2):213–224
Sluyter R, Dalitz J, Wiley J (2004) P2X 7 receptor polymorphism impairs extracellular adenosine 5′-triphosphate-induced interleukin-18 release from human monocytes. Genes Immun 5(7):588–591
Heitmeier MR, Scarim AL, Corbett JA (1998) Double-stranded RNA-induced inducible nitric-oxide synthase expression and interleukin-1 release by murine macrophages requires NF-κB activation. J Biol Chem 273(24):15301–15307
Baroja-Mazo A, Pelegrín P (2012) Modulating P2X7 receptor signaling during rheumatoid arthritis: new therapeutic approaches for bisphosphonates. J Osteoporos 2012:1–7
Bryant C, Fitzgerald KA (2009) Molecular mechanisms involved in inflammasome activation. Trends Cell Biol 19(9):455–464
Ryan L, Rachow J, McCarty D (1991) Synovial fluid ATP: a potential substrate for the production of inorganic pyrophosphate. J Rheumatol 18(5):716–720
Bresnihan B, Alvaro-Gracia JM, Cobby M, Doherty M, Domljan Z, Emery P, Nuki G, Pavelka K, Rau R, Rozman B (1998) Treatment of rheumatoid arthritis with recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist. Arthritis Rheum 41(12):2196–2204
Guile SD, Alcaraz L, Birkinshaw TN, Bowers KC, Ebden MR, Furber M, Stocks MJ (2009) Antagonists of the P2X7 receptor. From lead identification to drug development. J Med Chem 52(10):3123–3141
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank all individuals who willingly participated in the study.
Funding
This study was supported by a research grant (#2431) from Zahedan University of Medical Sciences.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
GB collected, analyzed, and interpreted data and approved the final version of the manuscript. FT contributed analysis and drafted the manuscript. MH designed the study and primers, analyzed and interpreted data, and drafted the manuscript. ZZ recruited the subjects, collected clinical data, and contributed to draft preparation. MT performed the data analysis and proofread the manuscript. All authors approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board and Ethics Committee of Zahedan University of Medical Sciences (approval ID: IR.ZAUMS.REC.1391.2431). The written informed consent was taken from all the participants.
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Bahari, G., Tabasi, F., Hashemi, M. et al. Association of P2X7 receptor genetic polymorphisms and expression with rheumatoid arthritis susceptibility in a sample of the Iranian population: a case-control study. Clin Rheumatol 40, 3115–3126 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05645-3
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-021-05645-3