Abstract
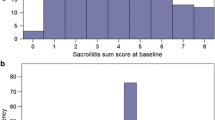
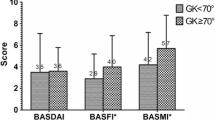
The objective of the present study was to compare two radiographic scoring methods (the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (mSASSS) and the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index-spine (BASRI-spine)) in terms of reliability, construct validity, and feasibility in Turkish ankylosing spondylitis (AS) patients. The study involved seventy-four patients. The patients were evaluated with 100-mm visual analog scale (VAS) for pain, global assessment of patient, and global assessment of doctor. The laboratory evaluations of patients comprised erythrocyte sedimentation rate and serum C-reactive protein. Bath AS Disease Activity Index (BASDAI), Bath AS Functional Index (BASFI), Bath AS Metrology Index (BASMI), and Bath AS Radiology Index (BASRI) were calculated. Bilateral cervical, lumbar spine, and anteroposterior pelvis radiographs of all patients were obtained and evaluated by two radiologists. Each radiograph was scored by two scoring methods, mSASSS and BASRI-spine, and these methods were tested according to the aspects of the Outcome Measures in Rheumatology Clinical Trials filter: reliability, construct validity, and feasibility. The BASRI-spine reached intra- and interobserver intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) of 0.726 and 0.689, respectively. The mSASSS scores more reliable, with ICC of 0.831 and 0.840, respectively. The BASMI and BASFI correlated significantly with the two scoring systems, respectively (mSASSS r: 0.557, r: 0.319; BASRI-spine r: 0.605, r: 0.285). For the two methods, the magnitude of the correlation with disease duration was similar (mSASSS p < 0.01 and BASRI p < 0.01), but no significant correlation was observed when compared to the BASDAI. It is known that the BASRI-spine is a feasible method that reliably detects damage in patients with AS. However, the present authors believe that, in AS patients, mSASSS should be the radiological scoring method to choose because of less radiation exposure, along with excellent intra- and interobserver reliability.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Rveille J (2008) Clinical features of ankylosing spondylitis. In: Hochberg MC, Silman AJ, Smolen JS, Weinblatt ME, Weisman MH (eds) Rheumatology, 4th edn. Elsevier, Spain, pp 1109–1114
Baek HJ, Shin KC, Lee YJ et al (2004) Clinical features of adult-onset ankylosing spondylitis in Korean patients: patients with peripheral joint disease (PJD) have less severe spinal disease course than those without PJD. Rheumatology (Oxford) 43:1526–1531
Spoorenberg A, van Tubergen A, Landewe R et al (2005) Measuring disease activity in ankylosing spondylitis: patient and physician have different perspectives. Rheumatology 44:789–795
Salaffi F, Carotti M, Garofalo G et al (2007) Radiological scoring methods for ankylosing spondylitis: a comparison between the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score. Clin Exp Rheumatol 25:67–74
MacKay K, Mack C, Brophy S et al (1998) The Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index (BASRI): a new, validated approach to disease assessment. Arthritis Rheum 41:2263–2270
Averns HL, Oxtoby J, Taylor HG et al (1996) Radiological outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: use of the Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score (SASSS). Br J Rheumatol 35:373–376
Creemers MC, Franssen MJ, van't Hof MA et al (2005) Assessment of outcome in ankylosing spondylitis: an extended radiographic scoring system. Ann Rheum Dis 64:127–129
Boers M, Brooks P, Strand CV et al (1998) The OMERACT filter for outcome measures in rheumatology. J Rheumatol 25:198–199
van der Linden S, Valkenburg HA, Cats A (1984) Evaluation of diagnostic criteria for ankylosing spondylitis. A proposal for modification of the New York criteria. Arthritis Rheum 27:361–368
Garret S, Jenksion T, Kennedy L et al (1994) A new approach to defining disease status in ankylosing spondylitis: the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index. J Rheumatol 21:2286–2291
Calin A, Garret S, Whitelock HC et al (1994) A new approach to defining functional ability in ankylosing spondylitis: the development of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index. J Rheumatol 21:2281–2285
Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA, Whitelock HC et al (1994) Defining spinal mobility in ankylosing spondylitis (AS). The Bath AS Metrology Index. J Rheumatol 21:1694–1698
Yanık B, Kurtais Gürsel Y, Kutlay S et al (2005) Adaptation of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Functional Index to the Turkish population, its reliability and validity: functional assessment in AS. Clin Rheumatol 24:41–47
Akkoç Y, Karatepe AG, Akar S et al (2005) The Turkish versions of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Disease Activity Index: reliability and validity. Rheumatol Int 25(4):280–284
Dale K (1979) Radiographic gradings of sacroiliitis in Bechterews syndrome and allied disorders. Scand J Rheumatol 32(Suppl 32):92–97
Wanders AJ, Landewé RB, Spoorenberg A et al (2004) What is the most appropriate radiologic scoring method for ankylosing spondylitis? A comparison of the available methods based on the outcome measures in rheumatology clinical trials filter. Arthritis Rheum 50:2622–2632
Spoorenberg A, de Vlam K, van der Linden S et al (2004) Radiological scoring methods in ankylosing spondylitis. Reliability and change over 1 and 2 years. J Rheumatol 31:125–132
Brophy S, Mackay K, Al-Saidi A et al (2002) The natural history of ankylosing spondylitis as defined by radiological progression. J Rheumatol 29:1236–1243
Wanders A, Landewé R, Spoorenberg A et al (2004) Scoring of radiographic progression in randomised clinical trials in ankylosing spondylitis: a preference for paired reading order. Ann Rheum Dis 63:1601–1604
Wanders A, Landewé R, Dougados M et al (2005) Association between radiographic damage of the spine and spinal mobility for individual patients with ankylosing spondylitis: can assessment of spinal mobility be a proxy for radiographic evaluation? Ann Rheum Dis 64:988–994
Landewé R, Dougados M, Mielants H et al (2008) Physical function in ankylosing spondylitis is independently determined by both disease activity and radiographic damage of the spine. Ann Rheum Dis Jul 15. (Epub ahead of print)
Kennedy LG, Jenkinson TR, Mallorie PA et al (1995) Ankylosing spondylitis: the correlation between a new metrology score and radiology. Rheumatol 34:767–770
Disclosures
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Başkan, B.M., Sivas, F., İnal, E.E. et al. Comparison of the Bath Ankylosing Spondylitis Radiology Index and the modified Stoke Ankylosing Spondylitis Spine Score in Turkish patients with ankylosing spondylitis. Clin Rheumatol 29, 65–70 (2010). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1290-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-009-1290-0