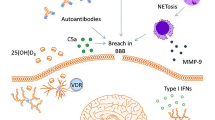
Abstract
Objective
Central nervous system disease occurs in over 20% of patients with systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) resulting in major morbidity and damage. Cognitive dysfunction is common in SLE, but the cause remains uncertain and treatment options are limited. This study explores the influence of clinical, neuropsychological factors and anti-neuronal antibodies on lupus damage accrual.
Method
A prospective cohort with 99 SLE patients recruited between 2008 and 2013 and followed up in 2016 was established. Baseline evaluations were depression (MINI-Plus), cognitive function evaluating attention, visuospatial memory and executive functions, and anti-neuronal antibodies. Activity index (SLEDAI-2K) and SLICC/ACR Damage Index (SDI) were assessed at baseline and last follow-up.
Results
At baseline, median (interquartile range) age was 36.0 years (27.0–45.0), disease duration 3.7 years (0.4–12.4), SLEDAI-2K 6.0 (3.0–12.0), and SDI score 1.0 (0–1.0). Major depression was present in 23%, cognitive deficit in 18%, and received immunomodulators in 36%. Anti-dsDNA/N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor antibodies were present in 19%, anti-ribosomal P in 12%, and anti-neuronal surface P antigen (NSPA) in 5%. After a median follow-up of 55 months (interquartile range 39–78), 11% had damage accrual. In a multivariate analysis, baseline SDI, SLEDAI-2K, and immunomodulators use were associated with final damage, whereas SLEDAI-2K and immunomodulator use were also associated with accrual damage. Models including anti-NSPA showed impact on final and accrual damage. Cognitive deficit, depression, and other autoantibodies were not predictors.
Conclusions
Disease activity and immunomodulator use associate with lupus damage. Of the anti-neuronal antibodies examined, anti-NSPA emerged as a potential poor prognostic factor, probably related to severe SLE onset requiring elevated corticosteroid doses.
Key Points • Anti-NSPA may be a worse prognostic factor in SLE. • Other neuropsychological factors do not influence damage. |
Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The datasets analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
References
Kaul A, Gordon C, Crow MK, Touma Z, Urowitz MB, van Vollenhoven R, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Hughes G (2016) Systemic lupus erythematosus. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16039
Sutton EJ, Davidson JE, Bruce IN (2013) The systemic lupus international collaborating clinics (SLICC) damage index: a systematic literature review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 43:352–361
Yee CS, Su L, Toescu V, Hickman R, Situnayake D, Bowman S, Farewell V, Gordon C (2015) Birmingham SLE cohort: outcomes of a large inception cohort followed for up to 21 years. Rheumatology (Oxford) 54:836–843
Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Goldsmith CH, Fortin P, Ginzler E, Gordon C, Hanly JG, Isenberg DA, Kalunian K, Nived O, Petri M, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Snaith M, Sturfelt G (1997) The reliability of the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics/American College of Rheumatology Damage Index in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:809–813
Taraborelli M, Cavazzana I, Martinazzi N, Lazzaroni MG, Fredi M, Andreoli L, Franceschini F, Tincani A (2017) Organ damage accrual and distribution in systemic lupus erythematosus patients followed-up for more than 10 years. Lupus 26:1197–1204
Alarcon GS, McGwin G Jr, Bartolucci AA, Roseman J, Lisse J, Fessler BJ, Bastian HM, Friedman AW, Reveille JD, Lumina Study Group. Lupus in Minority Populations NvN (2001) Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups. IX. Differences in damage accrual. Arthritis Rheum 44:2797–2806
Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Rahman P, Ibanez D, Tam LS (2003) Accrual of organ damage over time in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 30:1955–1959
Mok CC, Ho CT, Wong RW, Lau CS (2003) Damage accrual in southern Chinese patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 30:1513–1519
Bruce IN, O’Keeffe AG, Farewell V, Hanly JG, Manzi S, Su L, Gladman DD, Bae SC, Sanchez-Guerrero J, Romero-Diaz J, Gordon C, Wallace DJ, Clarke AE, Bernatsky S, Ginzler EM, Isenberg DA, Rahman A, Merrill JT, Alarcón GS, Fessler BJ, Fortin PR, Petri M, Steinsson K, Dooley MA, Khamashta MA, Ramsey-Goldman R, Zoma AA, Sturfelt GK, Nived O, Aranow C, Mackay M, Ramos-Casals M, van Vollenhoven RF, Kalunian KC, Ruiz-Irastorza G, Lim S, Kamen DL, Peschken CA, Inanc M, Urowitz MB (2015) Factors associated with damage accrual in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: results from the Systemic Lupus International Collaborating Clinics (SLICC) Inception Cohort. Ann Rheum Dis 74:1706–1713
