Abstract
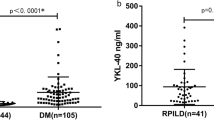
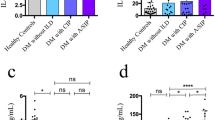
Autoantibodies against melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 (MDA5) are important serological markers in dermatomyositis (DM) with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease (ILD). Recent studies noted that anti-MDA5 antibody (anti-MDA5ab), ferritin, and IL-18 are useful biomarkers for evaluating the responses to treatment and the status of ILD in anti-MDA5ab-positive DM. In this study, we further studied the importance of anti-MDA5ab levels and of ferritin and IL-18 concentrations in our patients. These biomarkers could be sometimes useful for evaluating ILD status and/or predicting the prognosis in patients with anti-MDA5ab-positive DM with several exceptional cases. A single-point evaluation of anti-MDA5ab levels and of ferritin and IL-18 concentrations has limitations in predicting the prognosis of ILD with DM. We consider that the timing of initial therapy and the anti-MDA5ab isotype, in addition to the patient’s age, are also crucial factors for predicting the prognosis.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ye S, Chen XX, Lu XY et al (2007) Adult clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis with rapid progressive interstitial lung disease: a retrospective cohort study. Clin Rheumatol 26:1647–1654
Chen IJ, Jan Wu YJ, Lin CW et al (2009) Interstitial lung disease in polymyositis and dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol 28:639–646
Sato S, Hoshino K, Satoh T et al (2009) RNA helicase encoded by melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 is a major autoantigen in patients with clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis: association with rapidly progressive interstitial lung disease. Arthritis Rheum 60:2193–2200
Hoshino K, Muro Y, Sugiura K, Tomita Y, Nakashima R, Mimori T (2010) Anti-MDA5 and anti-TIF1-γ antibodies have clinical significance for patients with dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:1726–1733
Fiorentino D, Chung L, Zwerner J, Rosen A, Casciola-Rosen L (2011) The mucocutaneous and systemic phenotype of dermatomyositis patients with antibodies to MDA5 (CADM-140): a retrospective study. J Am Acad Dermatol 65:25–34
Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Satoh T et al (2010) Clinical manifestation and prognostic factor in anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibody-associated interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:1713–1719
Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Hara M et al (2010) Increased ferritin predicts development and severity of acute interstitial lung disease as a complication of dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:1354–1360
Gono T, Kawaguchi Y, Sugiura T et al (2010) Interleukin-18 is a key mediator in dermatomyositis: potential contribution to development of interstitial lung disease. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:1878–1881
Gono T, Sato S, Kawaguchi Y et al (2012) Anti-MDA5 antibody, ferritin and IL-18 are useful for the evaluation of response to treatment in interstitial lung disease with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:1563–1570
Muro Y, Sugiura K, Hoshino K, Akiyama M (2012) Disappearance of anti-MDA-5 autoantibodies in clinically amyopathic DM/interstitial lung disease during disease remission. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:800–804
Muro Y, Sugiura K, Hoshino K, Akiyama M, Tamakoshi K (2011) Epidemiologic study of clinically amyopathic dermatomyositis and anti-melanoma differentiation-associated gene 5 antibodies in central Japan. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R214
American Thoracic Society (2000) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: diagnosis and treatment. International consensus statement. American Thoracic Society (ATS), and the European Respiratory Society (ERS). Am J Respir Crit Care Med 161(2 Pt 1):646–664
Ishikawa A, Muro Y, Sugiura K, Akiyama M (2012) Development of an ELISA for detection of autoantibodies to nuclear matrix protein 2. Rheumatology (Oxford) 51:1181–1187
Kakumanu P, Yamagata H, Sobel ES, Reeves WH, Chan EK, Satoh M (2008) Patients with pulmonary tuberculosis are frequently positive for anti-cyclic citrullinated peptide antibodies, but their sera also react with unmodified arginine-containing peptide. Arthritis Rheum 58:1576–1581
Nakashima R, Imura Y, Kobayashi S et al (2010) The RIG-I-like receptor IFIH1/MDA5 is a dermatomyositis-specific autoantigen identified by the anti-CADM-140 antibody. Rheumatology (Oxford) 49:433–440
Muro Y (2012) Dermatomyositis. (in Japanese) Jpn J Dermatol 122:3358–3360
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Culture, Sports, Science and Technology of Japan (23591618 to YM and 23249058 to MA) and by a grant from the Ministry of Health, Labour and Welfare of Japan (to YM).
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Muro, Y., Sugiura, K. & Akiyama, M. Limitations of a single-point evaluation of anti-MDA5 antibody, ferritin, and IL-18 in predicting the prognosis of interstitial lung disease with anti-MDA5 antibody-positive dermatomyositis. Clin Rheumatol 32, 395–398 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2142-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2142-x