Abstract
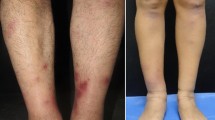
Episodic angioedema with eosinophilia is characterized by recurrent angioedema, peripheral eosinophilia, fever, weight gain, elevated serum immunoglobulin M (IgM), and a benign course lacking any internal organ involvement. A non-episodic variant has also been reported which is limited to a single attack and normally is less severe than the episodic type. We report a case of Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection with dermatological manifestation that was followed by non-episodic angioedema with eosinophilia including fever, weight gain, and elevated serum IgM. Even though the patient’s clinical characteristics resemble episodic angioedema with eosinophilia as reported by Gleich, angioedema was non-episodic. This may be due to systemic corticosteroid treatment which was prescribed because of persistent skin manifestation following M. pneumoniae infection. The current report is the first observation suggesting that angioedema associated with eosinophilia may be triggered by atypical bacterial infection.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gleich GJ, Schroeter AL, Marcoux P, Sachs MI, O’Connel EJ, Kohler PF (1984) Episodic angioedema associated with eosinophilia. N Engl J Med 310:1621–1626
Putterman C, Barak V, Caraco Y, Neuman T, Shalit M (1993) Episodic angioedema with eosinophilia: a case associated with T cell activation and cytokine production. Ann Allergy 70:243–248
Kawano M, Muramoto H, Tsunoda S, Koni I, Mabuchi H, Yachie A, Miyawaki T (1996) Absence of CD69 expression on peripheral eosinophils in episodic angioedema and eosinophilia. Am J Hematol 53:43–45
Nakashima K, Sakurada T, Imayama S, Masukawa S, Ember JA, Hugli TE, Abe M (1998) A case of episodic angioedema associated with blood eosinophilia: upregulated C5a receptor expression on eosinophils. Allergy 53:320–323
Morgan SJ, Prince HM, Westerman DA, McCormack C, Glaspole I (2003) Clonal T-helper lymphocytes and elevated IL-5 levels in episodic angioedema and eosinophilia (Gleich’s syndrome). Leuk Lymphoma 44:1623–1625
Okubo Y, Sato E, Hossain M, Ota T, Yoshikawa S, Sekiguchi M (1995) Periodic angioedema with eosinophilia: increased serum level of interleukin 5. Intern Med 34:108–111
Tillie-Leblond I, Gosset P, Janin A, Salez F, Prin L, Tonnel AB (1998) Increased interleukin-6 production during the acute phase of the syndrome of episodic angioedema and hypereosinophilia. Clin Exp Allergy 28:491–496
Lassalle P, Gosset P, Gruart V, Prin L, Capron M, Lagrue G, Kusnierz JP, Tonnel AB, Capron A (1990) Presence of antibodies against endothelial cells in the sera of patients with episodic angioedema and hypereosinophilia. Clin Exp Immunol 82:38–43
Matsuda M, Fushimi T, Nakamura A, Ikeda S (2006) Nonepisodic angioedema with eosinophilia: a report of two cases and a review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 25:422–425
Waites KB, Talkington DF (2004) Mycoplasma pneumoniae and its role as a human pathogen. Clin Microbiol Rev 17:697–728
Winter LK, Spiegel JH, King T (2007) Dermatopathic lymphadenitis of the head and neck. J Cutan Pathol 34:195–197
Sutherland ER, Martin RJ (2007) Asthma and atypical bacterial infection. Chest 132:1962–1966
Ruuth E, Praz F (1989) Interactions between mycoplasmas and the immune system. Immunol Rev 112:133–160
Shikiji T, Urano Y, Takiwaki H, Arase S (1997) A case of episodic angioedema associated with eosinophilia. J Med Invest 44:103–108
Oktenli C, Bulucu F, Gurbuz M, Bozoglu E, Oguz Y, Koc B (2001) Observations on edema formation and resolution in Gleich syndrome: essential role of the kidneys in effective arterial blood volume regulation. Am J Nephrol 21:154–161
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank Rajam Csordas for critical reading.
Disclosure
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stockner, I., Thaler, J., Fichtel, G. et al. Non-episodic angioedema associated with eosinophilia following Mycoplasma pneumoniae infection. Clin Rheumatol 27, 1573–1576 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0990-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0990-1