Fessler BJ, Alarcon GS, McGwin G Jr, Roseman J, Bastian HM, Friedman AW, Baethge BA, Vila L, Reveille JD, Group LS (2005) Systemic lupus erythematosus in three ethnic groups: XVI. Association of hydroxychloroquine use with reduced risk of damage accrual. Arthritis Rheum 52:1473–1480
Borowoy AM, Pope JE, Silverman E, Fortin PR, Pineau C, Smith CD, Arbillaga H, Gladman D, Urowitz M, Zummer M, Hudson M, Tucker L, Peschken C (2012) Neuropsychiatric lupus: the prevalence and autoantibody associations depend on the definition: results from the 1000 faces of lupus cohort. Semin Arthritis Rheum 42:179–185
Brey RL, Holliday SL, Saklad AR, Navarrete MG, Hermosillo-Romo D, Stallworth CL, Valdez CR, Escalante A, del Rincon I, Gronseth G, Rhine CB, Padilla P et al (2002) Neuropsychiatric syndromes in lupus: prevalence using standardized definitions. Neurology 58:1214–1220
Hanly JG (2014) Diagnosis and management of neuropsychiatric SLE. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10:338–347
Tomietto P, Annese V, D’Agostini S, Venturini P, La Torre G, De Vita S, Ferraccioli GF (2007) General and specific factors associated with severity of cognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 57:1461–1472
Petri M, Naqibuddin M, Carson KA, Sampedro M, Wallace DJ, Weisman MH, Holliday SL, Padilla PA, Brey RL (2008) Cognitive function in a systemic lupus erythematosus inception cohort. J Rheumatol 35:1776–1781
Conti F, Alessandri C, Perricone C, Scrivo R, Rezai S, Ceccarelli F, Spinelli FR, Ortona E, Marianetti M, Mina C, Valesini G (2012) Neurocognitive dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus: association with antiphospholipid antibodies, disease activity and chronic damage. PLoS One 7:e33824
Ceccarelli F, Perricone C, Pirone C, Massaro L, Alessandri C, Mina C, Marianetti M, Spinelli FR, Valesini G, Conti F (2018) Cognitive dysfunction improves in systemic lupus erythematosus: results of a 10 years prospective study. PLoS One 13:e0196103
Calderon J, Flores P, Babul M, Aguirre JM, Slachevsky A, Padilla O, Scoriels L, Henriquez C, Carcamo C, Bravo-Zehnder M, Gonzalez A, Massardo L (2014) Systemic lupus erythematosus impairs memory cognitive tests not affected by depression. Lupus 23:1042–1053
Massardo L, Bravo-Zehnder M, Calderon J, Flores P, Padilla O, Aguirre JM, Scoriels L, Gonzalez A (2015) Anti-N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor and anti-ribosomal-P autoantibodies contribute to cognitive dysfunction in systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus 24:558–568
Diamond B, Huerta PT, Mina-Osorio P, Kowal C, Volpe BT (2009) Losing your nerves? Maybe it’s the antibodies. Nat Rev Immunol 9:449–456
Tay SH, Fairhurst AM, Mak A (2017) Clinical utility of circulating anti-N-methyl-d-aspartate receptor subunits NR2A/B antibody for the diagnosis of neuropsychiatric syndromes in systemic lupus erythematosus and Sjogren’s syndrome: an updated meta-analysis. Autoimmun Rev 16:114–122
Gonzalez A, Massardo L (2018) Antibodies and the brain: antiribosomal P protein antibody and the clinical effects in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Neurol 31:300–305
Lakhan SE, Caro M, Hadzimichalis N (2013) NMDA receptor activity in neuropsychiatric disorders. Front Psychiatry 4:52
Bonfa E, Golombek SJ, Kaufman LD, Skelly S, Weissbach H, Brot N, Elkon KB (1987) Association between lupus psychosis and anti-ribosomal P protein antibodies. N Engl J Med 317:265–271
Matus S, Burgos PV, Bravo-Zehnder M, Kraft R, Porras OH, Farias P, Barros LF, Torrealba F, Massardo L, Jacobelli S, Gonzalez A (2007) Antiribosomal-P autoantibodies from psychiatric lupus target a novel neuronal surface protein causing calcium influx and apoptosis. J Exp Med 204:3221–3234
Segovia-Miranda F, Serrano F, Dyrda A, Ampuero E, Retamal C, Bravo-Zehnder M, Parodi J, Zamorano P, Valenzuela D, Massardo L, van Zundert B, Inestrosa NC, González A (2015) Pathogenicity of lupus anti-ribosomal P antibodies: role of cross-reacting neuronal surface P antigen in glutamatergic transmission and plasticity in a mouse model. Arthritis Rheumatol 67:1598–1610
Bravo-Zehnder M, Toledo EM, Segovia-Miranda F, Serrano FG, Benito MJ, Metz C, Retamal C, Alvarez A, Massardo L, Inestrosa NC, Gonzalez A (2015) Anti-ribosomal P protein autoantibodies from patients with neuropsychiatric lupus impair memory in mice. Arthritis Rheumatol 67:204–214
Calderon J, Flores P, Aguirre JM, Valdivia G, Padilla O, Barra I, Scoriels L, Herrera S, Gonzalez A, Massardo L (2017) Impact of cognitive impairment, depression, disease activity, and disease damage on quality of life in women with systemic lupus erythematosus. Scand J Rheumatol 46:273–280
