Abstract
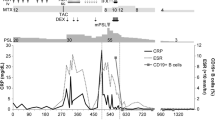
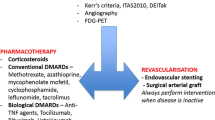
Takayasu arteritis (TA) is a rare form of chronic large vessel vasculitis of unknown origin involving the aorta and its major branches. Recently, the involvement of B lymphocytes in TA has been suggested, and active refractory TA patients were successfully treated with B cell depletion therapy (BCDT). We report two cases of patients with TA successfully treated with anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (rituximab). The favorable outcome of rituximab treatment in our patients also support the view that BCDT can be a useful option for refractory TA, and its potential should be evaluated in controlled trials.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arnaud L, Haroche J, Mathian A, Gorochov G, Amoura Z (2011) Pathogenesis of Takayasu's arteritis: a 2011 update. Autoimmun Rev 11:61–67
Sima D, Thiele B, Turowski A, Wilke K, Hiepe F, Volk D et al (1994) Anti-endothelial antibodies in Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 37:441–443
Inder SJ, Bobryshev YV, Cherian SM, Wang AY, Lord RS, Masuda K et al (2000) Immunophenotypic analysis of the aortic wall in Takayasu’s arteritis: involvement of lymphocytes, dendritic cells and granulocytes in immuno- inflammatory reactions. Cardiovasc Surg 8:141–148
Sharma BK, Jain S, Suri S, Numano F (1996) Diagnostic criteria for Takayasu arteritis. Int J Cardiol 54:S141–S147
Comarmond C, Plaisier E, Dahan K, Mirault T, Emmerich J, Amoura Z et al (2012) Anti TNF-α in refractory Takayasu's arteritis: cases series and review of the literature. Autoimmun Rev 11:678–684
Quartuccio L, Schiavon F, Zuliani F, Carraro V, Catarsi E, Tavoni AG et al (2012) Long-term efficacy and improvement of health-related quality of life in patients with Takayasu's arteritis treated with infliximab. Clin Exp Rheumatol 30(6):922–928
Hoffman GS, Merkel PA, Brasington RD, Lenschow DJ, Liang P (2004) Anti-tumor necrosis factor therapy in patients with difficult to treat Takayasu arteritis. Arthritis Rheum 50:2296–2304
Salvarani C, Magnani L, Catanoso M, Pipitone N, Versari A, Dardani L et al (2012) Tocilizumab: a novel therapy for patients with large-vessel vasculitis. Rheumatology 51:151–156
Nishimoto N, Nakahara H, Yoshio-Hoshino N, Mima T (2008) Successful treatment of a patient with Takayasu arteritis using a humanized anti interleukin-6 receptor antibody. Arthritis Rheum 58:1197–1200
Galarza C, Valencia D, Tobón GJ, Zurita L, Mantilla RD, Pineda-Tamayo R et al (2008) Should rituximab be considered as the first-choice treatment for severe autoimmune rheumatic diseases? Clin Rev Allergy Immunol 34:124–128
Hoyer BF, Mumtaz IM, Loddenkemper K, Bruns A, Sengler C, Hermann KG et al (2012) Takayasu arteritis is characterised by disturbances of B cell homeostasis and responds to B cell depletion therapy with rituximab. Ann Rheum Dis 71:75–79
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Caltran, E., Di Colo, G., Ghigliotti, G. et al. Two Takayasu arteritis patients successfully treated with rituximab. Clin Rheumatol 33, 1183–1184 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2506-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-014-2506-5