Abstract
Objectives
This study was aimed to investigate the association of the single nucleotide polymorphism of tumor necrosis factor receptor associated factor 6 (TRAF6), rs540386, with low bone mineral density (BMD) among patients with rheumatoid arthritis (RA).
Methods
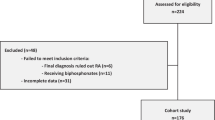
TRAF6 rs540386 genotyping was performed by mutagenically separated PCR in a cohort of 188 (23 men, 165 women, median age, 56.2 years) adult RA patients and 224 age and gender-matched controls. BMD was measured using dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) (Lunar Prodigy advance scans, GE Healthcare, USA).
Results
Among the RA patients, 64 (55 women, 9 men) had low BMD comprising of 57 patients with osteoporosis and 7 with osteopenia. Whereas TRAF6 rs540386 was not associated with RA susceptibility, it was however found to be a risk factor for reduced lumbar spine Z-score in the recessive model (OR = 3.34, 95% CI = (1.01–11.00), p = 0.038). This association was confirmed further in the multivariate logistic regression analysis taking into account several potential confounding factors (OR = 3.34 (1.01–11.00), p = 0.048). In addition, mean total femur Z-score was found to be reduced in TT patients when compared to CC + CT patients (− 1.30 ± 1.32 versus − 0.60 ± 1.05, p = 0.034). No association between TRAF6 rs540386 and local bone damage was observed.
Conclusions
This study for the first time ever demonstrated an association between a genetic variant of TRAF6 and low BMD among patients with RA. Further investigations are needed to elucidate the exact role of this variant.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Haugeberg G, Uhlig T, Falch JA, Halse JI, Kvien TK (2000) Bone mineral density and frequency of osteoporosis in female patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from 394 patients in the Oslo County rheumatoid arthritis register. Arthritis Rheum 43:522–530
Sinigaglia L, Nervetti A, Mela Q et al (2000) A multicenter cross sectional study on bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis. Italian study group on bone mass in rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 27:2582–2589
Xue AL, Wu SY, Jiang L, Feng AM, Guo HF, Zhao P (2017) Bone fracture risk in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 96:e6983. https://doi.org/10.1097/MD.0000000000006983
Güler-Yüksel M, Bijsterbosch J, Goekoop-Ruiterman YPM et al (2007) Bone mineral density in patients with recently diagnosed, active rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 66:1508–1512
Book C, Karlsson M, Akesson K et al (2008) Disease activity and disability but probably not glucocorticoid treatment predicts loss in bone mineral density in women with early rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol 37:248–254
Ibañez M, Ortiz AM, Castrejón I, García-Vadillo JA, Carvajal I, Castañeda S, González-Álvaro I (2010) A rational use of glucocorticoids in patients with early arthritis has a minimal impact on bone. Arthritis Res Ther 12:R50
Schett G, Hayer S, Zwerina J, Redlich K, Smolen JS (2005) Mechanisms of disease: the link between RANKL and arthritic bone disease. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 1:47–54
Gough AK, Peel NF, Eastell R, Holder RL, Lilley J, Emery P (1994) Excretion of pyridinium crosslinks correlates with disease activity and appendicular bone loss in early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 53:14–17
