Abstract
Objectives
In systemic sclerosis, baseline extent of radiological involvement is an important outcome predictor and baseline absence of radiological involvement suggests a more favourable prognosis. As current predictive models are based on cohorts with variable disease duration, we aim to assess disease dynamics in early disease.
Methods
Patients were included from the prospective longitudinal Belgian Systemic Sclerosis Cohort. We included patients with a disease duration < = 36 months at baseline with available baseline thoracic high-resolution computed tomography (HRCT) images and longitudinal pulmonary function test (PFT) results until 42 months of follow-up.
Results
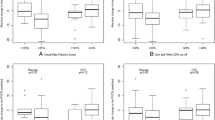
Fifty-two patients were included; 50% were male and 44% suffered from diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. A total of 46% carried anti-topoisomerase 1 antibodies. The mean disease duration at baseline visit was 11 months. At baseline visit, 40.4% (21/52) patients had HRCT abnormalities. Patients with abnormal HRCT findings more frequently suffered from diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (p < 0.05) and less frequently carried anti-centromere antibodies (p < 0.05). Patients without CT abnormalities at baseline had a shorter disease duration (9 ± 7 months versus 14 ± 12 months). After 42 months, 8/52 patients, including 3 patients with normal HRCT findings at baseline, died due to SSc-related manifestations. Progression of lung fibrosis occurred in 16 patients at month 42, including 7 patients with normal CT at baseline. No clear predictors of progression could be identified.
Conclusion
In early SSc patients, the disease dynamics differ from the large published cohorts. Progressive lung fibrosis and mortality can also occur in patients without radiological abnormalities at baseline.
Key Points • Disease dynamics in early SSc differ from more established SSc. • In early SSc, progressive pulmonary fibrosis can occur in patients without CT abnormalities at baseline. • In early SSc, more stringent pulmonary follow-up is warranted both in lcSSc and dcSSc. |

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Steen VD, Medsger TA (2007) Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972-2002. Ann Rheum Dis 66:940–944
Tyndall AJ, Bannert B, Vonk M, Airo P, Cozzi F, Carreira PE, Bancel DF, Allanore Y, Muller-Ladner U, Distler O, Iannone F, Pellerito R, Pileckyte M, Miniati I, Ananieva L, Gurman AB, Damjanov N, Mueller A, Valentini G, Riemekasten G, Tikly M, Hummers L, Henriques MJ, Caramaschi P, Scheja A, Rozman B, Ton E, Kumanovics G, Coleiro B, Feierl E, Szucs G, von Muhlen CA, Riccieri V, Novak S, Chizzolini C, Kotulska A, Denton C, Coelho PC, Kotter I, Simsek I, de la Pena Lefebvre PG, Hachulla E, Seibold JR, Rednic S, Stork J, Morovic-Vergles J, Walker UA (2010) Causes and risk factors for death in systemic sclerosis: a study from the EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research (EUSTAR) database. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1809–1815
Man A, Davidyock T, Ferguson LT, Ieong M, Zhang Y, Simms RW (2015) Changes in forced vital capacity over time in systemic sclerosis: application of group-based trajectory modelling. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54:1464–1471
Wu W, Jordan S, Becker MO, Dobrota R, Maurer B, Fretheim H, Ye S, Siegert E, Allanore Y, Hoffmann-Vold AM, Distler O (2018) Prediction of progression of interstitial lung disease in patients with systemic sclerosis: the SPAR model. Ann Rheum Dis 77:1326–1332
Volkmann ER, Tashkin DP, Sim M, Li N, Goldmuntz E, Keyes-Elstein L, Pinckney A, Furst DE, Clements PJ, Khanna D, Steen V, Schraufnagel DE, Arami S, Hsu V, Roth MD, Elashoff RM, Sullivan KM, SLS I and SLS II study groups (2019) Short-term progression of interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis predicts long-term survival in two independent clinical trial cohorts. Ann Rheum Dis 78:122–130
Goh NS, Desai SR, Veeraraghavan S, Hansell DM, Copley SJ, Maher TM et al (2008) Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a simple staging system. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:1248–1254
Hoffmann-Vold AM, Aalokken TM, Lund MB, Garen T, Midtvedt O, Brunborg C et al (2015) Predictive value of serial high-resolution computed tomography analyses and concurrent lung function tests in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 67:2205–2212
Panopoulos S, Bournia VK, Konstantonis G, Fragiadaki K, Sfikakis PP, Tektonidou MG (2018) Predictors of morbidity and mortality in early systemic sclerosis: long-term follow-up data from a single-centre inception cohort. Autoimmun Rev 17:816–820
van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A, Matucci-Cerinic M, Naden RP, Medsger TA Jr, Carreira PE, Riemekasten G, Clements PJ, Denton CP, Distler O, Allanore Y, Furst DE, Gabrielli A, Mayes MD, van Laar JM, Seibold JR, Czirjak L, Steen VD, Inanc M, Kowal-Bielecka O, Müller-Ladner U, Valentini G, Veale DJ, Vonk MC, Walker UA, Chung L, Collier DH, Csuka ME, Fessler BJ, Guiducci S, Herrick A, Hsu VM, Jimenez S, Kahaleh B, Merkel PA, Sierakowski S, Silver RM, Simms RW, Varga J, Pope JE (2013) 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 65:2737–2747
Vanthuyne M, Smith V, De Langhe E, Van Praet J, Arat S, Depresseux G et al (2012) The Belgian Systemic Sclerosis Cohort: correlations between disease severity scores, cutaneous subsets, and autoantibody profile. J Rheumatol 39:2127–2133
Cutolo M, Sulli A, Pizzorni C, Accardo S (2000) Nailfold videocapillaroscopy assessment of microvascular damage in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 27:155–160
Sambataro G, Vancheri A, Torrisi SE, Colaci M, Pavone M, Libra A, Martorana E, Rosso R, Pignataro F, del Papa N, Malatino L, Palmucci S, Sambataro D, Vancheri C (2020) The morphological domain does not affect the rate of progression to defined autoimmune diseases in patients with interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features. Chest 157:238–242
Jaeger VK, Wirz EG, Allanore Y, Rossbach P, Riemekasten G, Hachulla E, Distler O, Airò P, Carreira PE, Balbir Gurman A, Tikly M, Vettori S, Damjanov N, Müller-Ladner U, Distler JHW, Li M, Walker UA, EUSTAR co-authors (2016) Incidences and risk factors of organ manifestations in the early course of systemic sclerosis: a longitudinal EUSTAR study. PLoS One 11:e0163894
Frantz C, Huscher D, Avouac J, Hachulla E, Balbir-Gurman A, Riemekasten G et al (2020) Outcomes of limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis patients: results on more than 12,000 patients from the EUSTAR database. Autoimmun Rev 19(2):102452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2019.102452
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Vanaken, L., Landini, N., Lenaerts, J. et al. Progressive lung fibrosis and mortality can occur in early systemic sclerosis patients without pulmonary abnormalities at baseline assessment. Clin Rheumatol 39, 3393–3400 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05105-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05105-4