Hochberg MC (1997) Updating the American College of Rheumatology revised criteria for the classification of systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheum 40:1725
Inouye SK, van Dyck CH, Alessi CA, Balkin S, Siegal AP, Horwitz RI (1990) Clarifying confusion: the confusion assessment method. A new method for detection of delirium. Ann Intern Med 113:941–948
Mioshi E, Dawson K, Mitchell J, Arnold R, Hodges JR (2006) The Addenbrooke’s Cognitive Examination Revised (ACE-R): a brief cognitive test battery for dementia screening. Int J Geriatr Psychiatry 21:1078–1085
Bombardier C, Gladman DD, Urowitz MB, Caron D, Chang CH (1992) Derivation of the SLEDAI. A disease activity index for lupus patients. The Committee on Prognosis Studies in SLE. Arthritis Rheum 35:630–640
Miyakis S, Lockshin MD, Atsumi T, Branch DW, Brey RL, Cervera R, Derksen RH, Groot PGDE, Koike T, Meroni PL, Reber G, Shoenfeld Y et al (2006) International consensus statement on an update of the classification criteria for definite antiphospholipid syndrome (APS). J Thromb Haemost 4:295–306
(1999) The American College of Rheumatology nomenclature and case definitions for neuropsychiatric lupus syndromes. Arthritis Rheum 42:599–608
Zigmond AS, Snaith RP (1983) The hospital anxiety and depression scale. Acta Psychiatr Scand 67:361–370
Sheehan DV, Lecrubier Y, Sheehan KH, Amorim P, Janavs J, Weiller E, Hergueta T, Baker R, Dunbar GC (1998) The Mini-International Neuropsychiatric Interview (M.I.N.I.): the development and validation of a structured diagnostic psychiatric interview for DSM-IV and ICD-10. J Clin Psychiatry 59(Suppl 20):22–33 quiz 4-57
Association AP (2004) Diagnostic and statistical manual of mental disorders-IV, 4th edn. Washington
Robbins TW, James M, Owen AM, Sahakian BJ, McInnes L, Rabbitt P (1994) Cambridge Neuropsychological Test Automated Battery (CANTAB): a factor analytic study of a large sample of normal elderly volunteers. Dementia 5:266–281
Ad Hoc Committee on Lupus Response Criteria: Cognition S-c, Mikdashi JA, Esdaile JM, Alarcon GS, Crofford L, Fessler BJ, Shanberg L, Brunner H, Gall V, Kalden JR, Lockshin MD, Liang MH et al (2007) Proposed response criteria for neurocognitive impairment in systemic lupus erythematosus clinical trials. Lupus 16:418–425
Yazdany J, Yelin EH, Panopalis P, Trupin L, Julian L, Katz PP (2008) Validation of the systemic lupus erythematosus activity questionnaire in a large observational cohort. Arthritis Rheum 59:136–143
Petri M, Purvey S, Fang H, Magder LS (2012) Predictors of organ damage in systemic lupus erythematosus: the Hopkins Lupus Cohort. Arthritis Rheum 64:4021–4028
Keeling SO, Vandermeer B, Medina J, Chatterley T, Nevskaya T, Pope J, Alaburubalnabi Z, Bissonauth A, Touma Z (2018) Measuring disease activity and damage with validated metrics: a systematic review on mortality and damage in systemic lupus erythematosus. J Rheumatol 45:1448–1461
Lopez R, Davidson JE, Beeby MD, Egger PJ, Isenberg DA (2012) Lupus disease activity and the risk of subsequent organ damage and mortality in a large lupus cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:491–498
Nery FG, Borba EF, Hatch JP, Soares JC, Bonfa E, Neto FL (2007) Major depressive disorder and disease activity in systemic lupus erythematosus. Compr Psychiatry 48:14–19
Acknowledgments
We thank the patients who participated in this study, Teresa Cole for the English version of the manuscript. We are indebted to Dr. Betty Diamond for performing the anti-dsDNA/NMDAR antibodies.
Funding
This work received financial support from Fondo Nacional de Desarrollo Científico y Tecnológico (FONDECYT) grant no. 1160513 to LM, and from Programa de Apoyo a Centros con Financiamiento Basal AFB 170005 and AFB 170004 from the Comisión Nacional de Investigación Científica y Tecnológica (CONICYT) to AG.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Ethical statement
All participants voluntarily signed an informed consent approved by the Pontificia Universidad Católica de Chile Ethical Committee prior to their inclusion in the study, in accordance with the ethical standards laid down in the 1964 Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
ESM 1
(DOCX 68 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mimica, M., Barra, I., Ormeño, R. et al. Predictors of damage accrual in systemic lupus erythematosus: a longitudinal observational study with focus on neuropsychological factors and anti-neuronal antibodies. Clin Rheumatol 38, 3129–3137 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04707-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04707-x