Takayanagi H (2007) Osteoimmunology: shared mechanisms and crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. Nat Rev Immunol 7:292–304
Nakashima T, Takayanagi H (2009) Osteoimmunology: crosstalk between the immune and bone systems. J Clin Immunol 29:555–567
Kong YY, Feige U, Sarosi I, Bolon B, Tafuri A, Morony S, Capparelli C, Li J, Elliott R, McCabe S, Wong T, Campagnuolo G, Moran E, Bogoch ER, van G, Nguyen LT, Ohashi PS, Lacey DL, Fish E, Boyle WJ, Penninger JM (1999) Activated T cells regulate bone loss and joint destruction in adjuvant arthritis through osteoprotegerin ligand. Nature 402:304–309
Lacey DL, Timms E, Tan HL, Kelley MJ, Dunstan CR, Burgess T, Elliott R, Colombero A, Elliott G, Scully S, Hsu H, Sullivan J, Hawkins N, Davy E, Capparelli C, Eli A, Qian YX, Kaufman S, Sarosi I, Shalhoub V, Senaldi G, Guo J, Delaney J, Boyle WJ (1998) Osteoprotegerin ligand is a cytokine that regulates osteoclast differentiation and activation. Cell 93:165–176
Hofbauer LC, Lacey DL, Dunstan CR, Spelsberg TC, Riggs BL, Khosla S (1999) Interleukin-1beta and tumor necrosis factor alpha, but not interleukin-6 stimulate osteoprotegerin ligand gene expression in human osteolastic cells. Bone 25:255–259
Xu S, Want Y, Lu J et al (2012) Osteoprotegerin and RANKL in the pathogenesis of rheumatoid arthritis- induced osteoporosis. Rheumatol Int 32:3397–3403
Ye H, Arron JR, Lamothe B, Cirilli M, Kobayashi T, Shevde NK, Segal D, Dzivenu OK, Vologodskaia M, Yim M, du K, Singh S, Pike JW, Darnay BG, Choi Y, Wu H (2002) Distinct molecular mechanism for initiating TRAF6 signaling. Nature 418:443–447
Wu H, Arron JR (2003) TRAF6. A molecular bridge spanning adaptive immunity, innate immunity and osteoimmunology. Bioessays 11:1096–1105
Loiarro M, Gallo G, Fantò N, de Santis R, Carminati P, Ruggiero V, Sette C (2009) Identification of critical residues of the MyD88 death domain involved in the recruitment of downstream kinases. J Biol Chem 284:28093–28103
Raychaudhuri S, Thomson BP, Remmers EF (2009) Genetic variants at CD28, PRDM1 and CD2/CD58 are associated with rheumatoid arthritis risk. Nat Genet 41:1313–1318
Saxena R, Plenge RM, Bjonnes AC, Dashti HS, Okada Y, Gad el Haq W, Hammoudeh M, al Emadi S, Masri BK, Halabi H, Badsha H, Uthman IW, Margolin L, Gupta N, Mahfoud ZR, Kapiri M, Dargham SR, Aranki G, Kazkaz LA, Arayssi T (2017) A Multinational Arab Genome-Wide Association Study iIdentifies New Genetic Associations for Rheumatoid Arthritis. Arthritis Rheumatol 69:976–985
Namjou B, Choi CB, Harley IT et al (2012) Evaluation of TRAF6 in a large multiancestral lupus cohort. Arthritis Rheum 64:1960–1969
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman AJ, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO III, Birnbaum NS, Burmester GR, Bykerk VP, Cohen MD, Combe B, Costenbader KH, Dougados M, Emery P, Ferraccioli G, Hazes JMW, Hobbs K, Huizinga TWJ, Kavanaugh A, Kay J, Kvien TK, Laing T, Mease P, Ménard HA, Moreland LW, Naden RL, Pincus T, Smolen JS, Stanislawska-Biernat E, Symmons D, Tak PP, Upchurch KS, Vencovský J, Wolfe F, Hawker G (2010) Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 62:2569–2581
