Abstract
Introduction/Objectives
A line blot (LB) assay is a multi-analyte platform capable of simultaneously detecting multiple anti-nuclear antibody specificities. Here, we evaluated the performance of a commercial LB assay developed for the identification of myositis- or systemic sclerosis (SSc)-related autoantibodies (autoAbs).
Method
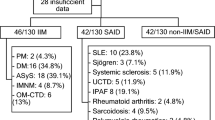
We screened 300 serum samples from patients with various connective tissue diseases using an LB assay and compared the results of myositis- or SSc-related autoAbs with those identified by RNA and protein immunoprecipitation (IP) assays or indirect immunofluorescence (IIF).
Results
The IP assays revealed anti-Jo-1 Abs in 14 patients, anti-EJ Abs in 12, anti-PL-7 Abs in 8, anti-PL-12 Abs in 4, anti-Mi-2 Abs in 6, anti-SRP Abs in 8, anti-topoisomerase I Abs in 54, anti-RNA polymerase III Abs in 24, anti-U3 RNP Abs in 9, anti-Th/To Abs in 9, anti-Ku Abs in 14 and anti-hUBF Abs in 4, whereas IIF identified anti-centromere in 35. Good agreement between the IP assays and the LB assay was found only for anti-Jo-1 and anti-centromere antibodies. When a cut-off was adjusted to reconcile with the results of IP assays, the detection performance of LB assay was improved for anti-EJ, anti-PL-7, anti-PL-12, anti-SRP, anti-topoisomerase I and anti-RNA polymerase III Abs. However, the results of anti-Mi-2, anti-U3 RNP, anti-Th/To, anti-hUBF and anti-Ku Abs remained discordant between the LB assay and IP assays at all cut-off levels.
Conclusions
Detection of myositis- or SSc-related autoAbs using a commercial LB assay requires great caution since it can yield analytically false-positive or false-negative results.
Key Points • A line blot (LB) assay is a multi-analyte platform capable of simultaneously detecting multiple antibodies with anti-nuclear specificities. • Detection of myositis- or systemic sclerosis-related autoantibodies using a commercial LB assay requires great caution since it can yield analytically false-positive or false-negative results. |
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Targoff IN (2002) Laboratory testing in the diagnosis and management of idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Rheumatic diseases clinics of North America 28(4):859–890
McHugh NJ, Tansley SL (2018) Autoantibodies in myositis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 14(5):290–302
Steen VD (2005) Autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 35(1):35–42
Hamaguchi Y (2010) Autoantibody profiles in systemic sclerosis: predictive value for clinical evaluation and prognosis. J Dermatol 37(1):42–53
Hamaguchi Y, Takehara K (2018) Anti-nuclear autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis: news and perspectives. J Scleroderma Relat Dis 3(3):201–213
Fujimoto M, Watanabe R, Ishitsuka Y, Okiyama N (2016) Recent advances in dermatomyositis-specific autoantibodies. Curr Opin Rheumatol 28(6):636–644
Ho KT, Reveille JD (2003) The clinical relevance of autoantibodies in scleroderma. Arthritis Res Ther 5(2):80–93
Cruellas MG, Viana Vdos S, Levy-Neto M, Souza FH, Shinjo SK (2013) Myositis-specific and myositis-associated autoantibody profiles and their clinical associations in a large series of patients with polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clinics (Sao Paulo) 68(7):909–914
Song JS, Hwang J, Cha HS, Jeong BH, Suh GY, Chung MP, Kang ES (2015) Significance of myositis autoantibody in patients with idiopathic interstitial lung disease. Yonsei Med J 56(3):676–683
Patterson KA, Roberts-Thomson PJ, Lester S, Tan JA, Hakendorf P, Rischmueller M, Zochling J, Sahhar J, Nash P, Roddy J, Hill C, Nikpour M, Stevens W, Proudman SM, Walker JG (2015) Interpretation of an extended autoantibody profile in a well-characterized australian systemic sclerosis (Scleroderma) cohort using principal components analysis. Arthritis Rheumatol 67(12):3234–3244
Sujau I, Ng CT, Sthaneshwar P, Sockalingam S, Cheah TE, Yahya F, Jasmin R (2015) Clinical and autoantibody profile in systemic sclerosis: baseline characteristics from a West Malaysian cohort. Int J Rheum Dis 18(4):459–465
Mejia M, Herrera-Bringas D, Perez-Roman DI, Rivero H, Mateos-Toledo H, Castorena-García P, Figueroa JE, Rojas-Serrano J (2017) Interstitial lung disease and myositis-specific and associated autoantibodies: Clinical manifestations, survival and the performance of the new ATS/ERS criteria for interstitial pneumonia with autoimmune features (IPAF). Respir Med 123:79–86
