Abstract
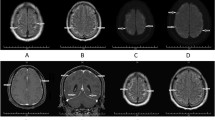
Central nervous system (CNS) involvement, including encephalopathy, encephalitis, leptomeningitis, and pachymeningitis, in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is rather rare. We report the case of a 61-year-old female with a history of RA in remission for 7 years, who presented with numbness, weakness of the left upper limb, dysarthria, and headache. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) of the brain showed meningeal enhancement in the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) examination detected high levels of both rheumatoid factor (RF) and anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody (ACPA), with a high ACPA-immunoglobulin G index (> 2.0). She was diagnosed with rheumatoid meningitis. Following combined therapy with oral prednisolone and intravenous infusion of cyclophosphamide, her symptoms promptly improved. After treatment, RF and ACPA levels in the CSF were reduced, and MRI showed improvement of the meningeal structures. This case, along with existing literature, suggests that the ACPA level in the CSF may serve as a useful marker for diagnosing of CNS involvement in RA, as well as an index of effectiveness of the associated treatment.




Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
22 June 2020
The authors regret that the original published version of the above article contained errors. The authors requested that these be noted.
References
Maher JA (1954) Dural nodules in rheumatoid arthritis. AMA Arch Pathol 58:354–359
Markenson J, McDougal J, Tsairis P, Lockshin MD, Christian CL (1979) Rheumatoid meningitis: a localized immune process. Ann Intern Med 90:786–789. https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-90-5-786
Ronald CK, George HC (1981) The neuropathology of rheumatoid disease. Hum Pathol 12:5–15
Kitamura E, Kondo Y, Kanazawa N, Akutsu T, Nishiyama K, Iizuka T (2019) Autoimmune encephalitis as an extra-articular manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis. Intern Med 58:1007–1009
Jones SE, Belsley NA, Mcloud TC, Mullins ME (2006) Rheumatoid meningitis: radiologic and pathologic correlation. AJR Am J Roentgenol 186:1181–1183
Mori K, Sasaki K, Oketani K, Nakamura S (1969) An autopsy case of rheumatoid encephalopathy. Rinsho Shinkeigaku (Clinical Neurology) 9:613 (conference proceedings)
Zolcinski M, Bazan-Socha S, Zwolinska G, Musial J (2008) Central nervous system involvement as a major manifestation of rheumatoid arthritis. Rheumatol Int 28:281–283
Radic M, Kaliterna DM, Radic J (2013) Overview of vasculitis and vasculopathy in rheumatoid arthritis—something to think about. Clin Rheumatol 32:937–942
Laskari K, Ahmadi-Simab K, Lamken M, Csernok E, Gross WL, Hellmich B (2010) Are anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide autoantibodies seromarkers for rheumatoid vasculitis in a cohort of patients with systemic vasculitis? Ann Rheum Dis 69:469–471
Chowdhry V, Kumar N, Lachance DH, Salomao DR, Luthra HS (2005) An unusual presentation of rheumatoid meningitis. J Neuroimaging 15:286–288. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1552-6569.2005.tb00325.x
Kato T, Hoshi K, Sekijima Y, Matsuda M, Hashimoto T, Otani M, Suzuki A, Ikeda S (2003) Rheumatoid meningitis: an autopsy report and review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 22:475–480. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-003-0788-0
Chou RC, Henson JW, Tian D, Hedley-Whyte ET, Reginato AM (2006) Successful treatment of rheumatoid meningitis with cyclophosphamide but not infliximab. Ann Rheum Dis 65:1114–1116. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2005.042093
Claassen J, Dwyer E, Maybaum S, Elkind MS (2006) Rheumatoid leptomeningitis after heart transplantation. Neurology 66:948–949. https://doi.org/10.1212/01.wnl.0000203516.48914.50
Graus F, Titulaer MJ, Balu R, Benseler S, Bien CG, Cellucci T, Cortese I, Dale RC, Gelfand JM, Geschwind M, Glaser CA, Honnorat J, Höftberger R, Iizuka T, Irani SR, Lancaster E, Leypoldt F, Prüss H, Rae-Grant A, Reindl M, Rosenfeld MR, Rostásy K, Saiz A, Venkatesan A, Vincent A, Wandinger KP, Waters P, Dalmau J (2016) A clinical approach to diagnosis of autoimmune encephalitis. Lancet Neurol 15:391–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1474-4422(15)00401-9
Ichiose S, Oohashi N, Watabe R, Satou S, Hoshi K, YahikoZawa H, Watanabe M (2013) A 57-year-old female case of rheumatoid meningitis with mental symptoms for which anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides antibody in the cerebrospinal fluid was useful for diagnosis. Med J Nagano Red Cross Hosp 27:110–111. (conference proceedings)
