Abstract
Objective
The diagnosis of adult-onset Still’s disease (AOSD) is based on nonspecific symptoms and laboratory data, and several infectious, autoimmune, and malignant diseases must be ruled out. This study aimed to elucidate the value of various laboratory inflammatory scores, including the systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), C-reactive protein/albumin ratio (CAR), albumin/globulin ratio (AGR), prognostic nutritional index (PNI), and ferritin/erythrocyte sedimentation rate ratio (FER) as assessment factors for diagnosis and evaluation of disease activity in AOSD.
Methods
The medical records of patients suspected of AOSD between January 1999 and June 2019 were examined. The inflammatory scores were compared between AOSD and non-AOSD groups, and receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis was performed to evaluate diagnostic utility.
Results
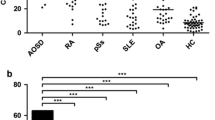
A total of 164 patients diagnosed with AOSD had higher values of SII, CAR, and FER, as well as lower values of AGR and PNI, than non-AOSD patients (n = 61). For an AOSD diagnosis, the area under the receiver operating characteristic curve (AUC) was 0.859 (95% confidence interval [CI], 0.806–0.911) for the SII, 0.769 (95% CI, 0.702–0.837) for the CAR, 0.749 (95% CI, 0.615–0.782) for the AGR, 0.699 (95% CI, 0.675–0.823) for the PNI, and 0.764 (95% CI, 0.693–0.834) for the FER, with optimal cut-off values of 2195.7, 1.8, 1.38, 48.8, and 17, respectively. The SII had the largest AUC and the highest specificity (91.5%). In further analysis, the AUC for the combination of SII and ferritin was 0.904 (95% CI, 0.863–0.945), with a cut-off value of 2615.4.
Conclusions
Laboratory inflammatory scores can be used as a practical tool for diagnosing AOSD. The SII and ferritin combination proved to be the most powerful assessment tool.
Key Points • The systemic immune-inflammation index (SII), C-reactive protein/albumin ratio (CAR), ferritin/erythrocyte sedimentation rate ratio (FER), prognostic nutritional index (PNI), and albumin/globulin ratio (AGR) can be used as initial assessment scores for AOSD. • SII combined with ferritin (AUC = 0.904; 95% CI, 0.863–0.945) appears to be the most effective and valuable assessment score for AOSD. |

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bywaters E (1971) Still’s disease in the adult. Ann Rheum Dis 30(2):121–133
Gerfaud-Valentin M, Jamilloux Y, Iwaz J, Sève P (2014) Adult-onset Still’s disease. Autoimmun Rev 13:708–722
Efthimiou P, Paik P, Bielory L (2006) Diagnosis and management of adult onset Still’s disease. Ann Rheum Dis 65:564–572
Giacomelli R, Ruscitti P, Shoenfeld Y (2018) A comprehensive review on adult onset Still’s disease. J Autoimmun 93:24–36
Kádár J, Petrovicz E (2014) Adult-onset Still’s disease. Best Pract Res Clin Rheum 18:663–676
Yamaguchi M, Ohta A, Tsunematsu T, Kasukawa R, Mizushima Y, Kashiwagi H, Kashiwazaki S, Tanimoto K, Matsumoto Y, Ota T (1992) Preliminary criteria for classification of adult Still’s disease. J Rheumatol 19:424–430
Magadur-Joly G, Billaud E, Barrier JH, Pennec YL, Masson C, Renou P, Prost A (1995) Epidemiology of adult Still’s disease: estimate of the incidence by a retrospective study in west France. Ann Rheum Dis 54:587–590
Wang MY, Jia JC, Yang CD, Hu QY (2019) Pathogenesis, disease course, and prognosis of adult-onset Still’s disease: an update and review. Chin Med J 132:2856–2864
Piero R, Paola C, Francesco M, Daniela I, Francesco C, Vasiliki L, Giuliana G, Francesco C, Onorina B, Paola DB, Marco V, Giovanni T, Gabriele V, Roberto G (2016) Adult-onset Still’s disease: evaluation of prognostic tools and validation of the systemic score by analysis of 100 cases from three centers. BMC Med 14:194. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12916-016-0738-8
Efthimiou P, Kadavath S, Mehta B (2014) Life-threatening complications of adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Rheumatol 33:305–314
Piero R, Carmela R, Luciana B, Paola C, Vasiliki L, Onorina B, Francesco C, Caterina DB, Alberto V, Roberto G (2017) Macrophage activation syndrome in Still’s disease: analysis of clinical characteristics and survival in paediatric and adult patients. Clin Rheumatol 36:2839–2845
Fang H, Zhang H, Wang Z, Zhou Z, Li Y, Lu L (2020) Systemic immune-inflammation index acts as a novel diagnostic biomarker for postmenopausal osteoporosis and could predict the risk of osteoporotic fracture. J Clin Lab Anal 34. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.23016
