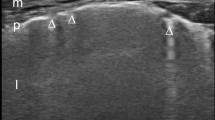
Abstract
Ultrasound (US) has an emergent and relevant role in the assessment of systemic sclerosis (SSc) even if there are many fields and applications that still have not been sufficiently explored. In this review, we will report an update of the available data regarding the use of US in lung involvement that might cause disability and mortality in SSc patients. Lung US does not employ ionizing radiation and is more rapid and less expensive than traditional high-resolution tomography (HRCT). Furthermore, recent initial studies have demonstrated that US scores correlated to HRCT and functional respiratory test results in SSc interstitial lung disease. The research agenda for the future should include a more profound investigation of its specificity (comparison with healthy subjects and other diseases) and sensitivity to change at follow-up, to adequately disseminate its use in daily practice and clinical trials.

Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- CT:
-
Computerized tomography
- DLCO:
-
Carbon monoxide lung diffusion
- HRCT:
-
High-resolution computerized tomography
- ILD:
-
Interstitial lung disease
- PFTs:
-
Pulmonary function tests
- SSc:
-
Systemic sclerosis
- US:
-
Ultrasound
References
Kaloudi O, Bandinelli F, Filippucci E et al (2010) High frequency ultrasound measurement of digital dermal thickness in systemic sclerosis. Ann Rheum Dis 69:1140–1143
Iagnocco A, Kaloudi O, Perella C et al (2010) Ultrasound elastography assessment of skin involvement in systemic sclerosis: lights and shadows. J Rheumatol 37:1688–1691
Bandinelli F, Kaloudi O, Miniati I et al (2010) Early detection of median nerve syndrome at the carpal tunnel with high-resolution 18 MHz ultrasonography in systemic sclerosis patients. Clin Exp Rheumatol S62:15–18
Bandinelli F, Matucci Cerinic M (2011) Ultrasound in scleroderma. Curr Rheumatol Rev 7:1–7
Silver RM (1996) Scleroderma. Clinical problems. The lungs. Rheum Dis Clin North Am 22:825–840
Steen VD, Medsger TA (2007) Changes in causes of death in systemic sclerosis, 1972–2002. Ann Rheum Dis 66:940–944
Wells AU, Steen V, Valentini G (2009) Pulmonary complications: one of the most challenging complications of systemic sclerosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:iii40–iii44
D’Angelo WA, Fries JF, Masi AT et al (1969) Pathologic observations in systemic sclerosis (scleroderma); a study of fifty-eight autopsy cases and fifty-eight matched controls. Am J Med 46:428–440
Wells AU, Cullinan P, Hansell DM et al (1994) Fibrosing alveolitis associated to systemic sclerosis has a better prognosis than lone cryptogenic fibrosing alveolitis. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 149:1583–1590
Diot E, Boissinot E, Asquier E et al (1998) Relationship between abnormalities on high resolutionct and pulmonary function in systemic sclerosis. Chest 114:1623–1629
Wells AU, Rubens MB, du Bois RM et al (1993) Serial CT in fibrosing alveolitis: prognostic significance of the initial pattern. AJR Am J Roentgenol 161:1159–1165
Ostojic P, Damjanov N (2006) Different clinical features in patients with limited and diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 25:453–457
Morelli S, Barbieri C, Sgreccia A et al (1997) Relationship between cutaneous and pulmonary involvement in systemic sclerosis. J Rheumatol 24:81–85
Toya SP, Tzelepis GE (2009) The many faces of scleroderma sine scleroderma: a literature review focusing on cardiopulmonary complications. Rheumatol Int 29:861–868
Matucci Cerinic M, Steen V, Nash P, Hachulla E (2009) The complexity of managing systemic sclerosis: screening and diagnosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:iii8–iii13
Avouac J, Fransen J, Walker UA et al (2011) Preliminary criteria for the very early diagnosis of systemic sclerosis: results of a Delphi Consesus Study from EULAR Scleroderma Trials and Research Group. Ann Rheum Dis 70:476–481
Hunninghake GW, Zimmerman MB, Schwartz MI et al (2001) Utility of a lung biopsy for the diagnosis of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Am J Respir Crit Med 164:193–196
Lynch DA, Travis WD, Muller NL et al (2005) Idiopathic interstitial pneumonias: CT features. Radiology 236:10–21
Kr F, Thwaite EL, Kazerooni EA et al (2003) Radiological versus histological diagnosis in UIP and NSIP: survival implications. Thorax 58:143–148
