Abstract
Background
Ankylosing spondylitis (AS) is a common chronic inflammatory arthritis, causing lasting back pain with progressive loss of spinal mobility. However, the exact pathogenesis of AS remains unclear. We aim to use the metabolomics analysis to characterize the metabolic profile of AS, in order to better understand the pathogenesis of AS and monitor disease activity and progression.
Methods
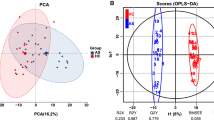
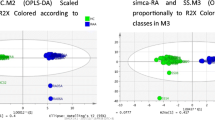
The ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry (UPLC-TQ-MS) was used for investigating the serum amino acid metabolomic profiling of 30 AS patients, in comparison with 32 rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients and 30 healthy controls, combined with multivariate statistical analysis. Metabolite association analysis with disease activity was performed using generalized linear regression. The metabolic pathway analysis for the important metabolites was performed using MetPA and the metabolic network was constructed.
Results
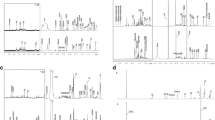
A total of 29 amino acids and biogenic amines were detected in all participants by UPLC-TQ-MS. It showed significant amino acid differences between the AS/RA patients and control subjects. Additionally, 4-hydroxy-L-proline, alanine, γ-aminobutyric acid, glutamine, and taurine were identified as candidate markers shared by AS/RA groups. Specifically, lysine, proline, serine, and alanine were found correlated with disease activity of AS. Furthermore, the most significant metabolic pathway identified were alanine, aspartate, and glutamate metabolism, arginine and proline metabolism, aminoacyl tRNA biosynthesis and glycine, serine, and threonine metabolism.
Conclusions
These preliminary results demonstrate that UPLC-TQ-MS analysis method is a powerful tool to identify metabolite profiles of AS. Research in identified disease activity–associated metabolites and biological pathways may provide assistance for clinical diagnosis and pathological mechanism of AS.
Key Points • There are perturbations of serum amino acid metabolism in AS, compared with RA and healthy controls, determined by UPLC-TQ-MS. • Metabolomics pathway is used to analysis for the differential metabolites of AS. • The altered serum amino acid could monitor disease activity of AS. |






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AS:
-
Ankylosing spondylitis
- RA:
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
- UPLC-TQ-MS:
-
Ultra-high performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole mass spectrometry
- ESI:
-
Electrospray ionization
- PCA:
-
Principal component analysis
- PLS-DA:
-
Partial least squares discriminant analysis
- VIP:
-
Variable importance for project
- KEGG:
-
The Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes
- CRP:
-
C reaction protein
- BCAAs:
-
Branched-chain amino acids
- AAs:
-
Amino acids
- HC:
-
healthy control
- QC:
-
control sample
- VIF:
-
Variance inflation factor
- BMI:
-
Body mass index
- ESR:
-
Erythrocyte sedimentation rate
- BASDAI:
-
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index
- BASFI:
-
Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index
- ASDAS-CRP:
-
Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Score
- mSASSS:
-
modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spinal Score
- ACPA:
-
anti-citrullinated protein/peptide antibodies
- DAS28:
-
Disease activity score 28
- RF:
-
Rheumatoid factor
- ANA:
-
Antinuclear antibodies
References
Nossent JC, Sagen-Johnsen S, Bakland G (2019) Disease activity and patient-reported health measures in relation to cytokine levels in ankylosing spondylitis. Rheumatol Ther. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40744-019-0161-7
Ciurtin C, Cojocaru VM, Miron IM, Preda F, Milicescu M, Bojincă M, Costan O, Nicolescu A, Deleanu C, Kovàcs E, Stoica V (2006) Correlationbetween different components of synovial fluid and pathogenesis of rheumatic diseases. Rom J Intern Med 44:171–181
Hanson A, Brown MA (2017 Aug) Genetics and the causes of ankylosing spondylitis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 43(3):401–414. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rdc.2017.04.006
Ranganathan V, Gracey E, Brown MA, Inman RD, Haroon N (2017) Pathogenesis ofankylosing spondylitis - recent advances and future directions. Nat Rev Rheumatol 13(6):359–367. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrrheum.2017.56
Reveille JD (2015) Biomarkers for diagnosis, monitoring of progression, and treatment responses in ankylosing spondylitis and axial spondyloarthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34(6):1009–1018. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2949-3
