Abstract
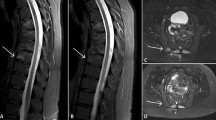
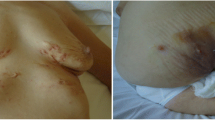
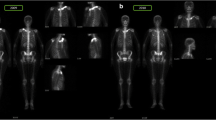
SAPHO (synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis) syndrome is a heterogeneous condition combining osteoarticular and cutaneous manifestations. Conventional treatments are mostly ineffective. We hereby report two patients, the first with an aggressive form of disease and the second with an incomplete response to two different anti-TNF-α agents. Both were successfully treated with tocilizumab and ustekinumab, respectively, over a long period of time. A narrative review of a biological therapy in SAPHO syndrome yielded very little information on the specific use of these agents. We highlight the advantages of personalising therapy and describe emerging promising treatments for this disease.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kahn M-F, Khan MA (1994) The SAPHO syndrome. Baillieres Clin Rheumatol 8:333–362. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-540-69375-8_77
Li C, Cao Y, Zhang W (2018) Clinical heterogeneity of SAPHO syndrome: challenge of diagnosis. Mod Rheumatol 28:432–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/14397595.2017.1416733
Li C, Zuo Y, Wu N, Li L, Li F, Zhang W, Xu W, Zhao X, Jing H, Pan Q, Zhou W, Shi X, Fan Y, Wang J, Liu S, Liu Z, Zhang F, Zeng X, Chen H, Zhang S, Liu J, Qiu G, Wu Z, Dong Z, Zhang W (2016) Synovitis, acne, pustulosis, hyperostosis and osteitis syndrome: a single centre study of a cohort of 164 patients. Rheumatology (Oxford) 55:1023–1030. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kew015
Firinu D, Garcia-Larsen V, Manconi PE, Del Giacco SR (2016) SAPHO syndrome: current developments and approaches to clinical treatment. Curr Rheumatol Rep 18. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11926-016-0583-y
Firinu D, Murgia G, Lorrai M, Barca M, Peralta M, Manconi P, Giacco S (2014) Biological treatments for SAPHO syndrome: an update. Inflamm Allergy Drug Targets 13:199–205. https://doi.org/10.2174/1871528113666140520100402
Daoussis D, Konstantopoulou G, Kraniotis P, Sakkas L, Liossis SN (2018) Biologics in SAPHO syndrome: a systematic review. Semin Arthritis Rheum 48:618–625. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2018.04.003
Colina M, Pizzirani C, Khodeir M, Falzoni S, Bruschi M, Trotta F, di Virgilio F (2010) Dysregulation of P2X7receptor-inflammasome axis in SAPHO syndrome: successful treatment with anakinra. Rheumatology 49:1416–1418. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keq074
Wendling D, Prati C, Aubin F (2012) Anakinra treatment of SAPHO syndrome: short-term results of an open study. Ann Rheum Dis 71:1098–1100. https://doi.org/10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200743
Cornillier H, Kervarrec T, Tabareau-Delalande F, Mammou S, Jonville Bera AP, Machet L (2016) Interstitial granulomatous dermatitis occurring in a patient with SAPHO syndrome one month after starting leflunomide, and subsequently disappearing with ustekinumab. Eur J Dermatol 26:614–615. https://doi.org/10.1684/EJD.2016.2854
Wendling D, Aubin F, Verhoeven F, Prati C (2017) IL-23/Th17 targeted therapies in SAPHO syndrome. A case series. Jt Bone Spine 84:733–735. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jbspin.2017.05.016
Sato H, Wada Y, Hasegawa E, Nozawa Y, Nakatsue T, Ito T, Kuroda T, Saeki T, Umezu H, Suzuki Y, Nakano M, Narita I (2017) Adult-onset chronic recurrent multifocal osteomyelitis with high intensity of muscles detected by magnetic resonance imaging, successfully controlled with tocilizumab. Intern Med 56:2353–2360. https://doi.org/10.2169/internalmedicine.8473-16
Adamo S, Nilsson J, Krebs A, Steiner U, Cozzio A, French LE, Kolios AGA (2018) Successful treatment of SAPHO syndrome with apremilast. Br J Dermatol 179:959–962. https://doi.org/10.1111/bjd.16071
Yang Q, Zhao Y, Li C, Luo Y, Hao W, Zhang W (2018) Case report: successful treatment of refractory SAPHO syndrome with the JAK inhibitor tofacitinib. Medicine (Baltimore) 97:23–26. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000011149
Wagner AD, Andresen J, Jendro MC, Hülsemann JL, Zeidler H (2002) Sustained response to tumor necrosis factor α-blocking agents in two patients with SAPHO syndrome. Arthritis Rheum 46:1965–1968. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.10539
