Abstract
Objectives
The aim of the present study is to identify the clinical manifestations and laboratory findings of children with Kawasaki disease (KD) in different age groups and to recognize and treat KD in a timely manner.
Methods
A total of 213 children with KD were divided into the following age groups: (1) infants, (2) toddlers, and (3) preschool age. Retrospective analysis of clinical data was performed among the groups. Categorical data were statistically compared by Chi-square analysis, and measurement data were compared using one-way ANOVA analysis.
Results
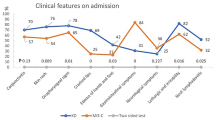
Our study showed that (1) cough (40.5%), diarrhea (16.9%), and vomiting (8.5%) were also very common in KD patients. (2) Patients in the infant group more commonly developed cough and diarrhea, but were less frequently documented with lymphadenopathy and skin rash. (3) Elevation of platelets was more common in the infant group. When urine tests were compared among the three groups, the toddler group had a higher proportion of sterile pyuria, and infants younger than 1 year old had a lower proportion of proteinuria and positive urine ketones.
Conclusion
Cough, diarrhea, vomiting, and sterile pyuria were very common in infant KD patients less than 1 year old. They should be noted in patients with suspected KD for earlier diagnosis and timely treatments.
Key Points | |
• Patients with Kawasaki disease (KD) in different age groups showed different clinical manifestations and laboratory findings. | |
• Cough, diarrhea, vomiting, and sterile pyuria were very common in infant KD patients less than 1 year old. | |
• Paying more attentions to respiratory, gastrointestinal, and urinary manifestations or abnormalities might be helpful for earlier diagnosis of KD, especially incomplete KD, though they were not list in the diagnostic criteria. |
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Newburger JW, Takahashi M, Burns JC (2016) Kawasaki Disease. J Am Coll Cardiol 67(14):1738–1749. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacc.2015.12.073
Soriano-Ramos M, Martinez-Del Val E, Negreira Cepeda S, Gonzalez-Tome MI, Cedena Romero P, Fernandez-Cooke E, Albert de la Torre L, Blazquez-Gamero D (2016) Risk of coronary artery involvement in Kawasaki disease. Arch Argent Pediatr 114(2):107–113. https://doi.org/10.5546/aap.2016.eng.107
McCrindle BW, Rowley AH, Newburger JW, Burns JC, Bolger AF, Gewitz M, Baker AL, Jackson MA, Takahashi M, Shah PB, Kobayashi T, Wu MH, Saji TT, Pahl E, American Heart Association Rheumatic Fever E, Kawasaki Disease Committee of the Council on Cardiovascular Disease in the Y, Council on C, Stroke N, Council on Cardiovascular S, Anesthesia, Council on E, Prevention (2017) Diagnosis, treatment, and long-term Management of Kawasaki Disease: a scientific statement for health professionals from the American Heart Association. Circulation 135(17):e927–e999. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIR.0000000000000484
Chen JJ, Ma XJ, Liu F, Yan WL, Huang MR, Huang M, Huang GY, Shanghai Kawasaki Disease Research G (2016) Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in Shanghai from 2008 through 2012. Pediatr Infect Dis J 35(1):7–12. https://doi.org/10.1097/INF.0000000000000914
Nakamura Y, Yashiro M, Uehara R, Sadakane A, Tsuboi S, Aoyama Y, Kotani K, Tsogzolbaatar EO, Yanagawa H (2012) Epidemiologic features of Kawasaki disease in Japan: results of the 2009-2010 nationwide survey. J Epidemiol 22(3):216–221
Kim JJ, Hong YM, Yun SW, Han MK, Lee KY, Song MS, Lee HD, Kim DS, Sohn S, Ha KS, Hong SJ, Kim KJ, Park IS, Jang GY, Lee JK, Korean Kawasaki Disease Genetics C (2012) Assessment of risk factors for Korean children with Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Cardiol 33(4):513–520. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00246-011-0143-1
Liu HC, Lo CW, Hwang B, Lee PC (2012) Clinical manifestations vary with different age spectrums in infants with Kawasaki disease. ScientificWorldJournal 2012:210382. https://doi.org/10.1100/2012/210382
Burns JC (2018) History of the worldwide emergence of Kawasaki disease. Int J Rheum Dis 21(1):13–15. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13214
Du ZD, Zhao D, Du J, Zhang YL, Lin Y, Liu C, Zhang T, Beijing Kawasaki Research G (2007) Epidemiologic study on Kawasaki disease in Beijing from 2000 through 2004. Pediatr Infect Dis J 26(5):449–451. https://doi.org/10.1097/01.inf.0000261196.79223.18
Huang SK, Lin MT, Chen HC, Huang SC, Wu MH (2013) Epidemiology of Kawasaki disease: prevalence from national database and future trends projection by system dynamics modeling. J Pediatr 163(1):126–131 e121. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2012.12.011
Anderson MS, Todd JK, Glode MP (2005) Delayed diagnosis of Kawasaki syndrome: an analysis of the problem. Pediatrics 115(4):e428–e433. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2004-1824
Wilder MS, Palinkas LA, Kao AS, Bastian JF, Turner CL, Burns JC (2007) Delayed diagnosis by physicians contributes to the development of coronary artery aneurysms in children with Kawasaki syndrome. Pediatr Infect Dis J 26(3):256–260
Soni PR, Noval Rivas M, Arditi M (2020) A comprehensive update on Kawasaki disease vasculitis and myocarditis. Curr Rheumatol Rep 22(2):6–11. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-020-0882-1
Yellen ES, Gauvreau K, Takahashi M, Burns JC, Shulman S, Baker AL, Innocentini N, Zambetti C, Pancheri JM, Ostrow A, Frazer JR, Sundel RP, Fulton DR, Newburger JW (2010) Performance of 2004 American Heart Association recommendations for treatment of Kawasaki disease. Pediatrics 125(2):e234–e241. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0606
Choi JY, Park SY, Choi KH, Park YH, Lee YH (2013) Clinical characteristics of Kawasaki disease with sterile pyuria. Korean J Pediatr 56(1):13–18. https://doi.org/10.3345/kjp.2013.56.1.13
Shiono N, Koga Y, Ito H, Egawa K, Ono S, Itami N (2004) Really sterile pyuria with Kawasaki disease? Pediatr Nephrol 19(1):124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1322-y
Wirojanan J, Sopontammarak S, Vachvanichsanong P (2004) Sterile pyuria in Kawasaki disease. Pediatr Nephrol 19(3):363. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-003-1394-8
Manlhiot C, Yeung RS, Clarizia NA, Chahal N, McCrindle BW (2009) Kawasaki disease at the extremes of the age spectrum. Pediatrics 124(3):e410–e415. https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2009-0099
Rosenfeld EA, Corydon KE, Shulman ST (1995) Kawasaki disease in infants less than one year of age. J Pediatr 126(4):524–529
Cai Z, Zuo R, Liu Y (2011) Characteristics of Kawasaki disease in older children. Clin Pediatr (Phila) 50(10):952–956. https://doi.org/10.1177/0009922811409027
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Fanlei Hu and the American Journal Experts for language editing.
Funding
This work was supported by grants from the National Natural Science Foundation of China (81501396) and Peking University International Hospital Research Funds (YN2017QX01).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shi, L., Li, J., Qie, D. et al. Clinical manifestations of Kawasaki disease in different age groups: retrospective data from Southwest China. Clin Rheumatol 39, 3027–3032 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05069-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05069-5