Abstract
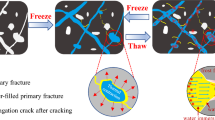
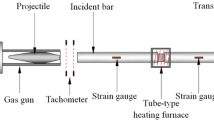
The failure of rocks in seasonal frozen areas under freeze–thaw cycles (FTCs) is a frequently problem in engineering construction, posing a huge threat to the stability of the engineering. In order to explore the mechanism of rock damage degradation. It is necessary to analyze the damage evolution process of rocks and establish an accurate FTCs rock damage constitutive model. Taking the granite in the seasonal frozen zone of Northeast China as the research object, the macro and meso parameters and microstructure of the FTCs granite were analyzed through indoor tests. A new method is proposed to define damage variables considering mesoscopic parameters to establish a mesoscopic damage constitutive model for rocks, further revealing the damage mechanism and failure law of rocks under freeze–thaw load coupling. The research results indicate that in the early stage of FTCs, 20 cycles contribute significantly to the damage and deterioration of rocks, accounting for about 50% of the 80 cycles. After 20 cycles, the degradation trend of various macroscopic and mesoscopic parameters is relatively slow. The residual strain of the rock accumulates as the number of FTCs increases, the brittleness of the rock weakens, and the plasticity strengthens. Based on the established new method of considering mesoscopic parameter damage variables, the viewpoint of introducing correction coefficients based on statistical constitutive models has been validated. After uniaxial compression test data verification, the model has shown good performance. This model expands the damage model of rock freeze–thaw compression coupling effect, providing reference for research on FTCs related to rocks.
















Similar content being viewed by others
Data Availability
This article introduces the available data generated during this study.
References
Amiri SAG, Grimstad G, Kadivar M et al (2016) Constitutive model for rate-independent behavior of saturated frozen soi-ls. Can Geotech J 53(10):1646–1657. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2015-0467
Ahmadi S, Ghasemzadeh H, Changizi F (2021a) Effects of a low-carbon emission additive on mechanical properties of finegrained soil under freeze-thaw cycles. J Clean Prod 304:127157. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.127157
Ahmadi S, Ghasemzadeh H, Changizi F (2021b) Effects of thermal cycles on microstructural and functional properties of nano treated clayey soil. Eng Geol 280:105929. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2020.105929
Chen RS, Kang ES, Wu LZ et al (2005) Discussion on the Distribution of Cold Regions in China [J]. Glacier Frozen so-Il 27(4):469–475 ((in Chinese))
Chu Y, Zhang D, Song S, et al (2023) Experimental study on the evolution of pore structure of coal samples under freeze–thaw. Physics of Fluids 35(3). https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0145187
Freire-Lista D M, Fort R, Varas-Muriel M J (2015) Freeze–thaw fracturing in building granites. Cold Regions Science and Technology 113: 40–51.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2015.01.008
Ghobadi MH, Babazadeh R (2014) Experimental studies on the effects of cyclic freezing–thawing, salt crystallization, and thermal shock on the physical and mechanical characteristics of selected sandstones. Rock Mech Rock Eng 48(3):1001–1016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00603-014-0609-6
Ghasemzadeh H, Ghoreishian Amiri SA (2013) A hydro-mechanical elastoplastic model for unsaturated soils under isotropic loading conditions. Comput Geotech 51:91–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compgeo.2013.02.006
Ghasemzadeh H, Sojoudi MH, Ghoreishian Amiri SA et al (2017) Elastoplastic model for hydro-mechanical behavior of unsaturated soils. Soils Found 57(3):371–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2017.05.005
Ghoreishian Amiri SA, Grimstad G, Kadivar M (2022) An elastic-viscoplastic model for saturated frozen soils. Eur J Environ Civ En 26(7):2537–2553. https://doi.org/10.1080/19648189.2016.1271361
Huang SB, Liu QS, Cheng AP, Liu YZ et al (2018) A statistical damage constitutive model under freeze-thaw and loading for rock and its engineering application. Cold Reg Sci Technol 145:142–150. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2017.10.015
Huang SB, Ye Y, Cui X et al (2020) Theoretical and experimental study of the frost heaving characteristics of the saturated sandstone under low temperature. Cold Reg Sci Technol 174:103036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.coldregions.2020.103036
Inada Y, Yokota K (1984) Some studies of low temperature rock stength. Intl J RockMech Mining Sci Geomech Abstracts 21(3):145–153. https://doi.org/10.1016/0148-9062(84)91532-8
Jia H, Xiang W, Krautblatter M (2015) Quantifying Rock Fatigue and Decreasing Compressive and Tensile Strength after Repeated Freeze-Thaw Cycles. Permafrost Periglac Process 26:368–377. https://doi.org/10.1002/ppp.1857
Jia H, Ding S, Zi F et al (2020) Evolution in sandstone pore structures with freeze-thaw cycling and interpretation of damage mechanisms in saturated porous rocks. CATENA 195:104915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.catena.2020.104915
Lemaitre J (1984) How to ues damage mechanics. Nucl Eng Des 80(3):233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-5493(84)90169-9