Ben Abdelghani K, Dran DG, Gottenberg JE et al (2010) Tumor necrosis factor-α blockers in SAPHO syndrome. J Rheumatol 37:1699–1704. https://doi.org/10.3899/jrheum.091086
Arias-Santiago S, Sanchez-Cano D, Callejas-Rubio JL, Fernández-Pugnaire MA, Ortego-Centeno N (2010) Adalimumab treatment for SAPHO syndrome. Acta Derm Venereol 90:301–302
Fujita S, Kosaka N, Mito T, Hayashi H, Morita Y (2015) Development of aseptic subcutaneous abscess after tocilizumab therapy in a patient with SAPHO syndrome complicated by amyloid A amyloidosis. Int J Rheum Dis 18:476–479. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185X.12525
Olivieri I, Padula A, Ciancio G, Salvarani C, Niccoli L, Cantini F (2002) Successful treatment of SAPHO syndrome with infliximab: report of two cases. Ann Rheum Dis 61:375–376
Iqbal M, Kolodney MS (2005) Acne fulminans with synovitis-acne-pustulosis-hyperostosis-osteitis (SAPHO) syndrome treated with infliximab. J Am Acad Dermatol 52:S118–S120. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaad.2004.09.006
Massara A, Cavazzini PL, Trotta F (2006) In SAPHO syndrome anti-TNF-α therapy may induce persistent amelioration of osteoarticular complaints, but may exacerbate cutaneous manifestations. Rheumatology 45:730–733. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/kei221
Sabugo F, Liberman C, Niedmann JP, Soto L, Cuchacovich M (2008) Infliximab can induce a prolonged clinical remission and a decrease in thyroid hormonal requirements in a patient with SAPHO syndrome and hypothyroidism. Clin Rheumatol 27:533–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0767-y
Moll C, Hernández MV, Cañete JD, Gómez-Puerta JA, Soriano A, Collado A, Sanmartí R (2008) Ilium osteitis as the main manifestation of the SAPHO syndrome: response to infliximab therapy and review of the literature. Semin Arthritis Rheum 37:299–306. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.semarthrit.2007.08.004
Fruehauf J, Cierny-Modrè B, El-Shabrawi Caelen L et al (2009) Response to infliximab in SAPHO syndrome. BMJ Case Rep 2009:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr.10.2008.1145
Castellví I, Bonet M, Narváez JA, Molina-Hinojosa JC (2010) Successful treatment of SAPHO syndrome with adalimumab: a case report. Clin Rheumatol 29:1205–1207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-010-1476-5
Vilar-Alejo J, Dehesa L, De La Rosa-del Rey P et al (2010) SAPHO syndrome with unusual cutaneous manifestations treated successfully with etanercept. Acta Derm Venereol 90:531–532. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-0895
de Souza A, Solomon GE, Strober BE (2011) SAPHO syndrome associated with hidradenitis suppurativa successfully treated with infliximab and methotrexate. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis 69:185–187
Zhang LL, Zhao JX, Liu XY (2012) Successful treatment of SAPHO syndrome with severe spinal disorder using entercept: a case study. Rheumatol Int 32:1963–1965. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-011-1916-9
Garcovich S, Amelia R, Magarelli N, Valenza V, Amerio P (2012) Long-term treatment of severe SAPHO syndrome with adalimumab. Am J Clin Dermatol 13:55–59. https://doi.org/10.2165/11593250-000000000-00000
Burgemeister LT, Baeten DLP, Tas SW (2012) Biologics for rare inflammatory diseases: TNF blockade in the SAPHO syndrome. Neth J Med 70:444–449
Hampton SL, Youssef H (2013) Successful treatment of resistant SAPHO syndrome with anti-TNF therapy. BMJ Case Rep:2012–2014. https://doi.org/10.1136/bcr-2012-007161
Naves JE, Cabré E, Mañosa M, Grados D, Olivé A, Domènech E (2013) A systematic review of SAPHO syndrome and inflammatory bowel disease association. Dig Dis Sci 58:2138–2147. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-013-2653-6
Kundu BK, Naik AK, Bhargava S, Srivastava D (2013) Diagnosing the SAPHO syndrome: a report of three cases and review of literature. Clin Rheumatol 32:1237–1243. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-013-2251-1
Kim CH, Kadhim S, Julien C (2014) Treatment of pain in SAPHO (synovitis, acne, Pustulosis, hyperostosis, and osteitis) syndrome. PM R 6:92–95. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pmrj.2013.08.610
Abourazzak FE, Hachimi H, Kadi N, Berrada K, Tizniti S, Harzy T (2014) Etanercept in the treatment of SAPHO syndrome: which place? Eur J Rheumatol 1:125–128. https://doi.org/10.5152/eurjrheumatol.2014.037
