Abstract
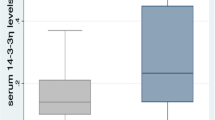
This study was set to investigate whether serum markers of lymphocytic activity are associated with patient-reported outcomes in Sjögren’s syndrome (SS). Forty-six patients with SS were included in this cross-sectional study. Patients with monoclonal gammopathy, history of malignant lymphoma, or with secondary SS were excluded. Serum levels of IgG, β2-microglobulin (β2M), soluble interleukin-2 receptor (sIL2-R), and free light chains (FLC) were assessed. Systemic disease activity was measured by the EULAR SS disease activity index (ESSDAI). Patient-reported symptoms were recorded by visual analogue scales (VAS) of pain, fatigue, and dryness, as compiled in the EULAR SS patient-reported index (ESSPRI). Depressive symptoms were determined by the Patient Health Questionnaire 9 (PHQ-9). Serum concentrations of κFLC (r = 0.491, p = 0.001), λFLC (r = 0.326, p = 0.027), and β2M (r = 0.421, p = 0.004) correlated with the ESSDAI, whereas sIL-2R and IgG did not. No correlations between serum markers of lymphocytic activity and the ESSPRI, or single VAS measures of pain, dryness, or fatigue, were found. In patients with VAS fatigue scores in the upper quartile, sIL-2R serum levels were even decreased (p = 0.019). Only depressive symptoms as determined by PHQ-9 were positively correlated with fatigue (r = 0.536, p < 0.001). In this well-defined cohort of patients with SS, serological lymphocytic activity was not correlated with patient-reported outcomes and sIL-2R levels were even decreased in patients with high fatigue scores. Only depressive symptoms were correlated with fatigue. This highlights the need to further understand the link between inflammation and disease characteristics in SS.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Fox RI (2005) Sjögren’s syndrome. Lancet 366:321–331
Pertovaara M, Korpela M (2011) Serum β2 microglobulin correlates with the new ESSDAI in patients with Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 70:2236–2237
Gottenberg J, Seror R, Miceli-Richard C, Benessiano J, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Dieude P et al (2013) Serum levels of beta2-microglobulin and free light chains of immunoglobulins are associated with systemic disease activity in primary Sjögren’s syndrome. Data at enrollment in the prospective ASSESS cohort. PLoS One 8:e59868
Spadaro A, Riccieri V, Benfari G, Scillone M, Taccari E (2001) Soluble interleukin-2 receptor in Sjögren’s syndrome: relation to main serum immunological and immunohistochemical parameters. Clin Rheumatol 20:319–323
Cornec D, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Mariette X, Jousse-Joulin S, Berthelot JM, Perdriger A, Puéchal X, Le Guern V, Sibilia J, Gottenberg JE, Chiche L, Hachulla E, Yves Hatron P, Goeb V, Hayem G, Morel J, Zarnitsky C, Dubost JJ, Saliou P, Pers JO, Seror R, Saraux A (2017) Severe health-related quality of life impairment in active primary Sjögren’s syndrome and patient-reported outcomes: data from a large therapeutic trial. Arthritis Care Res (Hoboken) 69:528–535
Ng WF, Bowman SJ (2010) Primary Sjögren’s syndrome: too dry and too tired. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:844–853. https://doi.org/10.1093/rheumatology/keq009
Hart BL (1988) Biological basis of the behavior of sick animals. Neurosci Biobehav Rev 12:123–137
Howard Tripp N, Tarn J, Natasari A, on behalf of the United Kingdom Primary Sjögren’s Syndrome Registry et al (2016) Fatigue in primary Sjögren’s syndrome is associated with lower levels of proinflammatory cytokines. RMD Open 2:e000282. https://doi.org/10.1136/rmdopen-2016-000282
Bax HI, Vriesendorp TM, Kallenberg CGM, Kalk WW (2002) Fatigue and immune activity in Sjögren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 61:284
