Abstract
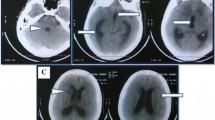
Chorea is a rare complication of systemic lupus erythematosus (SLE) and is strongly related to the presence of antiphospholipid antibodies. Various infections may also be triggering factors in the development of choreiform movements. Additionally, Salmonella infection is the most common opportunistic bacterial infection in SLE patients. We report a case of a 33-year-old woman with SLE who developed lupus erythematosus-associated chorea with multiple involuntary movements and cognitive disturbances. Because the methylprednisolone therapy administered appeared to lead to Salmonella enteritidis infection, intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIg) in a total dose 100 g was administered after which a remarkable improvement of the abnormal movements and cognitive function was noted. Within 7 days, the patient had returned to normal. We therefore conclude that IVIg therapy may be an effective therapeutic approach for the treatment of the acute cerebral complications of SLE, especially in cases in whom other therapeutic strategies are ineffective or harmful.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Asherson RA, Cervera R (2003) The antiphospholipid syndrome: multiple faces beyond the classical presentation. Autoimmunity Reviews 2(3):140–151
Asherson RA, Cervera R, Shepshelowich D, Shoenfeld Y (2006) Nonthrombotic manifestations of the antiphospholipid syndrome: away from thrombosis ? J Rheumatol 33(6):1038–1044
Blaauw AA, Tobe TJ, Derksen RW, Bijlsma JW (2000) A patient with systemic lupus erythematosus and Salmonella enteritidis bacteraemia complicated by rhabdomyolysis and acute cholecystitis. Rheumatology (Oxford) 39(1):110–112
Brey RL, Holliday SL, Saklad AR, Navarrete MG, Hermosillo-Romo D, Stallworth CL, Valdez CR, Escalante A, del Rincon I, Gronseth G, Rhine CB, Padilla P, McGlasson D (2002) Neuropsychiatric syndromes in lupus: prevalence using standardized definitions. Neurology 58(8):1214–1220
Cervera R, Asherson RA, Font J, Tikly M, Pallares L, Chamorro A, Ingelmo M (1997) Chorea in the antiphospholipid syndrome: clinical, radiologic and immunologic characteristics of 50 patients from our clinics and the recent literature. Medicine (Baltimore) 76(3):203–212
Hsu RB, Chen RJ, Chu SH (2004) Risk factors for recurrent bacteremia in adult patients with nontyphoid salmonellosis. Am J Med Sci 238(6):315–318
Janavs JL, Aminoff MJ (1998) Dystonia and chorea in aquired systemic disorders. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 65(4):436–445
Oh HM, Chng HH, Boey ML, Feng PH (1993) Infections in systemic lupus erythematosus. Singapore Med J 34(5):406–408
Rafai MA, El Moutawakil B, Gam I, Hakim K, Fadel H, Kissani N, Slassi I (2005) Systemic lupus erythematosus presenting with a choreoathetotic syndrome associated with antiphospholipid antibodies. Rev Neurol (Paris) 161(10):967–970
Rutberg SA, Ward DE, Roth BJ (2002) Churg–Strauss syndrome and pregnancy: successful treatment with intravenous immunoglobulin. J Clin Rheumatol 8(3):151–156
Sherer Y, Levy Y, Langewitz P, Lorber M, Fabrizzi F, Shoenfeld Y (1999) Successful treatment of systemic lupus erythematosus cerebritis with intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Rheumatol 18:170–173
Steinbrecher A, Berlit P (2006) Intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in vasculitis and connective tissue disorders. J Neurol 5(Suppl 253):v39–v49
Tomer Y, Shoenfeld Y (1992) Successful treatment of psychosis secondary to SLE with high dose intravenous immunoglobulin. Clin Exp Rheumatol 10(4):391–393
Wang TK, Ho PL, Wong SS (2005) Recurrent bacteraemia caused by different Salmonella species in a systemic lupus erythematosus patient. New Microbiol 28(2):151–156
Watanabe T, Onda H (2004) Hemichorea with antiphospholipid antibodies in a patient with lupus nephritis. Pediatr Nephrol 19(4):451–453
Wongchinsri J, Tantawichien T, Osiri M, Akkasilpa S, Deesomchok U (2002) Infection in Thai patients with systemic lupus erythematosus: a review of hospitalized patients. J Med Assoc Thail 85 (Suppl 1):34–39
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lazurova, I., Macejova, Z., Benhatchi, K. et al. Efficacy of intravenous immunoglobulin treatment in lupus erythematosus chorea. Clin Rheumatol 26, 2145–2147 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0627-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-007-0627-9