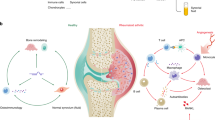
Abstract
The role of genetic and epigenetic factors in the development of rheumatic diseases has been an interesting field of research over the past decades all around the world. Research on the role of microRNAs (miRNAs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) has been active and ongoing, and investigations have attempted to use miRNAs as biomarkers in disease diagnosis, prognosis, and treatment. This review focuses on experimental researches in the field of miRNAs and RA to present the data available up to this date and includes researches searched by keywords “microRNA” and “rheumatoid arthritis” in PubMed from 2008 to January 2015. All references were also searched for related papers. miRNAs are shown to act as proinflammatory or anti-inflammatory agents in diverse cell types, and their role seems to be regulatory in most instances. Researchers have evaluated miRNAs in patients compared to controls or have investigated their role by overexpressing or silencing them. Multiple targets have been identified in vivo, in vitro, or in silico, and the researches still continue to show their efficacy in clinical settings.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Philippe L, Alsaleh G, Bahram S, Pfeffer S, Georgel P (2013) The miR-17 approximately 92 Cluster: a key player in the control of inflammation during rheumatoid arthritis. Front Immunol 4:70. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2013.00070
Nakamachi Y, Kawano S, Takenokuchi M, Nishimura K, Sakai Y, Chin T, Saura R, Kurosaka M, Kumagai S (2009) MicroRNA-124a is a key regulator of proliferation and monocyte chemoattractant protein 1 secretion in fibroblast-like synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 60(5):1294–1304. doi:10.1002/art.24475
Niederer F, Trenkmann M, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Neidhart M, Stanczyk J, Kolling C, Gay RE, Detmar M, Gay S, Jungel A, Kyburz D (2012) Down-regulation of microRNA-34a* in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts promotes apoptosis resistance. Arthritis Rheum 64(6):1771–1779. doi:10.1002/art.34334
Niimoto T, Nakasa T, Ishikawa M, Okuhara A, Izumi B, Deie M, Suzuki O, Adachi N, Ochi M (2010) MicroRNA-146a expresses in interleukin-17 producing T cells in rheumatoid arthritis patients. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 11:209. doi:10.1186/1471-2474-11-209
Pauley KM, Satoh M, Chan AL, Bubb MR, Reeves WH, Chan EK (2008) Upregulated miR-146a expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther 10(4):R101. doi:10.1186/ar2493
Murata K, Yoshitomi H, Tanida S, Ishikawa M, Nishitani K, Ito H, Nakamura T (2010) Plasma and synovial fluid microRNAs as potential biomarkers of rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12(3):R86. doi:10.1186/ar3013
Filkova M, Aradi B, Senolt L, Ospelt C, Vettori S, Mann H, Filer A, Raza K, Buckley CD, Snow M, Vencovsky J, Pavelka K, Michel BA, Gay RE, Gay S, Jungel A (2014) Association of circulating miR-223 and miR-16 with disease activity in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 73(10):1898–1904. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-202815
Trenkmann M, Brock M, Gay RE, Michel BA, Gay S, Huber LC (2013) Tumor necrosis factor alpha-induced microRNA-18a activates rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts through a feedback loop in NF-kappaB signaling. Arthritis Rheum 65(4):916–927. doi:10.1002/art.37834
Philippe L, Alsaleh G, Suffert G, Meyer A, Georgel P, Sibilia J, Wachsmann D, Pfeffer S (2012) TLR2 expression is regulated by microRNA miR-19 in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Immunol 188(1):454–461. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102348
