Abstract
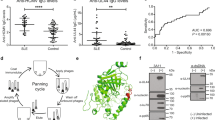
The role of human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) has been postulated as a trigger of systemic sclerosis (SSc). The aim of the study was to assess the prevalence of antibodies against HCMV UL44 and UL57 antigens not tested in the past. Sixty SSc patients, 40 multiple sclerosis and 17 normal controls (NCs), all anti-HCMV positive, were tested by immunoblotting. Reactivity to HCMV antigens, expressed as arbitrary units (AUs), was assessed for correlation with clinical and immunological parameters, including types of SSc-related autoantibodies. Anti-UL44 and anti-UL57 HCMV antibodies were present in 3/60 (5%) and 58/60 (96.7%) SSc patients, respectively (p < 0.001). Anti-UL57 antibodies were present in 35/40 (87.5%) MS patients and 16/17 (94.1%) NCs (SSc vs MS, MS vs NC, p = ns). Strong (50-75 AU) and very strong (75–100 AU) anti-UL57 immunoreactivity was found in 24 (41.4%) and 22 (37.9%) SSc patients, respectively (p = ns). Dilution experiments showed anti-UL57 antibody persistence in up to 1/5000. Overall, there was no difference in the frequency or the magnitude of anti-UL57 immunoreactivity between diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis and limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis patients (96.67 vs 96.67%; 65.45 ± 20.19 vs 64.31 ± 21.11 AU, p > 0.05) but strong anti-UL57 reactivity were more frequent in SSc compared to NCs (p = 0.007). Anti-UL57 reactivity was not inhibited by SSc-specific autoantigens. Anti-UL57 seropositivity did not correlate with demographic, clinical or immunological features of SSc. Anti-HCMV UL57 antibodies are universally present in anti-HCMV-positive patients with SSc, while those against UL44 are rarely seen. Because anti-UL57 lack disease specificity and are not involved in cross-reactive responses, their immunopathogenetic potential is to be questioned.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CEN:
-
Centromere
- dcSSc:
-
Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis
- lcSSc:
-
Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis
- RNA pol III:
-
RNA polymerase III
- Scl-70:
-
Scleroderma 70
- SSc:
-
Systemic sclerosis
References
Sakkas LI, Chikanza IC, Platsoucas CD (2012) Systemic sclerosis: from pathogenesis towards targeted immunotherapies. Curr Rheumatol Rev 8:45–55
Chora I, Guiducci S, Manetti M, Romano E, Mazzotta C, Bellando-Randone S, Ibba-Manneschi L, Matucci-Cerinic M, Soares R (2015) Vascular biomarkers and correlation with peripheral vasculopathy in systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 14(4):314–322. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2014.12.001
Ho YY, Lagares D, Tager AM, Kapoor M (2014) Fibrosis—a lethal component of systemic sclerosis. Nat Rev Rheumatol 10(7):390–402. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2014.53
Sakkas LI, Chikanza IC, Platsoucas CD (2006) Mechanisms of disease: the role of immune cells in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol 2(12):679–685. doi:10.1038/ncprheum0346
Domsic RT (2014) Scleroderma: the role of serum autoantibodies in defining specific clinical phenotypes and organ system involvement. Curr Opin Rheumatol 26(6):646–652. doi:10.1097/BOR.0000000000000113
Kayser C, Fritzler MJ (2015) Autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis: unanswered questions. Front Immunol 6:167. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00167
Sakkas LI, Bogdanos DP (2016) Systemic sclerosis: new evidence re-enforces the role of B cells. Autoimmun Rev 15(2):155–161. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2015.10.005
Pattanaik D, Brown M, Postlethwaite BC, Postlethwaite AE (2015) Pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. Front Immunol 6:272. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2015.00272
Riccieri V, Parisi G, Spadaro A, Scrivo R, Barone F, Moretti T, Bernardini G, Strom R, Taccari E, Valesini G (2005) Reduced circulating natural killer T cells and gamma/delta T cells in patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 32(2):283–286
Murdaca G, Contatore M, Gulli R, Mandich P, Puppo F (2016) Genetic factors and systemic sclerosis. Autoimmun Rev 15(5):427–432. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2016.01.016