Marí A, Morla A, Melero M, Schiavone R, Rodríguez J (2014) Diffuse sclerosing osteomyelitis (DSO) of the mandible in SAPHO syndrome: a novel approach with anti-TNF therapy. Systematic review. J Cranio-Maxillofac Surg 42:1990–1996. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcms.2014.09.004
Anić B, Padjen I, Mayer M et al (2014) Clinical features of the SAPHO syndrome and their role in choosing the therapeutic approach: report of four patients and review of the literature. Acta Dermatovenerol Croat 22:180–188
Sáez-Martín L-C, Gómez-Castro S, Román-Curto C, Palacios-Álvarez I, Fernández-López E (2015) Etanercept in the treatment of SAPHO syndrome. Int J Dermatol 54:e206–e208. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.12675
Kamata Y, Minota S (2015) Successful treatment of a patient with SAPHO syndrome with certolizumab pegol. Rheumatol Int 35:1607–1608. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-015-3263-8
Cotti E, Careddu R, Schirru E, Marongiu S, Barca MP, Manconi PE, Mercuro G (2015) A case of SAPHO syndrome with endodontic implications and treatment with biologic drugs. J Endod 41:1565–1570. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joen.2015.04.005
Su YS, Chang CH (2015) SAPHO syndrome associated with acne conglobata successfully treated with etanercept. J Formos Med Assoc 114:562–564. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfma.2013.10.001
Zhang L, Gao Z (2016) Etanercept in the treatment of refractory SAPHO syndrome. Am J Clin Exp Immunol 5:62–66
Mateo L, Sanint J, Rodríguez Muguruza S, Martínez Morillo M, Pérez Andrés R, Domenech Puigcerver S (2017) Lesión osteolítica cervical como presentación del síndrome SAPHO. Reumatol Clin 13:44–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.reuma.2015.11.016
Anić B, Padjen I, Barešić M, Težak S (2014) The lobster sign in SAPHO syndrome: unusually extensive osteitis of the anterior chest wall partially responsive to infliximab. Rheumatol Int 34:281–282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00296-012-2606-y
Cianci F, Zoli A, Gremese E, Ferraccioli G (2017) Clinical heterogeneity of SAPHO syndrome: challenging diagnose and treatment. Clin Rheumatol 36:2151–2158. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3751-1
Vekic DA, Woods J, Lin P, Cains GD (2018) SAPHO syndrome associated with hidradenitis suppurativa and pyoderma gangrenosum successfully treated with adalimumab and methotrexate: a case report and review of the literature. Int J Dermatol 57:10–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/ijd.13740
Axmann R, Böhm C, Krönke G, Zwerina J, Smolen J, Schett G (2009) Inhibition of interleukin-6 receptor directly blocks osteoclast formation in vitro and in vivo. Arthritis Rheum 60:2747–2756. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24781
Morales-Múnera C, Vilarrasa E, Puig L (2013) Efficacy of ustekinumab in refractory palmoplantar pustular psoriasis. Br J Dermatol 168:820–824
Kavanaugh A, Puig L, Gottlieb AB, Ritchlin C, You Y, Li S, Song M, Randazzo B, Rahman P, McInnes IB (2016) Efficacy and safety of ustekinumab in psoriatic arthritis patients with peripheral arthritis and physician-reported spondylitis: post-hoc analyses from two phase III, multicentre, double-blind, placebo-controlled studies (PSUMMIT-1/PSUMMIT-2). Ann Rheum Dis 75:1984–1988
Li C, Wu X, Cao Y, Zeng Y, Zhang W, Zhang S, Liu Y, Jin H, Zhang W, Li L (2019) Paradoxical skin lesions induced by anti-TNF-α agents in SAPHO syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 38:53–61. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4083-5
Sarzi-Puttini P, Ceribelli A, Marotto D, Batticciotto A, Atzeni F (2019) Systemic rheumatic diseases: from biological agents to small molecules. Autoimmun Rev 18:583–592. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2018.12.009
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Consent
Both patients gave informed consent for the publication of their case report and related images.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Figueiredo, A.S.B., Oliveira, A.L., Caetano, A. et al. SAPHO: has the time come for tailored therapy?. Clin Rheumatol 39, 177–187 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04675-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-019-04675-2