Abstract
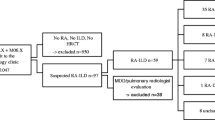
Interstitial lung disease (ILD) is a severe rheumatoid arthritis (RA) manifestation. The worst survival has been associated with usual interstitial pneumonia (UIP) definitive pattern in high-resolution chest tomography (HRCT) scans. Moreover, the use of methotrexate in RA-ILD is controversial. Our aim was to evaluate prognostic factors including methotrexate in an RA-ILD cohort and their association with survival. RA-ILD patients referred for medical evaluation and treatment at a single center were included. At the baseline, pulmonary function tests were carried out and a HRCT was obtained. A radiologist evaluated the ILD tomographic pattern and the extent of lung disease. Patients were considered as receiving methotrexate therapy if this drug was specifically prescribed for the treatment of RA-ILD at the beginning of follow up. Seventy-eight patients were included. UIP definite pattern in HRCT was not associated to worse survival. Variables associated with mortality reflected the severity of lung disease. Treatment with methotrexate was associated with survival (HR 0.13, 95% CI 0.02–0.64); older patients had worse prognosis (HR 1.04, 95% CI 1.003–1.09). After adjusting for confounding variables, methotrexate was strongly associated with survival. Methotrexate treatment during follow up was associated with survival. The severity of lung disease and not the tomographic pattern is associated with mortality; older patients had worse prognosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dawson JK, Fewins HE, Desmond J, Lynch MP, Graham DR (2001) Fibrosing alveolitis in patients with rheumatoid arthritis as assessed by high resolution computed tomography, chest radiography, and pulmonary function tests. Thorax 56:622–627
Young A, Koduri G, Batley M, Kulinskaya E, Gough A, Norton S, Dixey J, g. Early Rheumatoid Arthritis Study (2007) Mortality in rheumatoid arthritis. Increased in the early course of disease, in ischaemic heart disease and in pulmonary fibrosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 46:350–357
Koduri G, Norton S, Young A, Cox N, Davies P, Devlin J, Dixey J, Gough A, Prouse P, Winfield J, Williams P, Eras (2010) Interstitial lung disease has a poor prognosis in rheumatoid arthritis: results from an inception cohort. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:1483–1489
Bongartz T, Nannini C, Medina-Velasquez YF, Achenbach SJ, Crowson CS, Ryu JH, Vassallo R, Gabriel SE, Matteson EL (2010) Incidence and mortality of interstitial lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a population-based study. Arthritis Rheum 62:1583–1591
Assayag D, Lubin M, Lee JS, King TE, Collard HR, Ryerson CJ (2014) Predictors of mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease. Respirology 19:493–500
Sathi N, Urwin T, Desmond S, Dawson JK (2011) Patients with limited rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease have a better prognosis than those with extensive disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 50:620
Kelly CA, Saravanan V, Nisar M, Arthanari S, Woodhead FA, Price-Forbes AN, Dawson J, Sathi N, Ahmad Y, Koduri G, Young A, N. British Rheumatoid Interstitial Lung (2014) Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease: associations, prognostic factors and physiological and radiological characteristics—a large multicentre UK study. Rheumatology (Oxford) 53:1676–1682
Kim EJ, Elicker BM, Maldonado F, Webb WR, Ryu JH, Van Uden JH, Lee JS, King TE Jr, Collard HR (2010) Usual interstitial pneumonia in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J 35:1322–1328
Smolen JS, Landewe R, Breedveld FC, Buch M, Burmester G, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C, Gossec L, Nam J, Ramiro S, Winthrop K, de Wit M, Aletaha D, Betteridge N, Bijlsma JW, Boers M, Buttgereit F, Combe B, Cutolo M, Damjanov N, Hazes JM, Kouloumas M, Kvien TK, Mariette X, Pavelka K, van Riel PL, Rubbert-Roth A, Scholte-Voshaar M, Scott DL, Sokka-Isler T, Wong JB, van der Heijde D (2014) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs: 2013 update. Ann Rheum Dis 73:492–509
Choi HK, Hernan MA, Seeger JD, Robins JM, Wolfe F (2002) Methotrexate and mortality in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a prospective study. Lancet 359:1173–1177
Landewe RB (2013) Methotrexate saves lives: a pearl of observational research. Arthritis Rheum 65:307–309
