Abstract
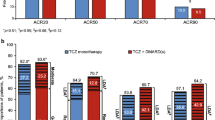
Several drug trials, predominantly of Caucasian patients, have demonstrated the therapeutic role of leflunomide (LEF) in the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis (RA). We report an Indian (Asian) experience from a prospective observational study. Two hundred thirty affording patients with moderately severe active RA (naïve for LEF), mostly failing methotrexate (MTX), were begun LEF (Arava™; 20 mg daily, post loading 100 mg od × 3 days) in a clinic setting and followed regularly in an open cohort as per standard of care practice guidelines. A priori, LEF was to be preferably used as a single-agent disease-modifying anti-rheumatic drug (DMARD). One hundred forty-three patients and 87 patients were clinically assigned to the LEF monotherapy and LEF + MTX combination, respectively; less than one third received prednisolone. We focus on 146 patients (64%) completing 1 year treatment. Patients improved significantly (p < 0.05, analysis of variance) in several measures (including Health Assessment Questionnaire). Though unintended (non-randomized), the treatment subgroups matched at baseline. Of patients, 42% and 24% in LEF monotherapy and LEF + MTX, respectively showed American College of Rheumatology 50% Response Criteria (ACR 50) improvement. LEF monotherapy showed a better ‘time to first ACR 20 improvement’ outcome over 1 year (survival function curve, Cox Hazard Ratio = 0.71, 95% confidence interval 0.52, 0.96). Ten percent to 30% patients reported diarrhea, hair loss, skin rash, and dyspepsia; <3% reported abnormal liver functions. Eighty-four patients (36.5%) withdrew (8.7% adverse events and 18.7% non-affordability). LEF is an effective and safe DMARD in our ethnic patient population and may suffice as a single agent (to treat moderately severe RA) during the initial 1 year.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Smolen JS, Kalden JR, Scott DL et al (1999) Efficacy and safety of leflunomide compared with placebo and sulphasalazine in active rheumatoid arthritis: a double-blind, randomized, multicentre trial. Lancet 353:259–266
Strand V, Cohen S, Schiff M et al (1999) Treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide compared with placebo and methotrexate. Arch Intern Med 159:2542–2550
Cohen S, Cannon GW, Schiff M et al (2001) For the Utilization of Leflunomide in the Treatment of Rheumatoid Arthritis Trial Investigator Group. Two year, blinded, randomized controlled trial of treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis with leflunomide compared with methotrexate. Arthritis Rheum 44(9):1984–92
Kalden JR, Schattenkirchner M, Soresen H et al (2003) The efficacy and safety of leflunomide in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: a five year follow up study. Arthritis Rheum 48:1513–1520
Osiri M, Beverley S, Robinson V et al (2003) Leflunomide for the treatment of rheumatoid arthritis: a systematic review and met analysis. J Rheumatol 30:1182–1190
Smolen JS, Emery P, Kalden JR et al (2004) The efficacy of leflunomide monotherapy in rheumatoid arthritis: Towards the goal of disease modifying antirheumatic drug therapy. J Rheumatol 31(Suppl 71):13–20
Kremer J, Genovese M, Cannon GW et al (2002) Concomitant Leflunomide therapy in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis despite stable doses of methotrexate. A randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. Ann Intern Med 137:726–733
Kremer J, Genovese M, Cannon GW et al (2004) Combination leflunomide and methotrexate (MTX) therapy for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis failing MTX monotherapy: open-label extension of a randomized, double-blind, placebo controlled trial. J Rheumatol 31:1521–1531
Avorn J (2007) In defense of pharmacoepidemiology—embracing the yin and yang of drug research. N Engl J Med 357:2210–2221
Arnett FC, Edworthy SM, Block DA et al (1988) The American Rheumatism Association 1987 revised criteria for the classification of rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 31:315–324
Fries JF, Spitz P, Kraines RG et al (1980) Measurement of patient outcome in arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 23:137–145
Chopra A (2004) Rheumatology: made in India (Camps, COPCORD, HLA, Ayurveda, HAQ, WOMAC and Drug Trials). J Indian Rheumatol Assoc 12:43–53
Felson DT, Anderson JJ, Boers M et al (1995) American College of Rheumatology preliminary definition of improvement in rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum 38:727–735
Aletaha D, Stamm T, Kapral T et al (2003) Survival and effectiveness of leflunomide compared with methotrexate and sulfasalazine in rheumatoid arthritis: a matched observational study. Ann Rheum Dis 62(10):944–951
Bettembourg-Brault I, Gossec L, Pham T et al (2006) Leflunomide in rheumatoid arthritis in daily practice: treatment discontinuation rates in comparison with other DMARDs. Clin Exp Rheumatol 24(2):168–171
Agarwal SK, Narsimulu G, Handa R et al (2002) Leflunomide (Aravaä)—the Indian experience: a multicenter assessment of its safety and effectiveness in the treatment of active rheumatoid arthritis. J Indian Rheumatol Assoc 10:30–35
Rao URK, Fatima F (2004) Leflunomide add-on therapy for patients with active rheumatoid arthritis—a report on adverse events. Ann Rheum Dis 63(Suppl 1):284
Saluja M, Joshi V, Chopra A (2007) I love my hair but I do not want rheumatoid arthritis. APLAR J Rheumatol 10:54–56
Dougados M, Emery P, Lemmel EM et al (2003) Efficacy and safety of leflunomide and predisposing factors for treatment response in patients with active rheumatoid arthritis: RELIEF 6-month data. J Rheumatol 30:2572–2579
Malaviya AN, Mehra NK, Dasgupta B et al (1983) Clinical and immunogenetic studies in rheumatoid arthritis in India. Rheumatol International 3:105–108
Chopra A, Raghunath D, Singh A et al (1988) Pattern of rheumatoid arthritis in the India population: a prospective study. British J Rheumatology 27:454–456
Chopra A, Patil J, Billampelly V et al (2001) Prevalence of rheumatic diseases in a rural population in Western India: A WHO-ILAR COPCORD Study. J Assoc Physicians India 49:240–246
Chopra A, Poulton K, Silman A et al (2001) HLA DRB1 Associations in a community based study of inflammatory arthritis in India. Arthritis Rheum 7(Suppl):S71
Yogita G, Chopra A, Joshi K, Patwardhan B (2008) Are thymidylate synthase and methylene tetrahydrofolate reductase genes linked with methotrexate response (efficacy, toxicity) in Indian (Asian) rheumatoid arthritis patients? J Clin Rheumatol (in press)
Chopra A, Lagu-Joshi V, Kunjeer V (2006) Our experience with anti-TNF therapy—a choice between devil and the deep sea. APLAR J Rheumatol 9(Suppl. 1):208
Acknowledgments
The Arthritis Research Care Foundation-CRD, Pune, generously provided much of the material and manpower. Several colleagues contributed to the LEF database—J Patil, V Kunjeer, S Deepak, P Neeta, K Amarjit, and S Garad. We also thank Dr Fredrick Wolfe (USA) for his encouragement, guidance and useful comments regarding this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
All authors actively participated in the study and had full access to this manuscript which was primarily prepared by AC.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chopra, A., Saluja, M., Lagu-Joshi, V. et al. Leflunomide (Arava™) is a useful DMARD in Indian (Asian) patients: a clinic-based observational study of 1-year treatment. Clin Rheumatol 27, 1039–1044 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0897-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-008-0897-x