Abstract
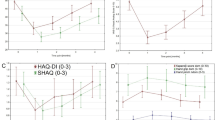
The purpose of this study was to examine the extent of lower extremity impairments in motion and strength in people with systemic sclerosis and the relationships of the impairments to limitations in activities of daily living primarily involving the lower extremities. Participants were 69 persons with SSc who received evaluations of lower extremity joint motion (Keitel function test), strength (timed-stands test), and basic mobility (timed up and go test) and completed a demographic questionnaire regarding symptoms in the lower extremities. Activity limitations were measured by the Rheumatoid and Arthritis Outcome Score (RAOS) which examines functional ability, pain, and quality of life. The participants had difficulty with items requiring external rotation of the hips and lower extremity strength. There were moderate correlations between the impairment measures of joint motion, strength, mobility, and activity limitations. Fair correlations were found between the skin scores and the RAOS sections except for pain. The results of this study show that lower extremity involvement is present in persons with SSc. The findings, regarding strength, mobility, and joint motion are related to the ability to perform everyday activities involving the lower extremities, suggest that these areas should be targeted for intervention in persons with SSc.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
van den Hoogen F, Khanna D, Fransen J, Johnson SR, Baron M, Tyndall A, Matucci-Cerinic M (2013) 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheum 65:2737–2747. doi:10.1002/art.38098, Epub 2013 Oct 3
Clements PJ, Wong WK, Hurwitz EL, Furst DE, Mayes M, White B et al (1999) Correlates of the disability index of the health assessment questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum 11:2372–2380
Schnitzer M, Hudson M, Baron M, Canadian Scleroderma Research Group (2011) Disability in systemic sclerosis—a longitudinal observational study. J Rheum 38:685–692. doi:10.3899/jrheum.100635
La Montagna G, Baruffo A, Tirri R, Buono G, Valentini G (2002) Foot involvement in systemic sclerosis: a longitudinal study. Semin Arthritis Rheum 31:248–255. doi:10.1053/sarh.2002.29493
Sari-Kouzel H, Hutchinson CE, Middleton A, Webb F, Moore T, Griffin K, Herrick AL (2001) Foot problems in patients with systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology 40:410–413. doi:10.1093/rheumatology/40.4.410
Ranque B, Authier FJ, Berezne A, Guillevin L, Mouthon L (2007) Systemic sclerosis-associated myopathy. Ann N Y Acad Sci 1108:268–82. doi:10.1196/annals.1422.029
Balint Z, Farkas H, Farkas N, Minier T, Kumanovics G, Horvath SAI, Czirjak L, Varju C (2014) A three-year follow-up study of the development of joint contractures in 131 patients with systemic sclerosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 32(suppl86):S68–S74
Rodnan GP, Lipinski E, Luksick J (1979) Skin thickness and collagen content in progressive systemic sclerosis and localized scleroderma. Arthritis Rheum 22:130–40
Clements PJ, Lachenbruch PA, Ng SC, Simmons M, Sterz M, Furst DE (1990) Skin score. A semiquantitative measure of cutaneous involvement that improves prediction of prognosis in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 33:1256–63
Eberl DR, Fasching V, Rahlfs V, Schleyer I, Wolf R (1976) Repeatability and objectivity of various measurements in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 19:1278–1286
Kalla AA, Kotze TJ, Meyers OL, Parkyn ND (1988) Clinical assessment of disease activity in rheumatoid arthritis: evaluation of a functional test. Ann Rheum Dis 47:773–779
Hakala M, Nieminen P (1996) Functional status assessment of physical impairment in a community based population with rheumatoid arthritis: severely incapacitated patients are rare. J Rheumatol 23:617–23
Jones CJ, Rikli RE, Beam WC (1999) A 30-s chair-stand test as a measure of lower body strength in community-residing older adults. Exercise and Sport 70:113–119
McCarthy EK, Horvat MA, Holtsberg PA, Wisenbaker JM (2004) Repeated chair stands as a measure of lower limb strength in sexagenarian women. J Gerontol A Biol Sci Med Sci 59A:1207–1212. doi:10.1093/gerona/59.11.1207
Podsiadlo D, Richardsons (1991) The timed “up & go”; a test of functional mobility for frail elderly persons. JAGS 39:142–148
Bremander ABI, Petersson IP, Roos EM (2003) Validation of the Rheumatoid and Arthritis Outcome Score (RAOS) for the lower extremity. Health Qual Life Outcomes 1:55. doi:10.1186/1477-7525-1-55
Soderlin MK, Nieminen P, Hakala M (1998) Functional status predicts mortality in a community based rheumatoid arthritis population. J Rheumatol 19:30–34
Isles RC, Choy NLL, Steer M, Nitz JC (2004) Normal values of balance tests in women aged 20–80. JAGS 52:1367–1372. doi:10.1111/j.1532-5415.2004.52370.x
Bohannon RW (2006) Reference values for the timed up and go test: a descriptive meta-analysis. Journal of Geriatric Phys Ther 29:64–68
Negahban H, Masoudpur F, Rajaei E, Nazarinia MA, Mazaheri M, Salavati M (2015) Reliabiliity, validity, and responsiveness of the Persian version of the rheumatoid and arthritis outcome score (RAOS) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34:35–42. doi:10.1007/s10067-014-2515-4
Karatepe AG, Gunaydin R, Turkmen G, Kaya T, Ozbek G (2009) The validity and reliability of the Turkish version of the rheumatoid and arthritis outcome score (RAOS) in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 28:47–51. doi:10.1007/s10067-008-0981-2
Lima TRL, Guimaraes FS, Silva LA, Silva DPG, Menezes SLS, Lopes AJ (2015) Relationship between functional capacity, joint mobility and pulmonary function in patients with systemic sclerosis. J Bodyw Mov Ther 19:17–24. doi:10.1016/j.jbmt.2014.01.002
Lima TRL, Guimaraes FS, Carvalho MN, Sousa TLM, Memezes SLS, Lopes AJ (2014) Lower limb muscle strength is associated with functional performance and quality of life in patients with systemic sclerosis. Braz J Phy Ther., http://dx.doi.org/10.1590/bjpt-rbf.2014.0084
Herrick A, Rooney B, Finn J, Silman A (2001) Lack of relationship between functional ability and skin score in patients with systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 28:292–295
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosures
None.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Poole, J.L., Brandenstein, J. Difficulty with daily activities involving the lower extremities in people with systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 35, 483–488 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3137-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-3137-1