Philippe L, Alsaleh G, Pichot A, Ostermann E, Zuber G, Frisch B, Sibilia J, Pfeffer S, Bahram S, Wachsmann D, Georgel P (2013) MiR-20a regulates ASK1 expression and TLR4-dependent cytokine release in rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. Ann Rheum Dis 72(6):1071–1079. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2012-201654
Lin J, Huo R, Xiao L, Zhu X, Xie J, Sun S, He Y, Zhang J, Sun Y, Zhou Z, Wu P, Shen B, Li D, Li N (2014) A novel p53/microRNA-22/Cyr61 axis in synovial cells regulates inflammation in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 66(1):49–59. doi:10.1002/art.38142
Zhu S, Pan W, Song X, Liu Y, Shao X, Tang Y, Liang D, He D, Wang H, Liu W, Shi Y, Harley JB, Shen N, Qian Y (2012) The microRNA miR-23b suppresses IL-17-associated autoimmune inflammation by targeting TAB2, TAB3 and IKK-alpha. Nat Med 18(7):1077–1086. doi:10.1038/nm.2815
Ham O, Lee CY, Song BW, Lee SY, Kim R, Park JH, Lee J, Seo HH, Lee CY, Chung YA, Maeng LS, Lee MY, Kim J, Hwang J, Woo DK, Chang W (2014) Upregulation of miR-23b enhances the autologous therapeutic potential for degenerative arthritis by targeting PRKACB in synovial fluid-derived mesenchymal stem cells from patients. Mol Cells 37(6):449–456. doi:10.14348/molcells.2014.0023
Murata K, Furu M, Yoshitomi H, Ishikawa M, Shibuya H, Hashimoto M, Imura Y, Fujii T, Ito H, Mimori T, Matsuda S (2013) Comprehensive microRNA analysis identifies miR-24 and miR-125a-5p as plasma biomarkers for rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS One 8(7):e69118. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0069118
Xu K, Xu P, Yao JF, Zhang YG, Hou WK, Lu SM (2013) Reduced apoptosis correlates with enhanced autophagy in synovial tissues of rheumatoid arthritis. Inflamm Res Off J Eur Histamine Res Soc 62(2):229–237. doi:10.1007/s00011-012-0572-1
Lu MC, Yu CL, Chen HC, Yu HC, Huang HB, Lai NS (2014) Increased miR-223 expression in T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis leads to decreased insulin-like growth factor-1-mediated interleukin-10 production. Clin Exp Immunol 177(3):641–651. doi:10.1111/cei.12374
Gantier MP, Stunden HJ, McCoy CE, Behlke MA, Wang D, Kaparakis-Liaskos M, Sarvestani ST, Yang YH, Xu D, Corr SC, Morand EF, Williams BR (2012) A miR-19 regulon that controls NF-kappaB signaling. Nucleic Acids Res 40(16):8048–8058. doi:10.1093/nar/gks521
Zhou Q, Long L, Shi G, Zhang J, Wu T, Zhou B (2013) Research of the methylation status of miR-124a gene promoter among rheumatoid arthritis patients. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:524204. doi:10.1155/2013/524204
Duroux-Richard I, Pers YM, Fabre S, Ammari M, Baeten D, Cartron G, Touitou I, Jorgensen C, Apparailly F (2014) Circulating miRNA-125b is a potential biomarker predicting response to rituximab in rheumatoid arthritis. Mediat Inflamm 2014:342524. doi:10.1155/2014/342524
Li J, Wan Y, Guo Q, Zou L, Zhang J, Fang Y, Zhang J, Zhang J, Fu X, Liu H, Lu L, Wu Y (2010) Altered microRNA expression profile with miR-146a upregulation in CD4+ T cells from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Res Ther 12(3):R81. doi:10.1186/ar3006
Nakasa T, Miyaki S, Okubo A, Hashimoto M, Nishida K, Ochi M, Asahara H (2008) Expression of microRNA-146 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial tissue. Arthritis Rheum 58(5):1284–1292. doi:10.1002/art.23429
Abou-Zeid A, Saad M, Soliman E (2011) MicroRNA 146a expression in rheumatoid arthritis: association with tumor necrosis factor-alpha and disease activity. Genet Test Mol Biomarkers 15(11):807–812. doi:10.1089/gtmb.2011.0026