Kanis JA (1994) (1994) Assessment of fracture risk and its application to screening for postmenopausal osteoporosis: synopsis of a WHO report. WHO Study Group. Osteoporos Int 4:368–381
Darnay BG, Ni J, Moore PA, Aggarwal BB (1999) Activation of NF-kappaB by RANK requires tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 and NF-kappaB-inducing kinase. Identification of a novel TRAF6 interaction motif. J Biol Chem 274:7724–7731
Naito A, Azuma S, Tanaka S, Miyazaki T, Takaki S, Takatsu K, Nakao K, Nakamura K, Katsuki M, Yamamoto T, Inoue JI (1999) Severe osteopetrosis, defective interleukin-1 signalling and lymph node organogenesis in TRAF6-deficient mice. Genes Cells 4:353–362
Kadono Y, Okada F, Perchonock C et al (2005) TRAF6 signalling determines osteoclastogenesis. EMBO Rep 71–6. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400345
Scofield RH, Bruner GR, Kelly JA, Kilpatrick J, Bacino D, Nath SK, Harley JB (2003) Thrombocytopenia identifies a severe familial phenotype of systemic lupus erythematosus and reveals genetic linkages at 1q22 and 11p13. Blood 101:992–997
Amos CI, Chen WV, Lee A, Li W, Kern M, Lundsten R, Batliwalla F, Wener M, Remmers E, Kastner DA, Criswell LA, Seldin MF, Gregersen PK (2006) High-density SNP analysis of 642 Caucasian families with rheumatoid arthritis identifies two new linkage regions on 11p12 and 2q33. Genes Immun 7:277–286
Zhu LJ, Dai L, Zheng DH, Mo YQ, Ou-Yang X, Wei XN, Shen J, Zhang BY (2012) Upregulation of tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor 6 correlated with synovitis severity in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 14:R133
Zhu LJ, Yang TC, Wu Q, Yuan LP, Chen ZW, Luo MH, Zeng HO, He DL, Mo CJ (2017) Tumor necrosis factor receptor-associated factor (TRAF) 6 inhibition mitigates the pro-inflammatory roles and proliferation of rheumatoid arthritis fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Cytokine 93:26–33
Slemenda CW, Christian JC, Williams CJ, Norton JA, Johnston CC Jr (1991) Genetic determinants of bone mass in adult women: a reevaluation of the twin model and the potential importance of gene interaction on heritability estimates. J Bone Miner Res 6:561–567
Pocock NA, Eisman JA, Hopper JL, Yeates MG, Sambrook PN, Eberl S (1987) Genetic determinants of bone mass in adults. A twin study J Clin Invest 80:706–710
Krall EA, Dawson-Hughes B (1993) Heritable and life-style determinants of bone mineral density. J Bone Miner Res 8:1–9
Estrada K, Styrkarsdottir U, Evangelou E, Hsu YH, Duncan EL, Ntzani EE, Oei L, Albagha OME, Amin N, Kemp JP, Koller DL, Li G, Liu CT, Minster RL, Moayyeri A, Vandenput L, Willner D, Xiao SM, Yerges-Armstrong LM, Zheng HF, Alonso N, Eriksson J, Kammerer CM, Kaptoge SK, Leo PJ, Thorleifsson G, Wilson SG, Wilson JF, Aalto V, Alen M, Aragaki AK, Aspelund T, Center JR, Dailiana Z, Duggan DJ, Garcia M, Garcia-Giralt N, Giroux S, Hallmans G, Hocking LJ, Husted LB, Jameson KA, Khusainova R, Kim GS, Kooperberg C, Koromila T, Kruk M, Laaksonen M, Lacroix AZ, Lee SH, Leung PC, Lewis JR, Masi L, Mencej-Bedrac S, Nguyen TV, Nogues X, Patel MS, Prezelj J, Rose LM, Scollen S, Siggeirsdottir K, Smith AV, Svensson O, Trompet S, Trummer O, van Schoor NM, Woo J, Zhu K, Balcells S, Brandi ML, Buckley BM, Cheng S, Christiansen C, Cooper C, Dedoussis G, Ford I, Frost M, Goltzman D, González-Macías J, Kähönen M, Karlsson M, Khusnutdinova E, Koh JM, Kollia P, Langdahl BL, Leslie