Liu QS, Xu XC (2000) Damage analysis of brittle rock under temperature[J]. J Rock Mech Eng 19(4):408–411 ((in Chinese))
Liu QS, Huang SB, Kang YS et al (2015) Research on rock mass freeze-thaw fatigue damage model and evaluation index[J]. J Rock Mech Eng 34(6):1116–1127 ((in Chinese))
Li SC, Xu J, Li KG (2007) Statistical constitutive model of rock damage based on the correction of initial damage coefficient[J]. J Sichuan Univ (Engineering Science Edition) 33(6):41–44 ((in Chinese))
Li B, Ren C, Wang Z et al (2020) Experimental study on damage and the permeability evolution process of methane-containing coal under different temperature conditions. J Petrol Sci Eng 184:106509. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2019.106509
Li C, Jin J, Wu P et al (2022) Effect of Freeze-Thaw Cycles on Shear Strength of Tailings and Prediction by Grey Model. Minerals 12(9):1125. https://doi.org/10.3390/min12091125
Matsuoka H, Nakai T (1974) Stress-deformation and strength characteristics of soil three different principal stress. Pro-Ceedings of JSCE 2:59–70. https://doi.org/10.2208/JSCEJ1969.1974.232-59
Matsuoka H, Hoshikawa T, Ueno K (1990) A general failure criterion and stress-strain retain for granual materials to metals. Soil Found 30(2):119–127. https://doi.org/10.3208/sandf1972.30.2_119
Meng XZ, Zhang HM, Liu XY (2021) Rock damage constitutive model based on the modified logistic equation under freeze–thaw and load conditions. J Cold Regions Eng 35(4):04021016. https://doi.org/10.1061/(ASCE)CR.1943-5495.000026
Polak J (1991) Cyclic Plasticity and Low Cycle Fatigue Life of Metal. Elsevier, New York
Sondergeld CH, Rat CS (2005) Observations of velocity and resistivity changes during freeze-thaw cycles in Berea sand-stone. SEG Tech Program Expanded Abstracts 24(6):1509–1512. https://doi.org/10.1190/1.2147977
Satake M (1976) Stress-deformation and strength characteristics of soil three different principal stress(Discus-sion). Proc.of Japan Society of Civil Engineers 246:137–138.
Song CY (2018) Research and application of micro structural characteristics and deformation failure mechanism of weakly cemented sandstone[J]. J Rock Mech Eng 37(3):779 ((in Chinese))
Song YJ, Yang HM, Tan H et al (2021) Research on damage evolution characteristics of sandstone with different saturation under freezing and thawing environment[J]. J Rock Mech Eng 40(8):1513–1524 ((in Chinese))
Xu GM, Liu QS (2005) Analysis of rock freeze-thaw failure mechanism and experimental study on freeze-thaw mechanics[J]. J Rock Mech Eng 24(17):3076–3082 ((in Chinese))
Yang GS, Xi JM, Li HJ et al (2010) Experimental study on the characteristics of frozen Rock mechanics under three-dimensional stress[J]. J Rock Mech Eng 29(3):459–464 ((in Chinese))
Yu Q, Dai Z, Zhang Z et al (2018) Estimation of Sandstone Permeability with SEM Images Based on Fractal Theory. Transp Porous Media 126(3):0701–0712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11242-018-1167-2
Yu Q, Xiong Z, Du C et al (2020) Identification of rock pore structures and permeabilities using electron microscopy experiments and deep learning interpretations. Fuel 268:117416. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117416
Yu Q, Lei P, Dai Z et al (2023) Damage Characteristics of Limestone under Freeze-Thaw Cycle for Tunnels in Seasonal Frozen Areas. Iranian J Sci Technol Trans Civil Eng 47(1):469–477. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40996-022-00979-7
Zhang QS, Yang GS, Ren JX (2003) A new approach to rock damage variables and constitutive equation[J]. J Rock Mech Eng 21(3):30–34 ((in Chinese))
Zhang HM, Lei LN, Yang GS (2014) Rock damage model based on Weibull statistical distribution[J]. J Hunan Univ Sci Technol (natural Science Edition) 29(3):29–32 ((in Chinese))
Zhang HM, Zhang MJ, Xie XM et al (2015) Experimental study on physical and mechanical properties of red sandstone under freeze-thaw cycle[J]. J Taiyuan Univ Technol 46(1):69–74 ((in Chinese))
Zhang HM, Wang YF (2022) Multi scale analysis of damage evolution of freeze-thaw red sandstone. Geotech Mech 43(8):2103–2114. https://doi.org/10.16285/j.rsm.2021.1726
Zhao T, Yang GS, Xi JM et al (2019) Experimental study on macro and meso freeze-thaw damage characteristics of Cretaceous sandstone[J]. J Xi’an Univ Sci Technol 39(2):241–248 ((in Chinese))
Zhou ST, Jiang N, Luo XD et al (2020) Uniaxial compression fractal damage constitutive model of rock subjected to freezing and thawing. Periodica Polytech Civil Eng 64(2):500–510. https://doi.org/10.3311/PPci.15313
Zhang Q, Li XC, Gao JX et al (2022) Macro-and Meso-Damage Evolution Characteristics of Coal Using Acoustic Emission and Keuence Testing Technique. Nat Resour Res 31:517–534. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-021-10006-7
Zhang Q, Li XC, Li B et al (2023) Continuous-Discontinuous Element Numerical Modeling of Damage and Fracture Characteristics of a Loaded Coal. Nat Resour Res 32:373–389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11053-022-10147-3
Acknowledgements
This work is funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (NSFC: U2267217, 42141011, 42002254).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing Interest
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jia, S., Yu, Q., Yin, H. et al. Analysis of damage evolution and study on mesoscopic damage constitutive model of granite under freeze–thaw cycling. Bull Eng Geol Environ 83, 236 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03741-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10064-024-03741-7