Lu LF, Boldin MP, Chaudhry A, Lin LL, Taganov KD, Hanada T, Yoshimura A, Baltimore D, Rudensky AY (2010) Function of miR-146a in controlling Treg cell-mediated regulation of Th1 responses. Cell 142(6):914–929. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2010.08.012
Zhou Q, Haupt S, Kreuzer JT, Hammitzsch A, Proft F, Neumann C, Leipe J, Witt M, Schulze-Koops H, Skapenko A (2014) Decreased expression of miR-146a and miR-155 contributes to an abnormal Treg phenotype in patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204377
Nakasa T, Shibuya H, Nagata Y, Niimoto T, Ochi M (2011) The inhibitory effect of microRNA-146a expression on bone destruction in collagen-induced arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 63(6):1582–1590. doi:10.1002/art.30321
Stanczyk J, Pedrioli DM, Brentano F, Sanchez-Pernaute O, Kolling C, Gay RE, Detmar M, Gay S, Kyburz D (2008) Altered expression of MicroRNA in synovial fibroblasts and synovial tissue in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 58(4):1001–1009. doi:10.1002/art.23386
Lu LF, Thai TH, Calado DP, Chaudhry A, Kubo M, Tanaka K, Loeb GB, Lee H, Yoshimura A, Rajewsky K, Rudensky AY (2009) Foxp3-dependent microRNA155 confers competitive fitness to regulatory T cells by targeting SOCS1 protein. Immunity 30(1):80–91. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2008.11.010
Smigielska-Czepiel K, van den Berg A, Jellema P, van der Lei RJ, Bijzet J, Kluiver J, Boots AM, Brouwer E, Kroesen BJ (2014) Comprehensive analysis of miRNA expression in T-cell subsets of rheumatoid arthritis patients reveals defined signatures of naive and memory Tregs. Genes Immun 15(2):115–125. doi:10.1038/gene.2013.69
Ceppi M, Pereira PM, Dunand-Sauthier I, Barras E, Reith W, Santos MA, Pierre P (2009) MicroRNA-155 modulates the interleukin-1 signaling pathway in activated human monocyte-derived dendritic cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106(8):2735–2740. doi:10.1073/pnas.0811073106
Kurowska-Stolarska M, Alivernini S, Ballantine LE, Asquith DL, Millar NL, Gilchrist DS, Reilly J, Ierna M, Fraser AR, Stolarski B, McSharry C, Hueber AJ, Baxter D, Hunter J, Gay S, Liew FY, McInnes IB (2011) MicroRNA-155 as a proinflammatory regulator in clinical and experimental arthritis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108(27):11193–11198. doi:10.1073/pnas.1019536108
Long L, Yu P, Liu Y, Wang S, Li R, Shi J, Zhang X, Li Y, Sun X, Zhou B, Cui L, Li Z (2013) Upregulated microRNA-155 expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells and fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Dev Immunol 2013:296139. doi:10.1155/2013/296139
Li X, Tian F, Wang F (2013) Rheumatoid arthritis-associated microRNA-155 targets SOCS1 and upregulates TNF-alpha and IL-1beta in PBMCs. Int J Mol Sci 14(12):23910–23921. doi:10.3390/ijms141223910
Bluml S, Bonelli M, Niederreiter B, Puchner A, Mayr G, Hayer S, Koenders MI, van den Berg WB, Smolen J, Redlich K (2011) Essential role of microRNA-155 in the pathogenesis of autoimmune arthritis in mice. Arthritis Rheum 63(5):1281–1288. doi:10.1002/art.30281
Zhou H, Huang X, Cui H, Luo X, Tang Y, Chen S, Wu L, Shen N (2010) miR-155 and its star-form partner miR-155* cooperatively regulate type I interferon production by human plasmacytoid dendritic cells. Blood 116(26):5885–5894. doi:10.1182/blood-2010-04-280156
Davis TE, Kis-Toth K, Tsokos GC (2014) A114: methylprednisolone-induced inhibition of miR-155 expression increases SOCS1-driven suppression of cytokine signaling. Arthritis Rheum 66(Suppl 11):S151. doi:10.1002/art.38535