Shibahara T, Matsushita T, Matsuo R, Fukushima Y, Fukuda K, Sugimori H, Kamouchi M, Kitazono T, Ago T (2016) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody positive meningoencephalitis in the preclinical period of rheumatoid arthritis. Case Rep Neurol 8:156–160. https://doi.org/10.1159/000447627
Lubomski M, Sy J, Buckland M, Lee AS, Richards B, Thompson E, Fulham M, Breen N, Morris K, Halmagyi GM (2019) Rheumatoid leptomeningitis presenting with an acute neuropsychiatric disorder. Pract Neurol 19:68–71. https://doi.org/10.1136/practneurol-2018-001978
Nissen MS, Nilsson AC, Forsberg J, Milthers J, Wirenfeldt M, Bonde C, Byg KE, Ellingsen T, Blaabjerg M (2019) Use of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers in diagnosis and monitoring of rheumatoid meningitis. Front Neurol 10:666
Asano K, Kamimura N, Tsuchihashi Y, Watanabe D, Takahashi R (2019) A 71-year-old female with rheumatoid meningitis who presented with characteristic imaging findings on brain MRI and was useful for diagnosis by anti-CCP antibody in cerebrospinal fluid. Rinsho Shinkeigaku (Clinical Neurology) 59:299. (conference proceedings)
Suzuki A, Inoue H, Saitou T, Aoki A, Nanzato K (2016) A 40-year-old female case of rheumatoid meningitis for which anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides antibody in the cerebrospinal fluid was useful. Rinsho Shinkeigaku (Clinical Neurology) 56:513 (conference proceedings)
Kawabata Y, Miyaji Y, Nakano T, Joki H, Tanaka F (2015) Aseptic meningitis in a patient with cerebrospinal fluid anti-agalactocyl IgG antibody-positive preclinical rheumatoid arthritis: a case report. Rinsho Shinkeigaku (Clinical Neurology) 55:904–908. https://doi.org/10.5692/clinicalneurol.cn-000754
Abe T, Mishima K, Uchino A, Sasaki A, Tanahashi N, Takao M (2016) A case of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptides antibody positive rheumatoid meningitis without arthritis at the onset of neurological symptoms. Rinsho Shinkeigaku (Clinical Neurology) 56:627–632 https://doi.org/10.5692/clinicalneurol.cn-000915
Ellman P, Cudkowicz L, Elwood JS (1954) Widespread serous membrane involvement by rheumatoid nodules. J Clin Pathol 7:239–244
Shimada K, Matsui T, Kawakami M, Hayakawa H, Futami H, Michishita K, Takaoka H, Ikenaka T, Komiya A, Nakayama H, Hagiwara F, Sugii S, Furukawa H, Ozawa Y, Thoma S (2009) Diffuse chronic leptomeningitis with seropositive rheumatoid arthritis: report of a case successfully treated as rheumatoid leptomeningitis. Mod Rheumatol 19:556–562
Matsushima M, Yamaguchi H, Niino M, Akimoto-Tsuji S, Yabe I, Onishi K, Sasaki H (2010) MRI and pathological findings of rheumatoid meningitis. J Clin Neurosci 17:129–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jocn.2009.01.033
Pascale B, Jean R, Christian B (2014) Rheumatoid meningitis presenting with stroke-like episodes. Neurology 82:1564–1565. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000000366
Bathon JM, Moreland LW, DiBartolomeo AG (1989) Inflammatory central nervous system involvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Semin Arthritis Rheum. 18:258–266. https://doi.org/10.1016/0049-0172(89)90047-4
Magaki S, Chang E, Hammond RR, Yang I, Mackenzie IR, Chou BT, Choi SI, Jen JC, Pope WB, Bell DA, Vinters HV (2016) Two cases of rheumatoid meningitis. Neuropathology 36:93–102. https://doi.org/10.1111/neup.12238
Mukaino A, Kinoshita I, Asai M, Toriyama F, Nakata R, Motomura M, Matsuo T, Hayashi T (2013) A case of meningeal disseminated sarcoidosis with marked hypoglycorrhachia in the CSF. Rinsho Shinkeigaku (Clinical Neurology) 53:367–371. https://doi.org/10.5692/clinicalneurol.53.367
Calabrese LH, Mallek JA (1988) Primary angiitis of the central nervous system. Report of 8 new cases, review of the literature, and proposal for diagnostic criteria. Medicine (Baltimore) 67:20–39. https://doi.org/10.1097/00005792-198801000-00002
Inan AS, Masatlioglu S, Ozyurek SC, Engin D, Erdem I (2011) Unusual central nervous system involvement of rheumatoid arthritis: successful treatment with steroid and azathioprine. Rheumatol Int 31:1383–1385
Choi SJ, Park YH, Kim JA, Han JH, Choe GY, Kim SY (2017) Pearls & Oy-sters: asymmetric meningeal involvement is a common feature of rheumatoid meningitis. Neurology 88:e108–e110. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000003744
Yücel AE, Kart H, Aydin P, Ağildere AM, Benli S, Altinörs N, Demirhan B (2001) Pachymeningitis and optic neuritis in rheumatoid arthritis: successful treatment with cyclophosphamide. Clin Rheumatol 20:136–139. https://doi.org/10.1007/PL00011193
Schmid L, Müller M, Treumann T, Arnold W, Möller B, Aeberli D, Villiger PM (2009) Induction of complete and sustained remission of rheumatoid pachymeningitis by rituximab. Arthritis Rheum 60:1632–1634. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24577
Huys AC, Guerne PA, Horvath J (2012) Rheumatoid meningitis occurring during adalimumab and methotrexate treatment. Joint Bone Spine 79:90–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2011.07.008