Yang H, Peng Q, Yin L, Li S, Shi J, Zhang Y, Lu X, Shu X, Zhang S, Wang G (2017) Identification of multiple cancer-associated myositis-specific autoantibodies in idiopathic inflammatory myopathies: a large longitudinal cohort study. Arthritis Res Ther 19(1):259–267
Aouizerate J, De Antonio M, Bader-Meunier B, Barnerias C, Bodemer C, Isapof A, Quartier P, Melki I, Charuel JL, Bassez G, Desguerre I, Gherardi RK, Authier FJ, Gitiaux C (2018) Muscle ischaemia associated with NXP2 autoantibodies: a severe subtype of juvenile dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford). 57(5):873–879
Chen F, Li S, Wang T, Shi J, Wang G (2018) Clinical heterogeneity of interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis patients with or without specific autoantibodies. Am J Med Sci. 355(1):48–53
Bohan A, Peter JB (1975) Polymyositis and dermatomyositis (second of two parts). N Engl J Med 292(8):403–407
Anonymous (1980) Preliminary criteria for the classification of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma). Subcommittee for Scleroderma Criteria of the American Rheumatism Association Diagnostic and Therapeutic Criteria Committee. Arthritis Rheum 23:581–590
Tan EM, Cohen AS, Fries JF, Masi AT, McShane DJ, Rothfield NF, Schaller JG, Talal N, Winchester RJ (1982) The 1982 revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 25:1271–1277
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Bloch DA, Mcshane DJ, Fries JF, Cooper NS, Healey LA, Kaplan SR, Liang MH, Luthra HS, Medsger TA Jr, Mitchell DM, Neustadt DH, Pinals RS, Schaller JG, Sharp JT, Wilder RL, Hunder GG (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31(3):315–324
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan SS, Pillemer SR, Talal N, Weisman MH, European Study Group on Classification Criteria for Sjögren's Syndrome (2002) Classification criteria for Sjogren's syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European Consensus Group. Ann Rheum Dis 61(6): 554-558
Moroi Y, Peebles C, Fritzler MJ, Steigerwald J, Tan EM (1980) Autoantibody to centromere (kinetochore) in scleroderma sera. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 77(3):1627–1631
Hamaguchi Y, Kuwana M, Hoshino K, Hasegawa M, Kaji K, Matsushita T, Komura K, Nakamura M, Kodera M, Suga N, Higashi A, Ogusu K, Tsutsui K, Furusaki A, Tanabe H, Sasaoka S, Muro Y, Yoshikawa M, Ishiguro N, Ayano M, Muroi E, Fujikawa K, Umeda Y, Kawase M, Mabuchi E, Asano Y, Sodemoto K, Seishima M, Yamada H, Sato S, Takehara K, Fujimoto M (2011) Clinical correlations with dermatomyositis-specific autoantibodies in adult Japanese patients with dermatomyositis: a multicenter cross-sectional study. Arch Dermatol 147(4):391–398
Fujimoto M, Matsushita T, Hamaguchi Y, Asano Y, Ogawa F, Yamaoka T, Fujikawa K, Tsukada T, Sato K, Echigo T, Hasegawa M, Takehara K (2013) Autoantibodies to small ubiquitin-like modifier activating enzymes in Japanese patients with dermatomyositis: comparison with a UK Caucasian cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 72(1):151–153
Hamaguchi Y, Hasegawa M, Fujimoto M, Matsushita T, Komura K, Kaji K, Kondo M, Nishijima C, Hayakawa I, Ogawa F, Kuwana M, Takehara K, Sato S (2018) The clinical relevance of serum antinuclear antibodies in Japanese patients with systemic sclerosis. Br J Dermatol 158(3):487–495
Suzuki S, Satoh T, Sato S, Otomo M, Hirayama Y, Sato H, Kawai M, Ishihara T, Suzuki N, Kuwana M (2008) Clinical utility of anti-signal recognition particle antibody in the differential diagnosis of myopathies. Rheumatology (Oxford) 47(10):1539–1542
Hamaguchi Y, Fujimoto M, Matsushita T, Kaji K, Komura K, Hasegawa M, Kodera M, Muroi E, Fujikawa K, Seishima M, Yamada H, Yamada R, Sato S, Takehara K, Kuwana M (2013) Common and distinct clinical features in adult patients with anti-aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase antibodies: heterogeneity within the syndrome. PLoS One 8(4):e60442
Satoh T, Ishikawa O, Ihn H, Endo H, Kawaguchi Y, Sasaki T, Goto D, Takahashi K, Takahashi H, Misaki Y, Mimori T, Muro Y, Yazawa N, Sato S, Takehara K, Kuwana M (2009) Rheumatology (Oxford) 48(12):1570–1574