Zaixing Y, Zhiyu Z, Feng L, Yingpeng R, Donghong L, Renqian Z, Yan L (2017) Comparisons of neutrophil-, monocyte-, eosinophil-, and basophil-lymphocyte ratios among various systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases. Apmis 125:863–871
Kim Y, Choi H, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park YB, Lee SW (2019) Systemic immune-inflammation index could estimate the cross-sectional high activity and the poor outcomes in immunosuppressive drug-naïve patients with antineutrophil cytoplasmic antibody-associated vasculitis. Nephrology 24:711–717
Wei-ming Y, Wei-heng Z, Hou-qun Y, Yan-mei X, Jing Z, Qing-hua M, Bo H, Jin L, Juan-juan C, Xiao-zhong W (2018) Two new inflammatory markers associated with disease activity score-28 in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: albumin to fibrinogen ratio and C-reactive protein to albumin ratio. Int Immunopharmacol 62:293–298
Ahn SS, Yoo J, Jung SM, Song JJ, Park Y-B, Lee S-W (2019) Clinical role of albumin to globulin ratio in microscopic polyangiitis: a retrospective monocentric study. Clin Rheumatol 38:487–494
Ahn S, Jung S, Song J, Park Y, Lee S (2018) Prognostic nutritional index is correlated with disease activity in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 27:1697–1705
Eloseily EM, Minoia F, Crayne CB, Beukelman T, Ravelli A, Cron RQ (2019) Ferritin to erythrocyte sedimentation rate ratio: simple measure to identify macrophage activation syndrome in systemic juvenile idiopathic arthritis. ACR Open Rheumatol 1:345–349
Pouchot J, Sampalis JS, Beaudet F, Carette S, Décary F, Salusinsky-Sternbach M, Hill RO, Gutkowski A, Harth M, Myhal D (1991) Adult Still’s disease: manifestations, disease course, and outcome in 62 patients. Medicine 70:118–136
Fest J, Ruiter R, Mulder M, Groot Koerkamp B, Ikram MA, Stricker BH, van Eijck HJC (2020) The systemic immune-inflammation index is associated with an increased risk of incident cancer—a population-based cohort study. Int J Cancer 146:692–698
Lin J-X, Lin J-P, Xie J-W, Wang J-b LJ, Chen Q-Y, L-l C, Lin M, Tu R, Zheng C-H, Huang C-M, Li P (2020) Complete blood count-based inflammatory score (CBCS) is a novel prognostic marker for gastric cancer patients after curative resection. BMC Cancer 20:1–10
Mitrovic S, Feist E, Fautrel B (2020) Adult-onset Still’s disease. In: Cimaz R (ed) Periodic and non-periodic fevers. Rare Diseases of the Immune System. Springer, Cham, pp 93–132
Maria ATJ, Le Quellec A, Jorgensen C, Touitou I, Riviere S, Guilpain P (2014) Adult onset Still’s disease (AOSD) in the era of biologic therapies: dichotomous view for cytokine and clinical expressions. Autoimmun Rev 13:1149–1159
Mitrovic S, Fautrel B (2018) New markers for adult-onset Still’s disease. Joint Bone Spine 85(3):285–293
Zhao J, Guo N, Zhang L, Wang L (2018) Serum CA125 in combination with ferritin improves diagnostic accuracy for epithelial ovarian cancer. Br J Biomed Sci 75:66–70
Wang X, An P, Zeng J, Liu X, Wang B, Fang X, Wang F, Ren G, Min J (2017) Serum ferritin in combination with prostate-specific antigen improves predictive accuracy for prostate cancer. Oncotarget 8:17862–17872
Seo J-Y, Suh C-H, Jung J-Y, Kim A-R, Yang JW, Kim H-A (2017) The neutrophil-to-lymphocyte ratio could be a good diagnostic marker and predictor of relapse in patients with adult-onset Still’s disease: a STROBE-compliant retrospective observational analysis. Medicine. 96:e7546. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000007546
Yoshikawa T, Furukawa T, Tamura M, Hashimoto T, Morimoto M, Azuma N, Kitano M, Matsui K (2019) Systemic immune-inflammation index in rheumatoid arthritis patients: relation to disease activity. BMJ. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2019-eular.4481
Fu H, Qin B, Hu Z, Ma N, Yang M, Wei T, Tang Q, Huang Y, Huang F, Liang Y, Yang Z, Zhong R (2015) Neutrophil-and platelet-to-lymphocyte ratios are correlated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Lab 61:269–273
Funding
This research was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health and Welfare, Republic of Korea (grant numbers: HI14C1731 and HI16C0992).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
This study was approved by the Institutional Review Board of Ajou University Hospital (AJIRB-MED-OBS-20-113).
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, JW., Jung, JY., Suh, CH. et al. Systemic immune-inflammation index combined with ferritin can serve as a reliable assessment score for adult-onset Still’s disease. Clin Rheumatol 40, 661–668 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05266-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05266-2