Wasko MC, Dasgupta A, Hubert H, Fries JF, Ward MM (2013) Propensity-adjusted association of methotrexate with overall survival in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 65:334–342
Yunt ZX, Solomon JJ (2015) Lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis. Rheum Dis Clin N Am 41:225–236
Rojas-Serrano J, Gonzalez-Velasquez E, Mejia M, Sanchez-Rodriguez A, Carrillo G (2012) Interstitial lung disease related to rheumatoid arthritis: evolution after treatment. Reumatol Clin 8:68–71
Kazerooni EA, Martinez FJ, Flint A, Jamadar DA, Gross BH, Spizarny DL, Cascade PN, Whyte RI, Lynch JP III, Toews G (1997) Thin-section CT obtained at 10-mm increments versus limited three-level thin-section CT for idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: correlation with pathologic scoring. AJR Am J Roentgenol 169:977–983
Travis WD, Costabel U, Hansell DM, King TE Jr, Lynch DA, Nicholson AG, Ryerson CJ, Ryu JH, Selman M, Wells AU, Behr J, Bouros D, Brown KK, Colby TV, Collard HR, Cordeiro CR, Cottin V, Crestani B, Drent M, Dudden RF, Egan J, Flaherty K, Hogaboam C, Inoue Y, Johkoh T, Kim DS, Kitaichi M, Loyd J, Martinez FJ, Myers J, Protzko S, Raghu G, Richeldi L, Sverzellati N, Swigris J, Valeyre D, A. E. C. o. I. I. Pneumonias (2013) An official American Thoracic Society/European Respiratory Society statement: update of the international multidisciplinary classification of the idiopathic interstitial pneumonias. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 188:733–748
Hozumi H, Nakamura Y, Johkoh T, Sumikawa H, Colby TV, Kono M, Hashimoto D, Enomoto N, Fujisawa T, Inui N, Suda T, Chida K (2013) Acute exacerbation in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease: a retrospective case control study. BMJ Open 3(9):e003132
Suissa S (2007) Immortal time bias in observational studies of drug effects. Pharmacoepidemiol Drug Saf 16:241–249
Suissa S (2008) Immortal time bias in pharmaco-epidemiology. Am J Epidemiol 167:492–499
Walker AM (1996) Confounding by indication. Epidemiology 7:335–336
Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S, May S (2008) Model development. In: Hosmer DW, Lemeshow S, May S (eds) Applied survival analysis. Regression modeling of time-to-event data, 2nd edn. Wiley interscience, New Jersey, pp 132–168
Krause D, Schleusser B, Herborn G, Rau R (2000) Response to methotrexate treatment is associated with reduced mortality in patients with severe rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 43:14–21
Wolfe F, Caplan L, Michaud K (2006) Treatment for rheumatoid arthritis and the risk of hospitalization for pneumonia: associations with prednisone, disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs, and anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy. Arthritis Rheum 54:628–634
Conway R, Low C, Coughlan RJ, O'Donnell MJ, Carey JJ (2014) Methotrexate and lung disease in rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheumatol 66:803–812
Conway R, Low C, Coughlan RJ, O'Donnell MJ, Carey JJ (2015) Methotrexate use and risk of lung disease in psoriasis, psoriatic arthritis, and inflammatory bowel disease: systematic literature review and meta-analysis of randomised controlled trials. BMJ 350:h1269
Fischer A, Brown KK, Du Bois RM, Frankel SK, Cosgrove GP, Fernandez-Perez ER, Huie TJ, Krishnamoorthy M, Meehan RT, Olson AL, Solomon JJ, Swigris JJ (2013) Mycophenolate mofetil improves lung function in connective tissue disease-associated interstitial lung disease. J Rheumatol 40:640–646
Solomon JJ, Chung JH, Cosgrove GP, Demoruelle MK, Fernandez-Perez ER, Fischer A, Frankel SK, Hobbs SB, Huie TJ, Ketzer J, Mannina A, Olson AL, Russell G, Tsuchiya Y, Yunt ZX, Zelarney PT, Brown KK, Swigris JJ (2016) Predictors of mortality in rheumatoid arthritis-associated interstitial lung disease. Eur Respir J 47:588–596
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Mr. Colin Herron and Mrs. Lis Silva for their review of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rojas-Serrano, J., Herrera-Bringas, D., Pérez-Román, D.I. et al. Rheumatoid arthritis-related interstitial lung disease (RA-ILD): methotrexate and the severity of lung disease are associated to prognosis. Clin Rheumatol 36, 1493–1500 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3707-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3707-5