Suzuki S, Hayashi YK, Kuwana M, Tsuburaya R, Suzuki N, Nishino I (2012) Myopathy associated with antibodies to signal recognition particle: disease progression and neurological outcome. Arch Neurol 69(6):728–732
Hamaguchi Y, Kodera M, Matsushita T et al (2015) Clinical and immunologic predictors of scleroderma renal crisis in japanese systemic sclerosis patients with anti-rna polymerase III autoantibodies. Arthritis Rheumatol 67(4):1045–1052
Aggarwal R, Dhillon N, Fertig N, Koontz D, Qi Z, Oddis CV (2017) A negative antinuclear antibody does not indicate autoantibody negativity in myositis: role of anticytoplasmic antibody as a screening test for antisynthetase syndrome. J Rheumatol 44(2):223–229
Homer KL, Warren J, Karayev D, Khanna PP, Young A, Nagaraja V, Metzger AL, Khanna D (2018) Performance of anti-topoisomerase i antibody testing by multiple-bead, enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay and immunodiffusion in a university setting. J Clin Rheumatol
Cavazzana I, Fredi M, Ceribelli A, Mordenti C, Ferrari F, Carabellese N, Tincani A, Satoh M, Franceschini F (2016) Testing for myositis specific autoantibodies: Comparison between line blot and immunoprecipitation assays in 57 myositis sera. J Immunol Methods 433:1–5
Kuwana M (2017) Circulating Anti-Nuclear Antibodies in Systemic Sclerosis: Utility in Diagnosis and Disease Subsetting J Nippon Med Sch 84(2):56–63
Hamaguchi Y, Kuwana M, Takehara K (2017) Comparison of anti-OJ antibody detection assays between an immunoprecipitation assay and line blot assay. Mod Rheumatol. 27(3):551–552
Vulsteke JB, Satoh M, Malyavantham K, Bossuyt X, De Langhe E, Mahler M (2019) Anti-OJ autoantibodies: Rare or underdetected? Autoimmun Rev 18(7):658–664
Espinosa-Ortega F, Holmqvist M, Alexanderson H, Storfors H, Mimori T, Lundberg IE, Rönnelid J (2019) Comparison of autoantibody specificities tested by a line blot assay and immunoprecipitation-based algorithm in patients with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies. Ann Rheum Dis 78(6):858–860
Mahler M, Betteridge Z, Bentow C, Richards M, Seaman A, Chinoy H, McHugh N (2019) Comparison of three immunoassays for the detection of myositis specific antibodies. Front Immunol 10:848
Vulsteke JB, De Langhe E, Claeys KG, Dillaerts D, Poesen K, Lenaerts J, Westhovens R, Van Damme P, Blockmans D, De Haes P, Bossuyt X (2019) Detection of myositis-specific antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis 78(1):e7
Montagnese F, Babacic H, Eichhorn P, Schoser B (2019) Evaluating the diagnostic utility of new line immunoassays for myositis antibodies in clinical practice: a retrospective study. J Neurol 266(6):1358–1366
Zampeli E, Venetsanopoulou A, Argyropoulou OD, Mavragani CP, Tektonidou MG, Vlachoyiannopoulos PG, Tzioufas AG, Skopouli FN, Moutsopoulos HM (2019) Myositis autoantibody profiles and their clinical associations in Greek patients with inflammatory myopathies. Clin Rheumatol 38(1):125–132
Bundell C, Rojana-Udomsart A, Mastaglia F, Hollingsworth P, McLean-Tooke A (2016) Diagnostic performance of a commercial immunoblot assay for myositis antibody testing. Pathology 48(4):363–366
Chang WS, Schollum J, White DH, Solanki KK (2015) A cross-sectional study of autoantibody profiles in the Waikato systemic sclerosis cohort, New Zealand. Clin Rheumatol 34(11):1921–1927
Foocharoen C, Watcharenwong P, Netwijitpan S, Mahakkanukrauh A, Suwannaroj S, Nanagara R (2017) Relevance of clinical and autoantibody profiles in systemic sclerosis among Thais. Int J Rheum Dis 20(10):1572–1581
Acknowledgments
We thank Ms. Masako Matsubara and Natsuho Yoshifuji for their technical assistance.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Financial support
None.
Informed consent
All study participants provided written informed consent. The protocol was approved by Kanazawa University and Keio University.
Disclosures
M.K. received patent fees from MBL, INOVA, and Phadia. Other authors have no conflict of interest to declare.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hamaguchi, Y., Kuwana, M. & Takehara, K. Performance evaluation of a commercial line blot assay system for detection of myositis- and systemic sclerosis-related autoantibodies. Clin Rheumatol 39, 3489–3497 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04973-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-020-04973-0