Klareskog L, Rönnelid J, Lundberg K, Padyukov L, Alfredsson L (2008) Immunity to citrullinated proteins in rheumatoid arthritis. Annu Rev Immunol. 26:651–675. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev.immunol.26.021607.090244
Felgenhauer K (1982) Differentiation of the humoral immune response in inflammatory diseases of the central nervous system. J Neurol 228:223–237. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf00313413
De Bosscher K, Vanden Berghe W, Haegeman G (2003) The Interplay between the Glucocorticoid Receptor and Nuclear Factor-κB or Activator Protein-1: Molecular Mechanisms for Gene Repression. Endocrine Reviews 24(4):488–522
Hurd ER, Giuliano VJ (1975) The effect of cyclophosphamide on b and t lymphocytes in patients with connective tissue diseases. Arthritis Rheum 18:67–75. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.1780180113
Cambridge G, Leandro MJ, Edwards JC, Ehrenstein MR, Salden M, Bodman-Smith M, Webster AD (2003) Serologic changes following B lymphocyte depletion therapy for rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 48:2146–2154. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.11181
Alessandri C, Bombardieri M, Papa N, Cinquini M, Magrini L, Tincani A, Valesini G (2004) Decrease of anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor following anti-TNFalpha therapy (infliximab) in rheumatoid arthritis is associated with clinical improvement. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1218–1221. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2003.014647
Chen HA, Lin KC, Chen CH, Liao HT, Wang HP, Chang HN, Tsai CY, Chou CT (2006) The effect of etanercept on anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies and rheumatoid factor in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 65:35–39. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2005.038851
Noguchi A, Yasuda S, Hisada R, Kato M, Oku K, Bohgaki T, Suzuki M, Matsumoto Y, Atsumi T (2019) Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody titers decrease in rheumatoid arthritis patients treated with tocilizumab: a pilot study. Mod Rheumatol 21:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2019.1583784
Papadopoulos NG, Tsiaousis GZ, Pavlitou-Tsiontsi A, Giannakou A, Galanopoulou VK (2008) Does the presence of anti-CCP autoantibodies and their serum levels influence the severity and activity in rheumatoid arthritis patients? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 34:11–15. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12016-007-8018-1
Bobbio-Pallavicini F, Alpini C, Caporali R, Avalle S, Bugatti S, Montecucco C (2004) Autoantibody profile in rheumatoid arthritis during long-term infliximab treatment. Arthritis Res Ther 6:R264–R272. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar1173
Clark RA, Gallin JI, Fauci AS (1979) Effects of in vivo prednisone in vitro eosinophil and neutrophil adherence and chemotaxis. Blood 53:633–641
Reiber H, Peter JB (2001) Cerebrospinal fluid analysis: disease-related data patterns and evaluation programs. J Neurol Sci 184:101–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0022-510X(00)00501-3
Acknowledgments
The authors are grateful to Ms. Manami Koyama for supporting data collection in this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Misako Higashida-Konishi, M.D. designed the study; had full access to all of the data used for analyses in this study; contributed to acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data; and wrote the initial draft of the manuscript. Keisuke Izumi, M.D., Ph.D. designed the study, contributed to analysis and interpretation of data, and assisted in drafting the manuscript. All the other authors contributed to data interpretation and critically reviewed the manuscript. All authors approved the final version of the manuscript and agree to be responsible for the accuracy and integrity of the work.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethics approval
All procedures performed in the study were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Consent to participate
The patient provided written informed consent.
Consent for publication
The patient agreed to display all material presented here in any form or medium, in a journal or in any other kind of publication.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Higashida-Konishi, M., Izumi, K., Tsukamoto, M. et al. Anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibody in the cerebrospinal fluid in patients with rheumatoid arthritis who have central nervous system involvement. Clin Rheumatol 39, 2441–2448 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05044-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-05044-0