Chen C, Rong T, Li Z, Shen J (2019) Noncoding RNAs involved in the pathogenesis of ankylosing spondylitis. Biomed Res Int 2019:6920281. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6920281 eCollection 2019
Yin R, Yang T, Su H, Ying L, Liu L, Sun C (2016) Saturated fatty acids as possibleimportant metabolites for epithelial ovarian cancer based on the free and esterified fatty acid profiles determined by GC-MS analysis. Cancer Biomark 17:259–269
Zheng K, Shen N, Chen H, Ni S, Zhang T et al (2017) Global and targeted metabolomicsof synovial fluid discovers special osteoarthritis metabolites. J Orthop Res 35:1973–1981
Li J, Che N, Xu L, Zhang Q, Wang Q, Tan W, Zhang M (2018) LC-MS-based serum metabolomics reveals a distinctive signature in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 37:1493–1502
Chen R, Han S, Liu X, Wang K, Zhou Y, Yang C, Zhang X (2018) Perturbations in amino acids and metabolic pathways in osteoarthritis patients determined by targeted metabolomics analysis. J Chromatogr B Analyt Technol Biomed Life Sci 1085:54–62
Karami J, Aslani S, Jamshidi A, Garshasbi M, Mahmoudi M (2019) Genetic implications in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis; an updated review. Gene 702:8–16
Moran-Moguel MC, Petarra-Del Rio S, Mayorquin-Galvan EE, Zavala-Cerna MG (2018) Rheumatoid arthritis and miRNAs: a critical review through a functional view. J Immunol Res 2018:2474529
Jiang M, Chen T, Feng H, Zhang Y, Li L, Zhao A, Niu X, Liang F, Wang M, Zhan J, Lu C, He X, Xiao L, Jia W, Lu A (2013) Serum metabolic signatures of four types of human arthritis. J Proteome Res 12(8):3769–3779. https://doi.org/10.1021/pr400415a
Chen R, Han S, Dong D, Wang Y, Liu Q, Xie W, Li M, Yao M (2015) Serum fatty acid profiles and potential biomarkers of ankylosing spondylitis determined by gas chromatography-mass spectrometry and multivariate statistical analysis. Biomed Chromatogr 29(4):604–611. https://doi.org/10.1002/bmc.3321
Fischer R, Trudgian DC, Wright C, Thomas G, Bradbury LA, Brown MA, Bowness P, Kessler BM (2012) Discovery of candidate serum proteomic and metabolomic biomarkers in ankylosing spondylitis. Mol Cell Proteomics 11(2):M111013904
Gao P, Lu C, Zhang F, Sang P, Yang D, Li X, Kong H, Yin P, Tian J, Lu X, Lu A, Xu G (2008) Integrated GC-MS and LC-MS plasma metabonomics analysis of ankylosing spondylitis. Analyst 133(9):1214–1220
Sasaki C, Hiraishi T, Oku T, Okuma K, Suzumura K et al (2019) Metabolomic approach to the exploration of biomarkers associated with disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 14(7):e0219400. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0219400 eCollection 2019
Miyagi Y, Higashiyama M, Gochi A, Akaike M, Ishikawa T et al (2011) Plasma free amino acid profiling of five types of cancer patients and its application for early detection. PLoS One 6:e24143
Smolenska Z, Smolenski RT, Zdrojewski Z (2016) Plasma concentrations of amino acid and nicotinamide metabolites in rheumatoid arthritis--potential biomarkers of disease activity and drug treatment. Biomarkers 21:218–224
Hisamatsu T, Okamoto S, Hashimoto M, Muramatsu T, Andou A et al (2012) Novel, objective, multivariate biomarkers composed of plasma amino acid profiles for the diagnosis and assessment of inflammatory bowel disease. PLoS One 7:e31131
Mahbub MH, Yamaguchi N, Takahashi H, Hase R, Amano H et al (2017) Alteration in plasma free amino acid levels and its association with gout. Environ Health Prev Med 22(1):7. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12199-017-0609-8
He M, Harms AC, Wijk E, Wang M, Berger R et al (2019) Role of amino acids in rheumatoid arthritis studied by metabolomics. Int J Rheum Dis 22(1):38–46. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.13062
Rudwaleit M, Braun J, Sieper J (2009) ASAS classification criteria for axial spondyloarthritis. Z Rheumatol 68:591–593
Law L, Beckman Rehnman J, Deminger A, Klingberg E, Jacobsson LTH, Forsblad-d’Elia H (2018) Factors related to health-related quality of life in ankylosing spondylitis, overall and stratified by sex. Arthritis Res Ther 20(1):284. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1784-8
Law L, Beckman Rehnman J, Deminger A, Klingberg E, Jacobsson LTH, Forsblad-d'Elia H (2018) Factorsrelatedtohealth-related quality of lifeinankylosing spondylitis, overall andstratifiedbysex. Arthritis Res Ther 20(1):284. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13075-018-1784-8
Creemers MC, Franssen MJ, van't Hof MA, Gribnau FW, van de Putte LB et al (2005) Assessment of outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: an extended radiographic scoringsystem. Ann Rheum Dis 64(1):127–129