Seror R, Ravaud P, Mariette X, Bootsma H, Theander E, Hansen A, Ramos-Casals M, Dörner T, Bombardieri S, Hachulla E, Brun JG, Kruize AA, Praprotnik S, Tomsic M, Gottenberg JE, Devauchelle V, Devita S, Vollenweider C, Mandl T, Tzioufas A, Carsons S, Saraux A, Sutcliffe N, Vitali C, Bowman SJ, Sjögren's Task Force EULAR (2011) EULAR Sjogren’s Syndrome Patient Reported Index (ESSPRI): development of a consensus patient index for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 70:968–972
Vitali C, Bombardieri S, Jonsson R, Moutsopoulos HM, Alexander EL, Carsons SE, Daniels TE, Fox PC, Fox RI, Kassan SS, Pillemer SR, Talal N, Weisman MH, European Study Group on Classification Criteria for Sjögren’s Syndrome (2002) Classification criteria for Sjögren’s syndrome: a revised version of the European criteria proposed by the American-European consensus group. Ann Rheum Dis 61:554–558
Seror R, Ravaud P, Bowman SJ, Baron G, Tzioufas A, Theander E, Gottenberg JE, Bootsma H, Mariette X, Vitali C, Sjögren's Task Force EULAR (2010) EULAR Sjogren’s syndrome disease activity index: development of a consensus systemic disease activity index for primary Sjogren’s syndrome. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1103–1109
Kroenke K, Spitzer RL, Williams JB (2001) The PHQ-9: validity of a brief depression severity measure. J Gen Intern Med 16:606–613
Rubin LA, Kurman CC, Fritz ME, Biddison WE, Boutin B, Yarchoan R, Nelson DL (1985) Soluble interleukin 2 receptors are released from activated human lymphoid cells in vitro. J Immunol 135:3172–3177
Pratt G (2008) The evolving use of serum free light chain assays in haematology. Br J Haematol 141:413–422. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2141.2008.07079.x
Karlsson FA, Wibell L, Evrin PE (1980) Beta 2-Microglobulin in clinical medicine. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl 154:27–37
Brito-Zerón P, Baldini C, Bootsma H, Bowman SJ, Jonsson R, Mariette X, Sivils K, Theander E, Tzioufas A, Ramos-Casals M (2016) Sjögren syndrome. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16047. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.47. Review.
Harboe E, Tjensvoll AB, Vefring HK, Gøransson LG, Kvaløy JT, Omdal R (2009) Fatigue in primary Sjögren’s syndrome—a link to sickness behaviour in animals? Brain Behav Immun 23:1104–1108
Devauchelle-Pensec V, Mariette X, Jousse-Joulin S, Berthelot J, Perdriger A, Puéchal X et al (2014) Treatment of primary Sjögren syndrome with rituximab: a randomized trial. Ann Intern Med 160:233–242. https://doi.org/10.7326/M13-1085
Mariette X, Seror R, Quartuccio L, Baron G, Salvin S, Fabris M, Desmoulins F, Nocturne G, Ravaud P, de Vita S (2015) Efficacy and safety of belimumab in primary Sjögren’s syndrome: results of the BELISS open-label phase II study. Ann Rheum Dis 74:526–531
Gottenberg J, Ravaud P, Puéchal X, Le Guern V, Sibilia J, Goeb V, Larroche C, Dubost J, Rist S, Saraux A, Devauchelle-Pensec V, Morel J, Hayem G, Hatron P, Perdriger A, Sene D, Zarnitsky C, Batouche D, Furlan V, Benessiano J, Perrodeau E, Seror R, Mariette X (2014) Effects of hydroxychloroquine on symptomatic improvement in primary Sjögren syndrome: the JOQUER randomized clinical trial. JAMA 312:249–258. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2014.7682
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the patients who contributed to this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical standards
This study has been approved by the ethics committee of the University of Freiburg and was conducted in compliance with the Declaration of Helsinki and its later amendments. All patients gave their informed consent prior to inclusion in the study.
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jülich, M., Kanne, AM., Sehnert, B. et al. Serological lymphocytic activity and patient-reported outcomes in Sjögren’s syndrome. Clin Rheumatol 37, 2361–2366 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4159-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4159-2