Halenius A, Hengel H (2014) Human cytomegalovirus and autoimmune disease. Biomed Res Int 2014:472978. doi:10.1155/2014/472978
Marie I, Gehanno JF (2015) Environmental risk factors of systemic sclerosis. Semin Immunopathol. doi:10.1007/s00281-015-0507-3
Bogdanos DP, Smyk DS, Rigopoulou EI, Sakkas LI, Shoenfeld Y (2015) Infectomics and autoinfectomics: a tool to study infectious-induced autoimmunity. Lupus 24(4–5):364–373. doi:10.1177/0961203314559088
Bogdanos DP, Smyk DS, Invernizzi P, Rigopoulou EI, Blank M, Sakkas L, Pouria S, Shoenfeld Y (2013) Tracing environmental markers of autoimmunity: introducing the infectome. Immunol Res 56(2–3):220–240. doi:10.1007/s12026-013-8399-6
Elisa T, Antonio P, Giuseppe P, Alessandro B, Giuseppe A, Federico C, Marzia D, Ruggero B, Giacomo M, Andrea O, Daniela R, Mariaelisa R, Claudio L (2015) Endothelin receptors expressed by immune cells are involved in modulation of inflammation and in fibrosis: relevance to the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis. J Immunol Res 2015:147616. doi:10.1155/2015/147616
Magro CM, Crowson AN, Ferri C (2007) Cytomegalovirus-associated cutaneous vasculopathy and scleroderma sans inclusion body change. Hum Pathol 38(1):42–49. doi:10.1016/j.humpath.2006.06.002
Pandey JP (2004) Immunoglobulin GM genes and IgG antibodies to cytomegalovirus in patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 22(3 Suppl 33):S35–S37
Pandey JP, LeRoy EC (1998) Human cytomegalovirus and the vasculopathies of autoimmune diseases (especially scleroderma), allograft rejection, and coronary restenosis. Arthritis Rheum 41(1):10–15. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199801)41:1<10::AID-ART2>3.0.CO;2-P
Moinzadeh P, Khan K, Ong VH, Denton CP (2012) Sustained improvement of diffuse systemic sclerosis following human cytomegalovirus infection offers insight into pathogenesis and therapy. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51(12):2296–2298. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/kes137
Vaughan JH, Shaw PX, Nguyen MD, Medsger TA Jr, Wright TM, Metcalf JS, Leroy EC (2000) Evidence of activation of 2 herpesviruses, Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus, in systemic sclerosis and normal skins. J Rheumatol 27(3):821–823
Dolcino M, Puccetti A, Barbieri A, Bason C, Tinazzi E, Ottria A, Patuzzo G, Martinelli N, Lunardi C (2015) Infections and autoimmunity: role of human cytomegalovirus in autoimmune endothelial cell damage. Lupus 24(4–5):419–432. doi:10.1177/0961203314558677
Muryoi T, Kasturi KN, Kafina MJ, Cram DS, Harrison LC, Sasaki T, Bona CA (1992) Antitopoisomerase I monoclonal autoantibodies from scleroderma patients and tight skin mouse interact with similar epitopes. J Exp Med 175(4):1103–1109
Arnson Y, Amital H, Guiducci S, Matucci-Cerinic M, Valentini G, Barzilai O, Maya R, Shoenfeld Y (2009) The role of infections in the immunopathogensis of systemic sclerosis—evidence from serological studies. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1173:627–632. doi:10.1111/j.1749-6632.2009.04808.x
Pastano R, Dell’Agnola C, Bason C, Gigli F, Rabascio C, Puccetti A, Tinazzi E, Cetto G, Peccatori F, Martinelli G, Lunardi C (2012) Antibodies against human cytomegalovirus late protein UL94 in the pathogenesis of scleroderma-like skin lesions in chronic graft-versus-host disease. Int Immunol 24(9):583–591. doi:10.1093/intimm/dxs061
Namboodiri AM, Rocca KM, Pandey JP (2004) IgG antibodies to human cytomegalovirus late protein UL94 in patients with systemic sclerosis. Autoimmunity 37(3):241–244
Lunardi C, Bason C, Navone R, Millo E, Damonte G, Corrocher R, Puccetti A (2000) Systemic sclerosis immunoglobulin G autoantibodies bind the human cytomegalovirus late protein UL94 and induce apoptosis in human endothelial cells. Nat Med 6(10):1183–1186. doi:10.1038/80533
Lunardi C, Dolcino M, Peterlana D, Bason C, Navone R, Tamassia N, Beri R, Corrocher R, Puccetti A (2006) Antibodies against human cytomegalovirus in the pathogenesis of systemic sclerosis: a gene array approach. PLoS Med 3(1):e2. doi:10.1371/journal.pmed.0030002