Liu L, Feng R, Guo F, Li Y, Jiao J, Sun C (2015) Targeted metabolomic analysis reveals the association between the postprandial change in palmitic acid, branched-chain amino acids and insulin resistance in young obese subjects. Diabetes Res Clin Pract 108:84–93
Liu L, Wang X, Li Y, Sun C (2015) Postprandial differences in the amino acid and biogenic amines profiles of impaired fasting glucose individuals after intake of highland barley. Nutrients 7:5556–5571
Wang W, Yang GJ, Zhang J, Chen C, Jia ZY et al (2016) Plasma, urine and ligament tissue metabolite profiling reveals potential biomarkers of ankylosing spondylitis using NMR-based metabolic profiles. Arthritis Res Ther 18:244
Carlson AK, Rawle RA, Adams E, Greenwood MC, Bothner B et al (2018) Application of global metabolomic profiling of synovial fluid for osteoarthritis biomarkers. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 499:182–188
Jain A, Kumar D, Guleria A, Misra DP, Zanwar A, Chaurasia S, Kumar S, Kumar U, Mishra SK, Goel R, Danda D, Misra R (2018) NMR-based serum metabolomics of patients with takayasu arteritis: relationship with disease activity. J Proteome Res 17(9):3317–3324. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.jproteome.8b00456
Li Y, Xiao W, Luo W, Zeng C, Deng Z et al (2016) Alterations of amino acid metabolism in osteoarthritis: its implications for nutrition and health. Amino Acids 48:907–914
Zhou J, Chen J, Hu C, Xie Z, Li H, Wei S, Wang D, Wen C, Xu G (2016) Exploration of the serum metabolite signature in patients with rheumatoid arthritis using gas chromatography-mass spectrometry. J Pharm Biomed Anal 127:60–67
Vuckovic D (2012) Current trends and challenges in sample preparation for global metabolomics using liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry. Anal Bioanal Chem 403:1523–1548
Marcinkiewicz J, Kontny E (2014) Taurine and inflammatory diseases. Amino Acids 46:7–20
Yang G, Zhang H, Chen T, Zhu W, Ding S, Xu K, Xu Z, Guo Y, Zhang J (2016) Metabolic analysis of osteoarthritis subchondral bone based on UPLC/Q-TOF-MS. Anal Bioanal Chem 408:4275–4286
Glass GG (2006) Osteoarthritis. Dis Mon 52:343–362
Tatar Z, Migne C, Petera M, Gaudin P, Lequerre T, Marotte H, Tebib J, Pujos Guillot E, Soubrier M (2016) Variations in the metabolome in response to disease activity of rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 17(1):353. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12891-016-1214-5
Zhai G, Wang-Sattler R, Hart DJ, Arden NK, Hakim AJ, Illig T, Spector TD (2010) Serum branched-chain amino acid to histidine ratio: a novel metabolomic biomarker of knee osteoarthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 69(6):1227–1231. https://doi.org/10.1136/ard.2009.120857
Funding
This work was supported by the Harbin medical university scientific research innovation fund (No. 2017LCZX98) and the Foundation of Heilongjiang Provincial Health Bureau (No. 2017-146), and Heilongjiang province postdoctoral fund (LBH-Z17142).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
R.C., X.Z., and Y. Z. conceived and designed the experiments; R.C., Y.Z., X.Z., and S.H. performed the experiments; R.C. and S.H. analyzed the data; B.S., H.C., Y.L., X.L., M.G., C.Y., and D.L. contributed reagents/materials/analysis tools; R.C. and S.H. wrote the paper.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The study was approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University and conducted in accordance with the tenets of the Declaration of Helsinki. Written informed consent was approved by the Ethics Committee of Harbin Medical University and collected from each participant included in the study.
Disclosures
None.
Disclaimer
The funders had no role in study design, data collection and analysis, preparation of the manuscript, or decision to publish.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Supplementary date (Fig. S1-S2 and Table S1-S16) associated with this article can be found in the online version.
ESM 1
(DOC 411 kb)
Fig. S1
PCA scores plot showing clustering of quality control (QC) samples. Red, QC; Blue, Healthy control. (PNG 157 kb)
Fig. S2
Mapping the rheumatoid arthritis-related metabolites in metabolic pathways. The metabolites marked in red indicate significantly increased in rheumatoid arthritis, and green indicates decreased, blue indicates unchanged and gray indicates un-investigated. (PNG 102 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Zhang, X., Chen, R. et al. Serum amino acid metabolic profiles of ankylosing spondylitis by targeted metabolomics analysis. Clin Rheumatol 39, 2325–2336 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04974-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04974-z