WD, Lips P, Ljunggren Ö, Lorenc RS, Marc J, Mellström D, Obermayer-Pietsch B, Olmos JM, Pettersson-Kymmer U, Reid DM, Riancho JA, Ridker PM, Rousseau F, lagboom PES, Tang NLS, Urreizti R, van Hul W, Viikari J, Zarrabeitia MT, Aulchenko YS, Castano-Betancourt M, Grundberg E, Herrera L, Ingvarsson T, Johannsdottir H, Kwan T, Li R, Luben R, Medina-Gómez C, Th Palsson S, Reppe S, Rotter JI, Sigurdsson G, van Meurs JBJ, Verlaan D, Williams FMK, Wood AR, Zhou Y, Gautvik KM, Pastinen T, Raychaudhuri S, Cauley JA, Chasman DI, Clark GR, Cummings SR, Danoy P, Dennison EM, Eastell R, Eisman JA, Gudnason V, Hofman A, Jackson RD, Jones G, Jukema JW, Khaw KT, Lehtimäki T, Liu Y, Lorentzon M, McCloskey E, Mitchell BD, Nandakumar K, Nicholson GC, Oostra BA, Peacock M, Pols HAP, Prince RL, Raitakari O, Reid IR, Robbins J, Sambrook PN, Sham PC, Shuldiner AR, Tylavsky FA, van Duijn CM, Wareham NJ, Cupples LA, Econs MJ, Evans DM, Harris TB, Kung AWC, Psaty BM, Reeve J, Spector TD, Streeten EA, Zillikens MC, Thorsteinsdottir U, Ohlsson C, Karasik D, Richards JB, Brown MA, Stefansson K, Uitterlinden AG, Ralston SH, Ioannidis JPA, Kiel DP, Rivadeneira F (2012) Genome-wide meta-analysis identifies 56 bone mineral density loci and reveals 14 loci associated with risk of fracture. Nat Genet 44:491–501
Gough A, Sambrook P, Devlin J, Lilley J, Huisoon A, Betteridge J, Franklyn J, Nguyen T, Morrison N, Eisman J, Emery P (1998) Effect of vitamin D receptor gene alleles on bone loss in early rheumatoid arthritis. J Rheumatol 25:864–868
Rass P, Pákozdi A, Lakatos P, Zilahi E, Sipka S, Szegedi G, Szekanecz Z (2006) Vitamin D receptor gene polymorphism in rheumatoid arthritis and associated osteoporosis. Rheumatol Int 26:964–971
Yoshida S, Ikari K, Furuya T, Toyama Y, Taniguchi A, Yamanaka H, Momohara S (2014) An osteoprotegerin gene polymorphism is associated with an increased risk of hip fracture in Japanese patients with rheumatoid arthritis: results from the IORRA Observational Cohort Study. PLoS One 9:e104587. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0104587
Nava-Valdivia CA, Saldaña-Cruz AM, Murillo-Vazquez JD et al (2017) Polymorphism rs2073618 of the TNFRSF11B (OPG) gene and bone mineral density in Mexican women with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol Res. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/7680434
Harre U, Georgess D, Bang H, Bozec A, Axmann R, Ossipova E, Jakobsson PJ, Baum W, Nimmerjahn F, Szarka E, Sarmay G, Krumbholz G, Neumann E, Toes R, Scherer HU, Catrina AI, Klareskog L, Jurdic P, Schett G (2012) Induction of osteoclastogenesis and bone loss by human autoantibodies against citrullinated vimentin. J Clin Invest 122:1791–1802
Kleyer A, Finzel S, Rech J et al (2013) Bone loss before the clinical onset of rheumatoid arthritis in subjects with anti-citrullinated protein antibodies. Ann Rheum Dis 73:854–860
Acknowledgment
This study was supported by the college of Medicine Research center, Deanship of Scientific Research, King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hassine, H.B., Zemni, R., Nacef, I.B. et al. A TRAF6 genetic variant is associated with low bone mineral density in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 38, 1067–1074 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4362-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4362-1