Steen VD (2005) The lung in systemic sclerosis. J Clin Rheumatol 11:40–46
Goh NS, Veeraraghavan S, Desai SR et al (2008) Interstitial lung disease in systemic sclerosis: a simple staging system. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 177:1248–1254
Steen VD, Graham G, Conte C et al (1992) Isolated diffusing capacity reduction in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheum 35:765–770
Wells AU, Hansell DM, Rubens MB et al (1997) Fibrosing alveolitis in systemic sclerosis: indices of lung function in relation to the extent of disease on computerized tomography. Arthritis Rheum 40:1229–1236
Best AC, Meng J, Lynch AM et al (2008) Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: physiological tests, quantitative CT indices and CI visual scores as predictor of mortality. Radiology 246:935–940
Lichtenstein DA, Meziere G, Biderman P et al (1997) The comet-tail artifact. An ultrasound sign of alveolar-interstitial syndrome. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 156:1640–1646
Zoltan J, Monti C, Coppola V et al (2004) Usefulness of ultrasound comets as a nonradiologic sign of extravascular lung water. Am J Cardiol 93:1265–1270
Frassi F, Gargani L, Gligorova S et al (2007) Clinical and ecocardiographic determinants of ultrasound lung comets. Eur J Echocariogr 8:474–479
Lichtenstein DA (2007) Ultrasound in the management of thoracic disease. Crit Care Med 5(Suppl):S250–S261
Jambrik Z, Monti S, Coppola V et al (2004) Usefulness of ultrasound lung comets as a nonradiologic sign of extravascular lung water. Am J Cardiol 93:1265–1270
Agricola E, Bove T, Oppizzi M, Marino G, Zangrillo A, Margonato A, Picano E (2005) “Ultrasound comet-tail imags”: a marker of pulmonary edema. A comparative study with wedge pressure and extravascular lung water. Chest 127:1690–1695
Gargani L, Lionetti V, Di Cristofano C, Bevilacqua G, Recchia FA, Picano E (2007) Early detection of acute lung injury uncoupled to hypoxemia in pigs using ultrasound lung comets. Crit Care Med 35:2769–2774
Jambrick Z, Gargani L, Adamcza A, Kaszaki J, Varga A, Forster T, Boros M, Picano E (2010) B-lines quantify the lung water content: a lung ultrasound versus lung gravimetry study in acute lung injury. Ultrasound Med Biol 36:2004–2010
Pistolesi M, Giuntini C (1978) Assessment of extravascular lung water. Radiol Clin North Am 15:551–574
Picano E, Frassi F, Agricola E et al (2006) Ultrasound lung comets: a clinically useful sign of extravascular lung water. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 19:356–363
Doveri M, Frassi F, Consensi A et al (2008) Ultrasound lung comets: new echographic sign of lung interstitial fibrosis in systemic sclerosis. Reumatismo 60:180–184
Gargani L, Doveri M, D’Errico L et al (2009) Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: a chest sonography hallmark of pulmonary interstitial fibrosis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 48:1382–1387
Warrick JH, Bhalla M, Schabel SI et al (1991) High resolution computed tomography in early scleroderma lung disease. J Rheumatol 18:1520–1528
Delle Sedie A, Doveri M, Frassi F et al (2010) Ultrasound lung comets in systemic sclerosis: a useful tool to detect lung interstitial fibrosis. Clin Exp Rheumatol 28(Suppl 57):s54
Gutierrez M, Salaffi F, Carotti M et al (2011) Utility of a simplified ultrasound assessment to assess interstitial pulmonary fibrosis in connective tissue disorders—preliminary results. Arthritis Res Ther 13:R134
Frassi F, Pingitore A, Cialoni D, Picano E (2008) Chest sonography detects lung water accumulation in healthy elite apnea divers. J Am Soc Echocardiogr 21:1150–1155
Pratali L, Cavana M, Sicari R, Picano E (2010) Frequent subclinical high-altitude pulmonary edema detected by chest sonography as ultrasound lung comets in recreational climbers. Crit Care Med 38:1818–1823
Acknowledgments
Our grateful thanks go to Dr. Francesca Bandinelli for her critical reading of the manuscript.
Disclosures
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Delle Sedie, A., Carli, L., Cioffi, E. et al. The promising role of lung ultrasound in systemic sclerosis. Clin Rheumatol 31, 1537–1541 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2030-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-012-2030-4