Abstract
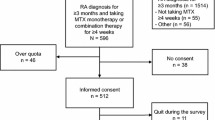
We conducted a survey among Japanese rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients to better understand what they expect from treatment and whether there is a difference between expectations of biologics-treated and disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)-treated patients. An anonymous survey was conducted with 165 outpatients from our clinic (with informed written consent). On the survey, they wrote their age, gender, medical history, and commented on: (1) expectations for treatment, (2) disappointment with treatment, (3) experience of, and thoughts about switching treatments, (4) information wanted before starting a new treatment, (5) expectations before administration and noticeable differences after treatment, (6) level of satisfaction with current treatment, and (7) expectations of possible treatments. Patients who had never been treated with DMARDs were excluded from the survey. For “treatment goals before administration,” 86 % responded with “assured efficacy,” while 73 % responded “suppress joint destruction” or “recover from joint destruction.” Also, more patients hoped for “long-lasting efficacy” (67 %) over “fast acting” (41 %), which suggests significance of the long-term improvement of QOL. Related to “disappointment with treatment,” patients also felt anxiety over switching treatment for possibilities of not responding enough, or side effects. RA patients have high expectations for medication in terms of assured improvement of conditions and long-lasting efficacy of drugs, while the biggest concern was if they would have side effects or not, and if so, what type. The results suggest patients hope to have worries over switching medications dispelled. The results also verified those who have used biologics before have higher treatment goals than those who have not.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Saag KG, Teng GG, Patkar NM, Anuntiyo J, Finney C, Curtis JR et al (2008) American College of Rheumatology 2008 recommendation for the use of nonbiologic and biologic disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 59:762–784
Smolen JS, Lande R, Breedveld FC, Dougados M, Emery P, Gaujoux-Viala C et al (2010) EULAR recommendations for the management of rheumatoid arthritis with synthetic and biological disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drugs. Ann Rheum Dis 69:964–975
Smolen JS, Aletaha D, Bijlsma JWJ, Breedveld FC, Boumpas D, Burmester G et al (2010) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 69:631–637
Aletaha D, Neogi T, Silman A, Funovits J, Felson DT, Bingham CO et al (2010) 2010 Rheumatoid arthritis classification criteria: an American College of Rheumatology/European League Against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1580–1588
Smolen JS, Aletala D, Bijlsma JW, Breedveld FC, Boumpas D, Burmester G et al (2010) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: recommendations of an international task force. Ann Rheum Dis 69:631–637
de Wit MPT, Smolen JS, Goossec L, van der Heijde DMFM (2011) Treating rheumatoid arthritis to target: the patient version of the international recommendations. Ann Rheum Dis 70:891–895
Miyasaka N (2011) Treatment trends of rheumatoid arthritis in Japan: changes toward globalization and its unique innovation. Inflam Regen 31:25–32
‘Nihon Ryumachi Tomo No Kai’ (The Japanese Rheumatoid Arthritis Patients Association) 2010
Pincus T, Summey JA, Soraci SA, Wallston KA, Hummon NP (1983) Assessment of patient satisfaction in activities of daily using a modified Stanford Health Assessment Questionnaire. Arthritis Rheum 26:1346–1353
Goekoop-Ruiterman YP, de Vries-Bouwstra JK, Allaart CF (2007) Patients’ preferences for treatment: report from a randomized combination of treatment strategies in early rheumatoid arthritis (BeSt trial). Ann Rheum Dis 66:1227–1232
“Enbrel.jp.” Enbrel.jp. Pfizer (2012) Web. http://www.enbrel.jp/ Accessed 25 May 2012
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to thank all patients for their participation. Also, special thanks to Mari Mizutani for her assistance in conducting the surveys.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Funahashi, K., Matsubara, T. What RA patients expect of their treatment—discussion over the result of our survey. Clin Rheumatol 31, 1559–1566 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2048-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2048-7