Stanczyk J, Ospelt C, Karouzakis E, Filer A, Raza K, Kolling C, Gay R, Buckley CD, Tak PP, Gay S, Kyburz D (2011) Altered expression of microRNA-203 in rheumatoid arthritis synovial fibroblasts and its role in fibroblast activation. Arthritis Rheum 63(2):373–381. doi:10.1002/art.30115
Pandis I, Ospelt C, Karagianni N, Denis MC, Reczko M, Camps C, Hatzigeorgiou AG, Ragoussis J, Gay S, Kollias G (2012) Identification of microRNA-221/222 and microRNA-323-3p association with rheumatoid arthritis via predictions using the human tumour necrosis factor transgenic mouse model. Ann Rheum Dis 71(10):1716–1723. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2011-200803
Fulci V, Scappucci G, Sebastiani GD, Giannitti C, Franceschini D, Meloni F, Colombo T, Citarella F, Barnaba V, Minisola G, Galeazzi M, Macino G (2010) miR-223 is overexpressed in T-lymphocytes of patients affected by rheumatoid arthritis. Hum Immunol 71(2):206–211. doi:10.1016/j.humimm.2009.11.008
Shibuya H, Nakasa T, Adachi N, Nagata Y, Ishikawa M, Deie M, Suzuki O, Ochi M (2013) Overexpression of microRNA-223 in rheumatoid arthritis synovium controls osteoclast differentiation. Mod Rheumatol Jpn Rheum Assoc 23(4):674–685. doi:10.1007/s10165-012-0710-1
Li YT, Chen SY, Wang CR, Liu MF, Lin CC, Jou IM, Shiau AL, Wu CL (2012) Brief report: amelioration of collagen-induced arthritis in mice by lentivirus-mediated silencing of microRNA-223. Arthritis Rheum 64(10):3240–3245. doi:10.1002/art.34550
Alsaleh G, Suffert G, Semaan N, Juncker T, Frenzel L, Gottenberg JE, Sibilia J, Pfeffer S, Wachsmann D (2009) Bruton’s tyrosine kinase is involved in miR-346-related regulation of IL-18 release by lipopolysaccharide-activated rheumatoid fibroblast-like synoviocytes. J Immunol 182(8):5088–5097. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0801613
Semaan N, Frenzel L, Alsaleh G, Suffert G, Gottenberg JE, Sibilia J, Pfeffer S, Wachsmann D (2011) miR-346 controls release of TNF-alpha protein and stability of its mRNA in rheumatoid arthritis via tristetraprolin stabilization. PloS One 6(5):e19827. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019827
Murata K, Yoshitomi H, Furu M, Ishikawa M, Shibuya H, Ito H, Matsuda S (2014) MicroRNA-451 down-regulates neutrophil chemotaxis via p38 MAPK. Arthritis Rheumatol 66(3):549–559. doi:10.1002/art.38269
Miao CG, Yang YY, He X, Li XF, Huang C, Huang Y, Zhang L, Lv XW, Jin Y, Li J (2013) Wnt signaling pathway in rheumatoid arthritis, with special emphasis on the different roles in synovial inflammation and bone remodeling. Cell Signal 25(10):2069–2078. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.04.002
Alevizos I, Illei GG (2010) MicroRNAs as biomarkers in rheumatic diseases. Nat Rev Rheumatol 6(7):391–398. doi:10.1038/nrrheum.2010.81
Mookherjee N, El-Gabalawy HS (2013) High degree of correlation between whole blood and PBMC expression levels of miR-155 and miR-146a in healthy controls and rheumatoid arthritis patients. J Immunol Methods 400–401:106–110. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2013.10.001
Kawano S, Nakamachi Y (2011) miR-124a as a key regulator of proliferation and MCP-1 secretion in synoviocytes from patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Ann Rheum Dis 70(Suppl 1):i88–i91. doi:10.1136/ard.2010.138669
Nakamachi Y, Ohnuma K, Uto K, Noguchi Y, Saegusa J, Kawano S (2015) MicroRNA-124 inhibits the progression of adjuvant-induced arthritis in rats. Ann Rheum Dis. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2014-206417
Conflict of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Salehi, E., Eftekhari, R., Oraei, M. et al. MicroRNAs in rheumatoid arthritis. Clin Rheumatol 34, 615–628 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2898-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-015-2898-x