Lunardi C, Dolcino M, Peterlana D, Bason C, Navone R, Tamassia N, Tinazzi E, Beri R, Corrocher R, Puccetti A (2007) Endothelial cells’ activation and apoptosis induced by a subset of antibodies against human cytomegalovirus: relevance to the pathogenesis of atherosclerosis. PLoS One 2(5):e473. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0000473
Lerner AM, Beqaj SH, Deeter RG, Fitzgerald JT (2002) IgM serum antibodies to human cytomegalovirus nonstructural gene products p52 and CM2(UL44 and UL57) are uniquely present in a subset of patients with chronic fatigue syndrome. Vivo 16(3):153–159
Efthymiou G, Dardiotis E, Liaskos C, Marou E, Tsimourtou V, Hadjigeorgiou GM, Scheper T, Meyer W, Daponte A, Sakkas LI, Bogdanos DP (2016) Anti-hsp60 antibody responses based on Helicobacter pylori in patients with multiple sclerosis: (ir)relevance to disease pathogenesis. J Neuroimmunol 298:19–23
Mavropoulos A, Simopoulou T, Varna A, Liaskos C, Katsiari CG, Bogdanos DP, Sakkas LI (2016) Breg cells are numerically decreased and functionally impaired in patients with systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol 68(2):494–504. doi:10.1002/art.39437
Neidhart M, Kuchen S, Distler O, Bruhlmann P, Michel BA, Gay RE, Gay S (1999) Increased serum levels of antibodies against human cytomegalovirus and prevalence of autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 42(2):389–392. doi:10.1002/1529-0131(199902)42:2<389::AID-ANR23>3.0.CO;2-P
Barzilai O, Sherer Y, Ram M, Izhaky D, Anaya JM, Shoenfeld Y (2007) Epstein-Barr virus and cytomegalovirus in autoimmune diseases: are they truly notorious? A preliminary report. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:567–577
Vanheusden M, Stinissen P, t Hart BA, Hellings N (2015) Cytomegalovirus: a culprit or protector in multiple sclerosis? Trends Mol Med 21(1):16–23. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2014.11.002
Riccieri V, Alessandri C, Germano V, Guiducci S, Rogai V, Colasanti T, Delunardo F, Margutti P, Ortona E, Cerinic MM, Valesini G (2010) Nedd5, a novel autoantigen in systemic sclerosis: is it a marker of more severe disease? Ann Rheum Dis 69(1):314–315. doi:10.1136/ard.2009.111302
Margutti P, Sorice M, Conti F, Delunardo F, Racaniello M, Alessandri C, Siracusano A, Rigano R, Profumo E, Valesini G, Ortona E (2005) Screening of an endothelial cDNA library identifies the C-terminal region of Nedd5 as a novel autoantigen in systemic lupus erythematosus with psychiatric manifestations. Arthritis Res Ther 7(4):R896–R903. doi:10.1186/ar1759
Riemekasten G, Cabral-Marques O (2016) Antibodies against angiotensin II type 1 receptor (AT1R) and endothelin receptor type A (ETAR) in systemic sclerosis (SSc)-response. Autoimmun Rev. doi:10.1016/j.autrev.2016.04.004
Acknowledgements
We thank EUROIMMUN, Germany, for providing antigens, kits and reagents.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
The protocol was approved by the Local Ethical Committee of the University General Hospital of Larissa (no. 1/14-1-2016).
Conflict of interest
T Scheper and W Meyer are employees of Euroimmun; all other authors do not have anything to disclose.
Source of work
Department of Rheumatology and Clinical Immunology, Faculty of Medicine, School of Health Sciences, University of Thessaly, Larissa, Greece.
Financial support
ELKE (Research Committee University of Thessaly).
Part of this work was presented as a poster at the 12th Dresden Symposium on Autoantibodies, Germany, September 23–26, 2015, in a study entitled ‘Human cytomegalovirus specific antibody responses in patients with systemic sclerosis’ by C. Liaskos, E. Marou, G. Euthymiou, T. Simopoulou, C. Katsiari, W. Meyer, D.P. Bogdanos and L.I. Sakkas, as presented in Autoantigens, Autoantibodies, Autoimmunity edited by K. Conrad, E.K.L. Chan, L.E.C. Andrade, G. Steiner, G.J.M. Pruijn and Y. Shoenfeld, Pabst Science Publishers (Berlin); vol. 10—2015, p 124
Additional information
Dimitrios P. Bogdanos and Lazaros I. Sakkas both shared senior authorship.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Marou, E., Liaskos, C., Simopoulou, T. et al. Human cytomegalovirus (HCMV) UL44 and UL57 specific antibody responses in anti-HCMV-positive patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 36, 863–869 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3553-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-017-3553-5