Abstract
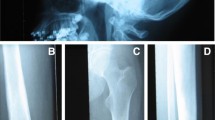
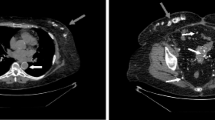
Camurati-Engelmann disease is a rare bone disorder characterized by cortical thickening of the diaphysis of tubular bones, with sparing of the epiphysis. It has variable degrees of penetrance and expression, but may be very disabling for the affected individuals who manifest the painful symptoms. The authors report on two women with typical presentation of severe Camurati-Engelmann disease whose treatment with bisphosphonates failed to add any improvement beyond that elicited by corticosteroids alone.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sparkes RS, Graham CB (1972) Camurati-Engelmann disease: genetic and clinical manifestations with a review of the literature. J Med Genet 9:73–85
Kinoshita A, Saito T, Tomita H et al (2000) Domain-specific mutations in TGFB1 result in Camurati-Engelmann disease. Nat Genet 26:19–20
Vanhoenacker FM, Janssens K, Van Hul W et al (2003) Camurati-Engelmann disease: review of radioclinical features. Acta Radiol 44:430–434
Applegate LJ, Applegate GR, Kemp SS (1991) MR of multiple cronical neuropathies in a patient with Camurati-Engelmann disease: case report. Am J Neuroradiol 12:557–559
Minford AMB, Hardy GJ, Forsythe WI et al (1981) Engelmann’s disease and the effect of corticosteroids: a case report. J Bone Joint Surg Br 63B:597–600
Greenspan A (1991) Sclerosing bone dysplasias—a target site approach. Skeletal Radiol 20:561–583
Kumar B, Murphy WA, Whyte MP (1981) Progressive diaphyseal dysplasia (Engelmann disease): scintigraphic-radiographic-clinical correlations. Radiology 140:87–92
Clybouw C, Desmyttere S, Bonduelle M, Piepsz A (1994) Camurati-Engelmann disease: contribution of bone scintigraphy to genetic counseling. Genet Couns 5:195–198
Hernadez MV, Peris P, Guañabens N et al (1997) Biochemical markers of bone turnover in Camurati-Engelmann disease: a report of four cases in one family. Calcif Tissue Int 61:48–51
Cherie-Lignière G, Santalena G, Parafioriti A (1999) Pamidronate in the treatment of progressive diaphyseal dysplasia (Camurati-Engelmann disease). Clin Exp Rheumatol 17:264
Rubin ZS, Ghiringhelli G, Mansur JL (1997) Evaluacion clinica, humoral y centellografica de un bisfosfonato como posible tratamiento em dos casos de displasias diafisarias: las enfermadades de Ribbing y Camurati-Engelmann. Medicina 57 [Suppl 1]:56–60
Smith R, Walton RJ, Corner BD, Gordom IRS (1977) Clinical and biochemical studies in Engelmann’s disease (progressive diaphyseal dysplasia). Q J Med 182:273–294
Inaoka T, Shuke N, Sato J et al (2001) Scintigraphic evaluation of pamidronate and corticosteroid therapy in a patient with progressive diaphyseal dysplasia (Camurati-Engelmann disease). Clin Nucl Med 26:680–682
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Castro, G.R., Appenzeller, S., Marques-Neto, J.F. et al. Camurati-Engelmann disease: failure of response to bisphosphonates: report of two cases. Clin Rheumatol 24, 398–401 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-1056-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-004-1056-7